Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Myositis is a heterogeneous family of diseases including dermatomyositis (DM), immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), antisynthetase syndrome (AS), and inclusion body myositis (IBM). Myositis-specific autoantibodies define different subtypes of myositis. For example, patients with anti-Mi2 autoantibodies targeting the CHD4/NuRD complex (a transcriptional repressor) have more severe muscle disease than other DM patients. This study aimed to define the transcriptional profile of muscle biopsies from anti-Mi2-positive DM patients.
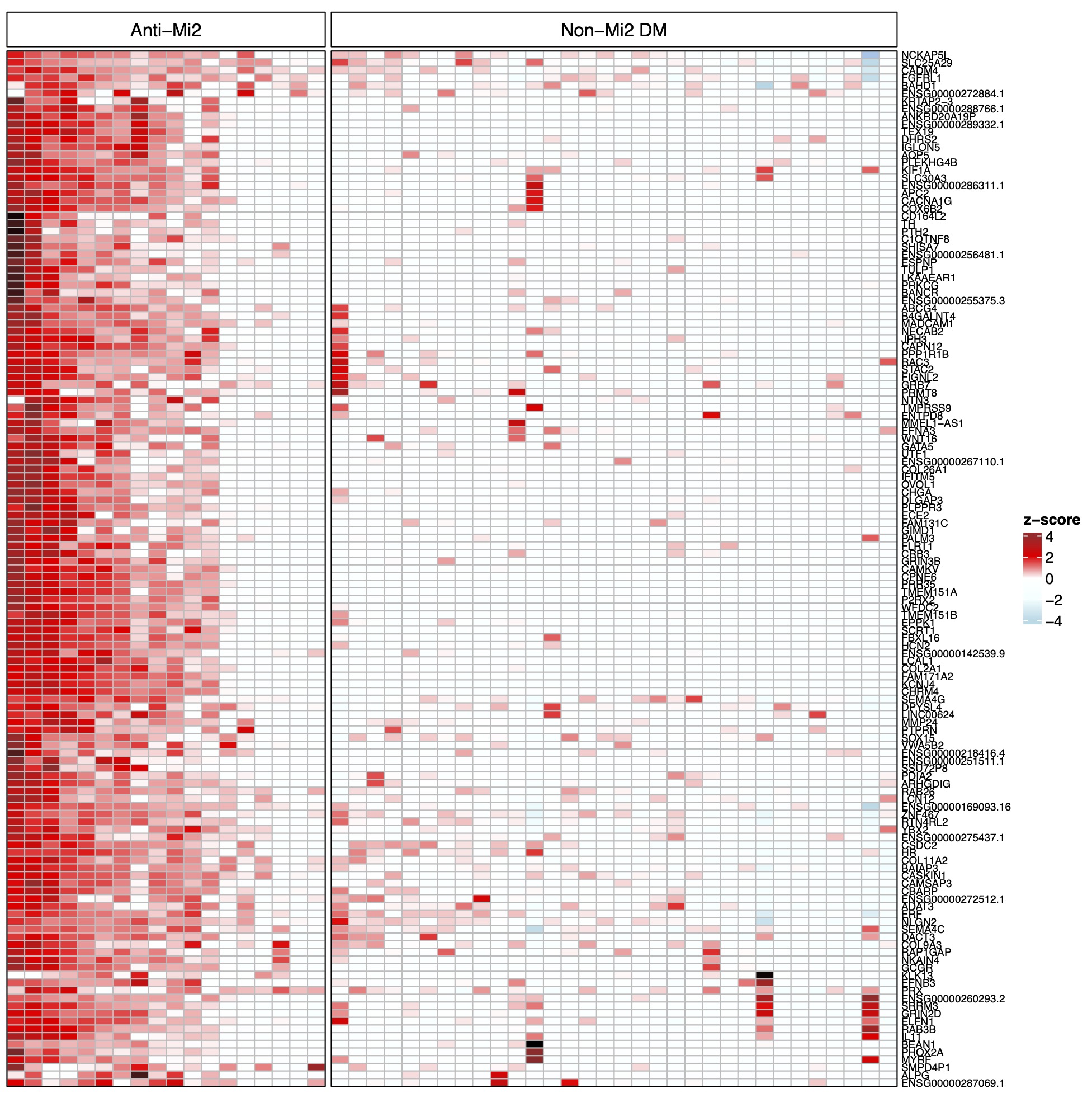
Methods: RNA sequencing was performed on muscle biopsies (n=171) from patients with anti-Mi2-positive DM (n=18), DM without anti-Mi2 autoantibodies (n=32), AS (n=18), IMNM (n=54), and IBM (n=16) as well as 33 normal muscle biopsies. Genes specifically upregulated in anti-Mi2-positive DM were identified. Muscle biopsies were stained for human immunoglobulin and protein products corresponding to genes specifically upregulated in anti-Mi2-positive muscle biopsies.
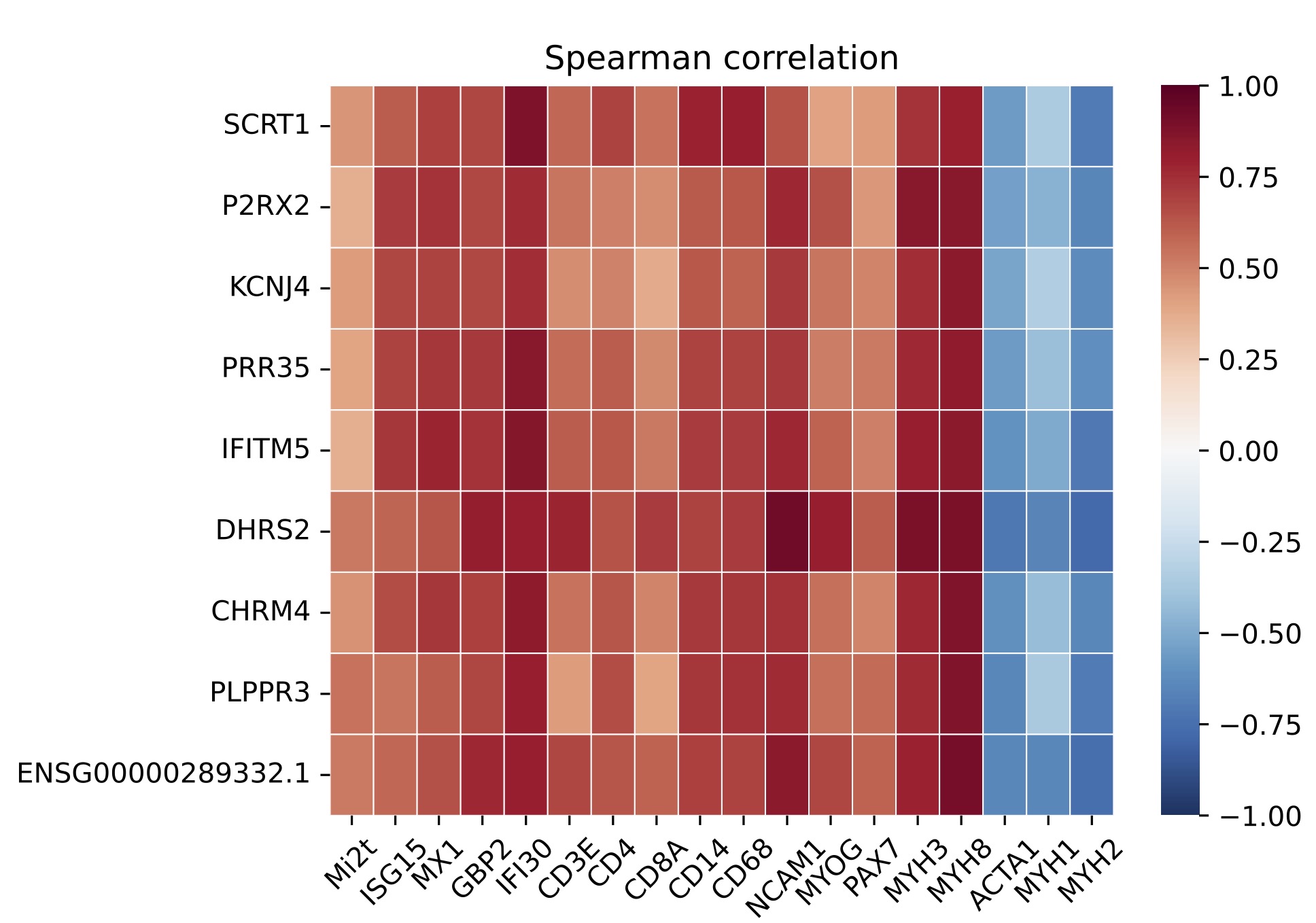
Results: A set of 135 genes, including SCRT1 and MADCAM, was specifically overexpressed in anti-Mi2-positive DM muscle. This set was enriched for CHD4/NuRD-regulated genes and included genes that are not otherwise expressed in skeletal muscle. The expression levels of these genes correlated with anti-Mi2 autoantibody titers, markers of disease activity, and with the other members of the gene set. In anti-Mi2-positive muscle biopsies, immunoglobulin was localized to the nucleus, MADCAM protein was present in the cytoplasm of perifascicular fibers, and SCRT1 protein was localized to myofiber nuclei.
Conclusion: Based on these findings, we hypothesize that anti-Mi2 autoantibodies could exert a pathogenic effect by entering damaged myofibers, inhibiting the CHD4/NuRD complex, and subsequently derepressing the unique set of genes defined in this study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pinal-Fernandez I, Milisenda J, Pak K, Muñoz-Braceras S, Casal-Dominguez M, Torres-Ruiz J, Dell´Orso S, Naz F, Gutierrez-Cruz G, Duque-Jaimez Y, Matas-Garcia A, Padrosa J, Garcia-Garcia F, Guitart-Manpel M, Garrabou G, Trallero-Araguas E, Wallit B, Paik J, Albayda J, Christopher-Stine L, Lloyd T, Grau J, Selva-O’Callaghan A, Mammen A. Transcriptional Derepression of CHD4/NuRD-regulated Genes in the Muscle of Patients with Dermatomyositis and anti-Mi2 Autoantibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptional-derepression-of-chd4-nurd-regulated-genes-in-the-muscle-of-patients-with-dermatomyositis-and-anti-mi2-autoantibodies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transcriptional-derepression-of-chd4-nurd-regulated-genes-in-the-muscle-of-patients-with-dermatomyositis-and-anti-mi2-autoantibodies/