Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis remains a highly prevalent disease in the elderly, and there are currently no approved treatments that can modify the disease course. Currently, both oral and topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (both COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors) are frequently utilized to reduce pain and joint inflammation. These studies were done to demonstrate that rofecoxib topical may be an effective topical pain therapy.
Methods: Three non-clinical experiments were performed to assess the utility of this newly formulated rofecoxib topical. The first experiment studied permeation across human cadaver skin, the second assessed the pain relief obtained in a rat inflammatory joint model, while a third experiment studied the dermal irritation and bioavailability of the topical drug.
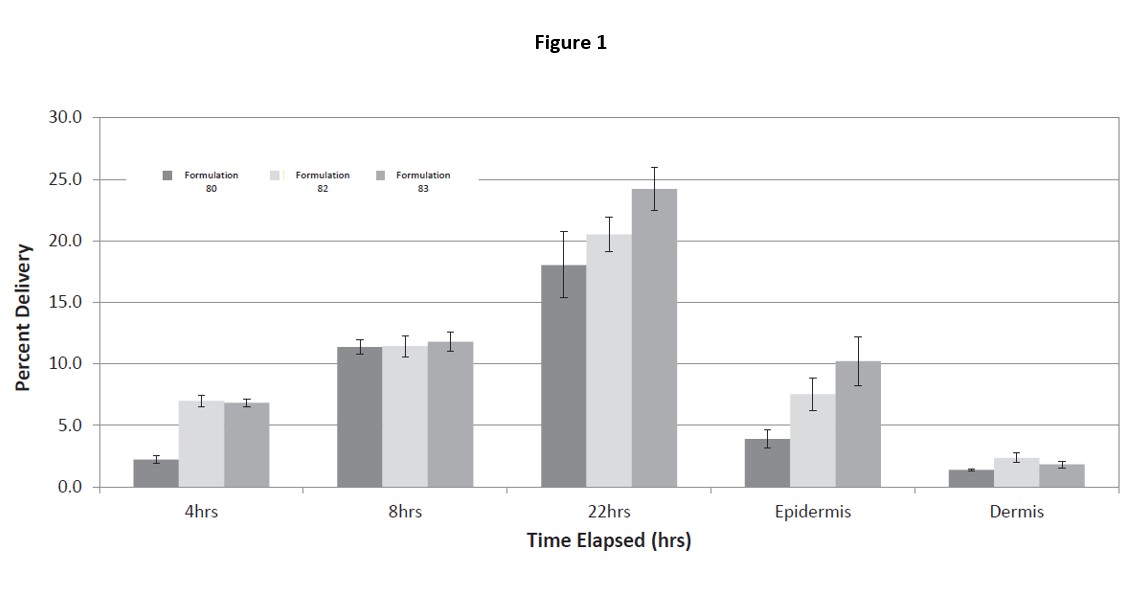
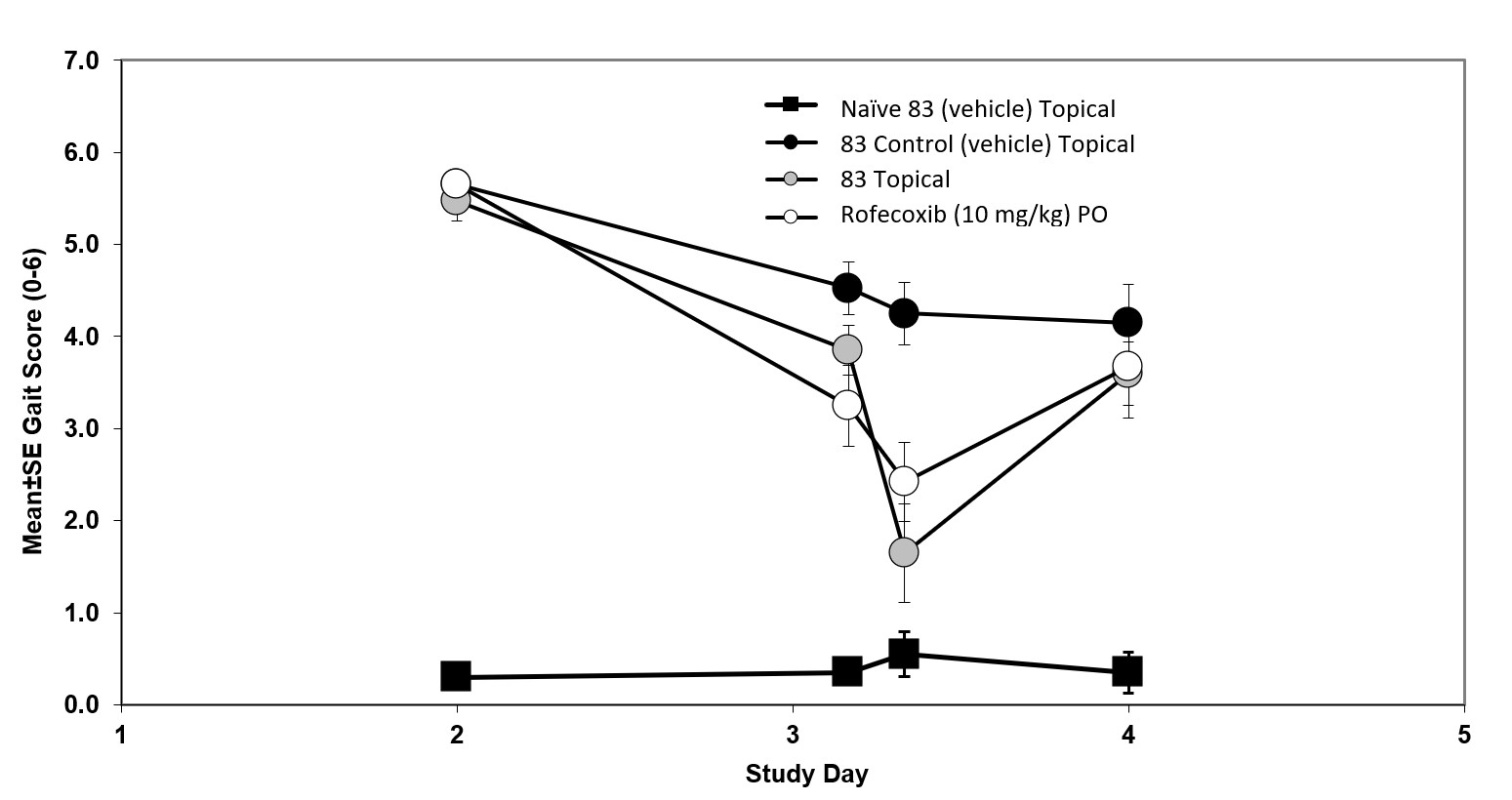
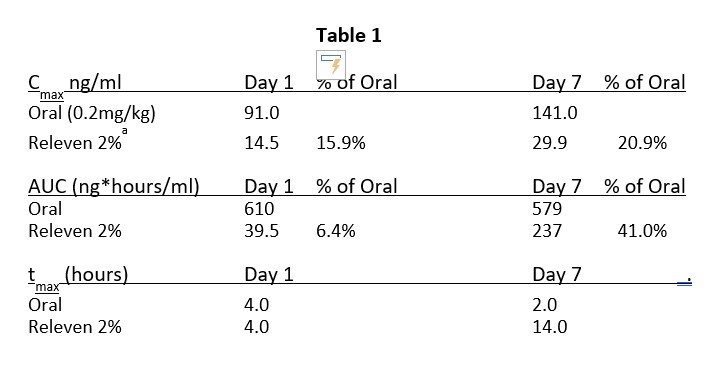
Results: Human skin Franz diffusion cell studies (Figure 1) were performed using human cadaver skin. Rofecoxib transferences of 6% at 4 hours and up to 24% at 22 hours were measured. Topical Rofecoxib was tested in an adjuvant-induced model (Figure 2) of pain in Rats. Day 0. Rats were weighed and randomized by body wight. The animals were then anesthetized and injected with Freund’s complete adjuvant into right rear joint to create severe joint inflammation and pain. Day 2. Rats were randomized by gait into groups of 10 with a score of “0” (normal) to “6” (hopping or carrying the leg). Day 3. Rats were dosed on the skin over the joint with: A. Ointment control (no API) on naive rats 100ul B. Ointment control (no API) C. Ointment with 2% API on test rats 100ul (1mg) D. Oral rofecoxib 10mg/kg. Following dosing the rats were gated for pain at 4, 8 and 24 hours. As shown in figure 2 at 8 hours topical rofecoxib showed efficacy equal to or greater than a super dose of oral rofecoxib. Study 3 was a Seven-Day Skin Irritation and Bioavailability Mini-Pig PK study (Table 1). Hanford miniature swine were dosed with topical rofecoxib for bioavailability. On day one 1.25ml of a 2% ointment was applied (25mg) to the 10% of the mini-pigs skin and a 24-hour pk study was done. On days 2 – 7 two applications of 1.25ml of the 2% ointment were applied and a 24-hour pk study was done on day 7. Draize scores for all animals through the end of the study on day 7 were all 0. One set of minipigs was dosed with 0.1mg/kg oral rofecoxib equivalent to a 12.5mg human dose of rofecoxib. The Day 1 tmax was the same as the oral rofecoxib demonstrating rapid absorption through the skin. The Cmax on Day 1 was 15% of the oral and the AUC 6.4% of oral which will provide sufficient rofecoxib to the local area of inflammation for pain relief. The Day 7 Cmax and AUC are significantly below the oral dose of rofecoxib reducing systemic exposure and potential side effects. No skin irritation was observed.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that that topical rofecoxib diffuses through human skin rapidly resulting in a dose that provides pain relief in a rat model of inflammatory arthritis. In addition, the topical dosing in mini pigs has been shown to have a lower systemic exposure then oral rofecoxib given at the lowest approved human dose. These results suggest topical rofecoxib may be an effective topical analgesic.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Register B, Lane N, Simon L, Newsam J, Kisak E, Pheneger J, Galvin J, Klein J, Hochberg M. Topical Rofecoxib for OA of the Knee [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/topical-rofecoxib-for-oa-of-the-knee/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/topical-rofecoxib-for-oa-of-the-knee/