Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab (TCZ) has demonstrated efficacy in improving signs/symptoms, reducing joint damage, and improving function and is well tolerated in patients (pts) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Elevated transaminase levels can occur, and, therefore, routine monitoring is recommended with TCZ treatment. This analysis examined the effect of TCZ on transaminase levels and evaluated hepatic serious adverse events (SAEs) observed in the clinical trial program.
Methods: Analyses were performed in all pts who received ≥1 dose of TCZ in 1 of 5 phase 3 placebo-controlled studies (OPTION, TOWARD, RADIATE, AMBITION, LITHE), a clinical pharmacology study, a phase 4 TCZ monotherapy study (ADACTA), or long-term extension studies. Pts with ALT/AST >1.5×ULN were excluded from the studies. Per protocol and consistent with recommendations in the USPI, DMARDs and TCZ dose were modified for ALT/AST elevations. Data were pooled and analyzed from initial TCZ exposure to May 2, 2012.
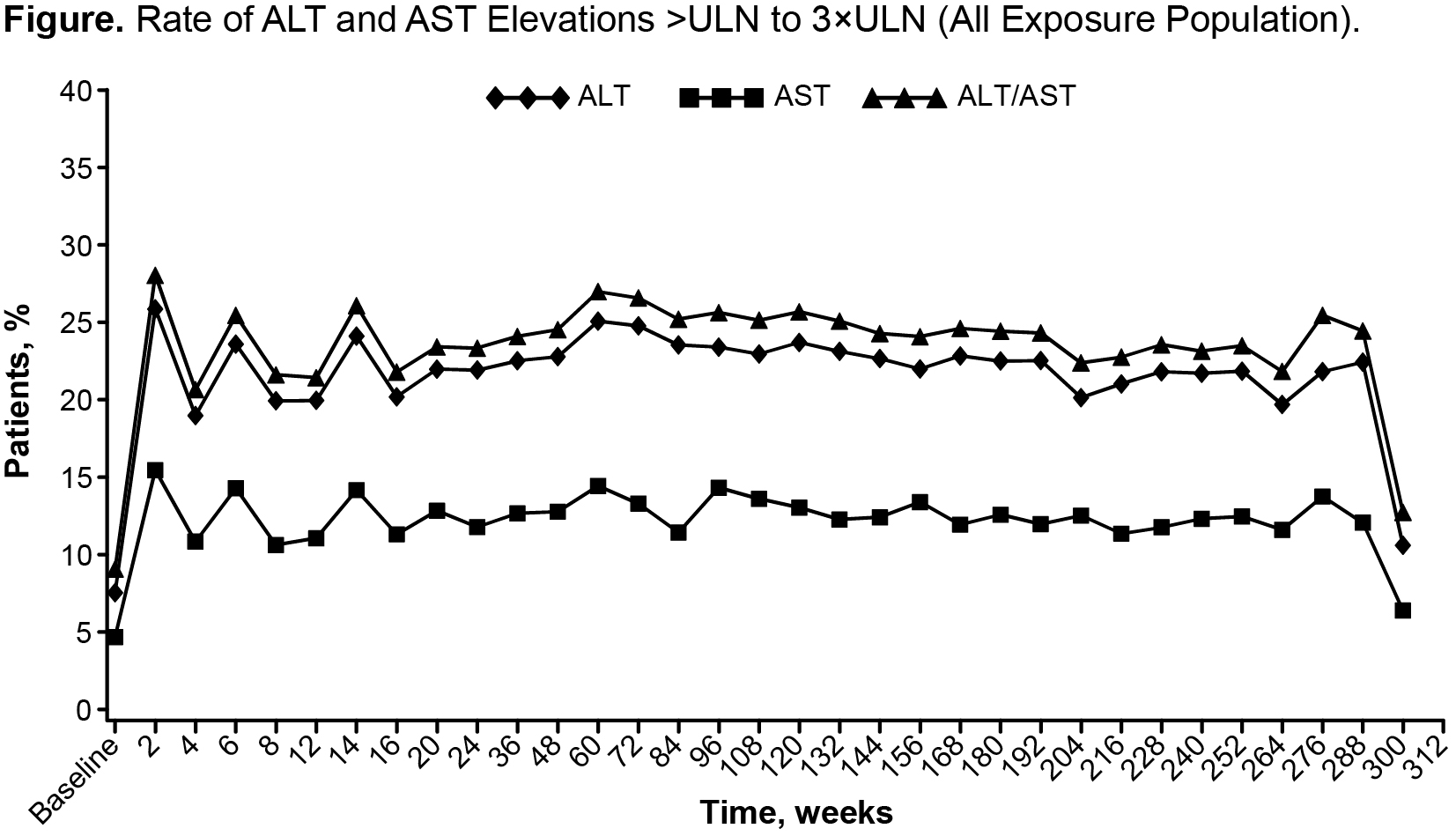
Results: In total, 4171 pts were included. Mean (median [range]) duration was 3.9 y (5.1 [0.0-6.8]); observation time was 16204.8 pt-y (PY). At baseline, 92.2%/95.2% of pts had ALT/AST levels within the normal range. Most pts were taking concomitant methotrexate at baseline or during the studies. Mean and median ALT/AST levels increased within the normal range after initiation of TCZ and remained stable at the higher level thereafter. ALT/AST levels increased from normal at baseline to >ULN at least once in 70.6% (2712/3839) and 59.4% (2357/3965) of pts, respectively, during the study period. In most of these pts, the highest postbaseline value was >1-≤3×ULN; elevations to >5×ULN occurred in 2.9% and 0.9% of pts, respectively. There was no trend for increased risk of transaminase level elevations over time (Figure). Analysis of ALT/AST increases >3×ULN over time showed that the elevations were single occurrences in most pts; at most, 0.2% of pts sustained elevations in ALT/AST during any 12-month study period. Elevated transaminase levels led to withdrawal in 2.5% of pts (105/4171); most withdrawals occurred during the first 12 months of treatment. There were 7 cases of hepatic SAEs (overall rate: 0.04/100 PY [95% CI: 0.02, 0.09]). Events were variable in nature with no pattern over time, and the rate was consistent with the background rate of hepatic SAEs estimated for RA pts treated with other biologic and conventional DMARDs.1, 2
Conclusion: Mean transaminase levels increased early in TCZ treatment, and the proportion of pts with elevations did not increase with continued TCZ exposure. In most pts, the elevations were single occurrences ≤3×ULN. To date, there is no evidence of increased rate of hepatic SAEs in pts treated with TCZ.
References: 1. Suissa S et al. Am J Med. 2004;117:87; 2. US MarketScan healthcare claims database analysis (Genentech, data on file; manuscript in prep).
Disclosure:
M. Genovese,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5;
J. M. Kremer,
Pfizer, Lilly,
2,
Pfizer, Lilly, Vertex,
5;
R. F. van Vollenhoven,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
2,
BMS,
2,
GSK,
2,
MSD,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
2,
UCB,
2,
Abbott Immunology Pharmaceuticals,
5,
BMS,
5,
GSK,
5,
MSD,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
UCB,
5;
R. Alten,
Horizon Pharma, Inc,
5;
J. J. Scali,
GSK, BMS, GADOR, Janssen, UCB-Montpellier, Roche,
8;
A. Kelman,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
3;
L. Rowell,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
3;
L. Pitts,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transaminase-levels-and-hepatic-events-observed-during-tocilizumab-treatment-pooled-analysis-of-long-term-clinical-trial-safety-data-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/