Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1990–2014) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) coadministered with pegloticase attenuates anti-drug antibody formation, leading to higher response rates and markedly reduced infusion reaction risk compared with pegloticase + placebo (PBO).1 Here, we evaluate overall MTX safety data in pts enrolled in the MIRROR RCT.
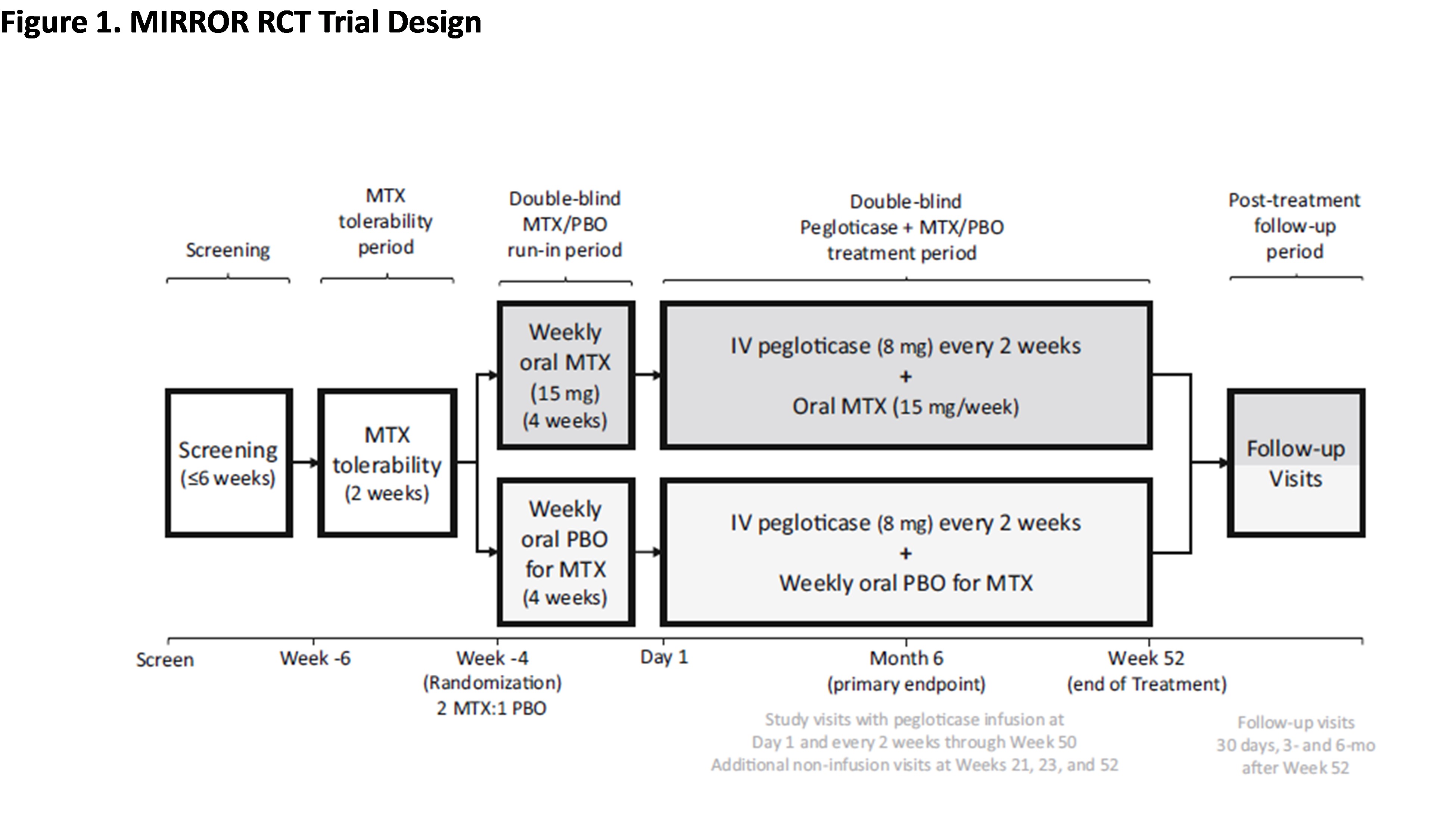
Methods: Patients (pts; Nf152) with uncontrolled gout (SU ≥7 mg/dL, oral ULT failure/intolerance, and tophi, ≥2 flares/yr, and/or gouty arthritis) received up to 52 wks of pegloticase (8 mg infusion Q2W) with either 15 mg oral MTX/wk or PBO and 1 mg folic acid daily; pts with eGFR < 40 ml/min/1.73 m2 were excluded. First infusion (Day 1) occurred after a 2-wk MTX tolerance period (Wk -6 to Wk -4) and a 4-wk MTX/PBO run-in (Wk -4 to Day 1). Baseline (BL) was prior to MTX exposure (Wk -6). Safety data from on-treatment pts (Nf96 MTX and Nf49 PBO; ≥1 pegloticase dose) were examined in aggregate (Figure 1).
Results: During the 52-wk tx period, the most common on treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) was gout flares (MTX: 66.7%; PBO: 71.4%).1 MTX-associated AEs (gastrointestinal disorders, skin disorders, infections) were similar between both groups.1 Pulmonary disorders (9.4% vs 4.1%) occurred more often in the MTX group, but with similar incidence rates (Table 1). More pts in the MTX vs PBO group had transient ALT levels >ULN (13.6% vs 6.3%; no >2 x ULN or above in either group). Pt proportion with AST levels >ULN was similar (6.9% MTX vs 6.3% PBO; >2 x ULN [n=2 vs 0] and >3 x ULN [n=1 vs 0]). However, ALT (+0.6 ± 23.3 vs. +2.5 ± 14.4 U/l), AST (+1.5 ± 22.1 vs. +1.5 ± 11.0 U/l), as well as Fib-4 index, a predictor of hepatic fibrosis progression, did not meaningfully change from BL at Wk 52.1,2 Occurrence of infections was similar (MTX: 18.8% vs PBO: 18.4%), with COVID-19 being most common (9.4% vs 6.1%; nominal p=0.35). Leukopenia and anemia each occurred in 1 pt in the MTX group (none in the PBO group; Table 1). Permanent MTX and PBO withdrawal due to TEAEs occurred in 11.5% and 16.3% of pts; 2 deaths occurred in the MTX group during the 52-wk tx (cardiac arrest and COVID-19 with multiple comorbidities), deemed unrelated to study tx. Renal function remained stable during tx in both groups.1 The change in creatinine from BL was -0.08 ± 0.15 and 0.01 ± 0.32 mg/dL. Stomatitis was uncommon (1 event during MTX run-in [1%], with no recurrence). MCV increased by ~4 fL from BL in the MTX group (3.8 ± 3.47]), with no change in the PBO group (0.0 ± 3.51), which is indicative of RBC macrocytosis, a surrogate marker for MTX compliance. Alcohol users (≥3 servings/wk) comprised 3.2% (4/126) of total screening failures. Among alcohol users enrolled (97/159; 61%), liver function did not worsen in the MTX vs PBO groups (ALT increase: 1 pt each [1.7% vs 3.4%]; AST increase: 1 pt [1.7%] vs 0).
Conclusion: MTX safety data from MIRROR RCT demonstrates that MTX in uncontrolled gout pts does not lead to an increased number/frequency of TEAEs vs PBO, including no increase in durable liver function changes and no increase in infections. These findings further underscore the safety of MTX coadministration with pegloticase during the 12 month MIRROR RCT.References1. Botson et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023;75:293-304.2. Schlesinger et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Domingues V, Woods A, Yang X, Lamoreaux B, Weinblatt M. Tolerance of Methotrexate Coadministered with Pegloticase in Patients with Uncontrolled Gout: Findings from MIRROR RCT [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tolerance-of-methotrexate-coadministered-with-pegloticase-in-patients-with-uncontrolled-gout-findings-from-mirror-rct/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tolerance-of-methotrexate-coadministered-with-pegloticase-in-patients-with-uncontrolled-gout-findings-from-mirror-rct/

.jpg)