Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a severe autoimmune disease targeting small vessels, with significant kidney involvement. Despite current therapies, up to 28% of patients progress to end-stage renal disease. To identify molecular pathways underlying AAV nephritis, we performed transcriptomic analysis of kidney biopsies from 22 patients (20 at diagnosis, 2 at relapse).
Methods: RNA sequencing was performed on RNA extracted from clinically indicated FFPE kidney biopsies. Five pre-implantation donor kidney biopsies were used as controls. Differentially expressed genes and pathways were identified using DESeq2 and gene set enrichment analysis. Transcriptomic profiles were correlated to kidney pathology for pathway analysis.
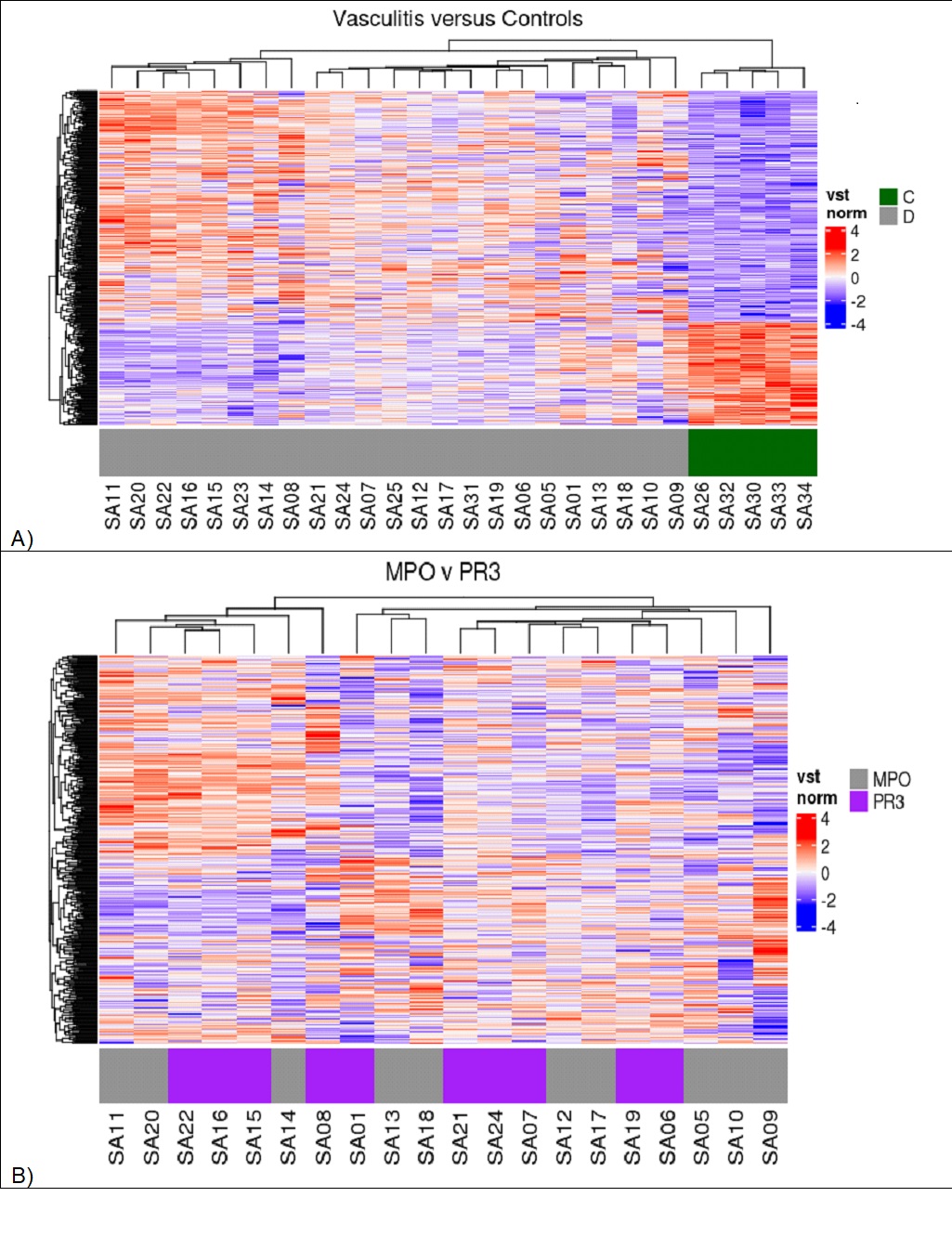
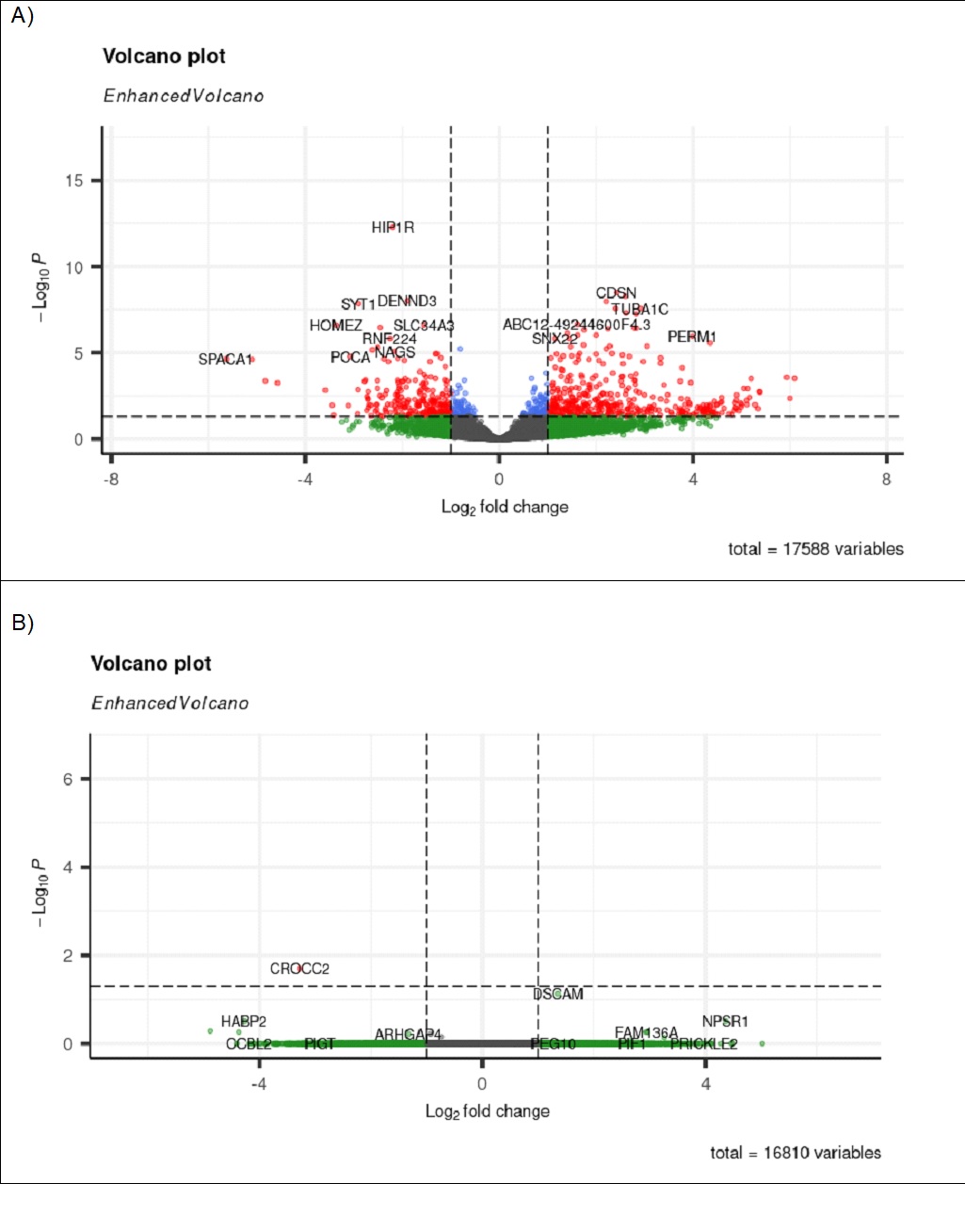
Results: Our cohort was predominantly female (13/23), White (21/23), and had a median age of 58 years. Compared to controls, 491 genes were upregulated and 297 downregulated in AAV patients (log2 fold change > 1.0, FDR < 0.05). MPO+ patients displayed 196 upregulated genes and 135 downregulated genes, while PR3+ patients had 413 upregulated and 339 downregulated genes compared to controls. Principal component analysis segregated AAV from controls but not MPO versus PR3 positive subgroups.
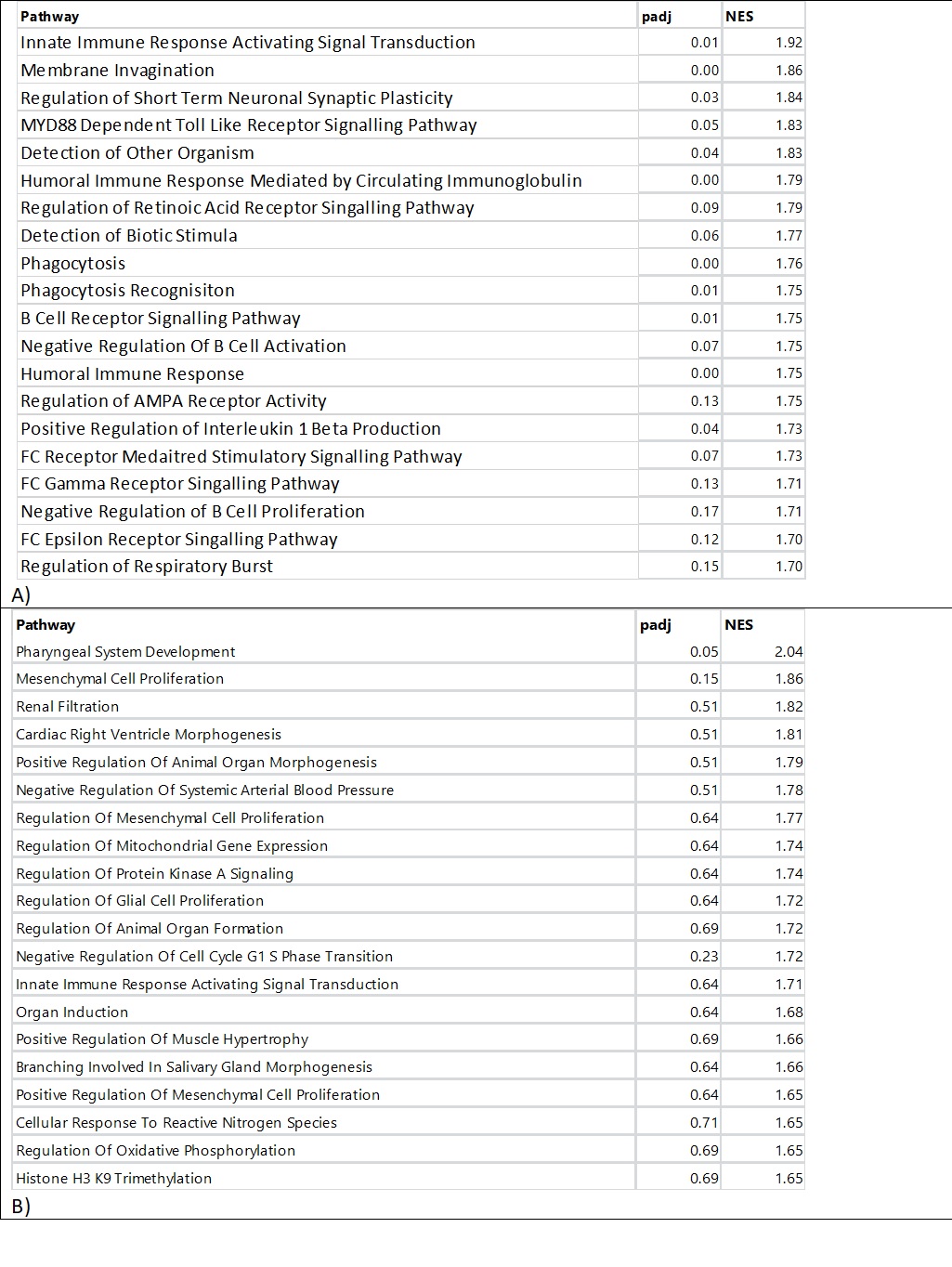
Consistent upregulation of immune genes including IL-17D, CD markers, and downregulation of IL10RA was observed. There was upregulation of pathways related to systemic lupus erythematosus, NK cell cytotoxicity, chemokine signaling, and B cell receptor signaling. Enrichment of genes associated with pattern recognition, antigen binding, and MHC class protein binding was consistently seen. Deconvolution by Cibersort confirmed diverse immune cell populations, including NK cells, M2 macrophages, and plasma cells in kidney tissue of patients with vasculitis. Lastly, pathway analysis of correlations to histology implicated Th17 pathways with percent sclerotic glomeruli and staph aureus infection with percent necrotic glomeruli.
Conclusion: Our data implicate Th17 pathway activation and immune cell infiltration in AAV pathogenesis and with the percentage of sclerotic glomeruli. Additionally, gene expression profiles do correlate with kidney damage. This study provides a transcriptomic and immunological signature of AAV nephritis. Our study provides evidence that MPO and PR3 positive patients do not segregate well on a genetic basis. Further investigations may facilitate improved stratification of patients and guide therapeutic development.
Vst norm = variance stabilized transformed normalized counts
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stojkic I, Arazi A, Song H, Yan P, Puchulu-Campanella E, Wang H, Fussner L, Rovin B, Parikh S, Ardoin S, Koboldt D, Fitch J, Almaani S. Transcriptomic Profiling of Kidney Biopsies Implicates Th17 and IL-17 in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptomic-profiling-of-kidney-biopsies-implicates-th17-and-il-17-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptomic-profiling-of-kidney-biopsies-implicates-th17-and-il-17-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/