Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and particularly those treated with B-cell-depleting agents frequently fail to develop humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations and have an increased risk of breakthrough infections and severe COVID-19 (Simon D, Arthritis Rheum (2022); Avouac J, Lancet Rheum (2022)). Passive immunization with monoclonal antibodies such as the FDA- and EMA-approved combination tixagevimab/cilgavimab could be an alternative option for this frail population. However, despite promising results from trials on healthy individuals (Levin MJ, NEJM (2022)), efficacy data on IMIDs are scarce. With our study, we aimed to investigate the effect of a pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with tixagevimab/cilgavimab on the humoral responses and on the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 in vaccine-refractory IMID patients.
Methods: A prospective interventional cohort study was performed on a cohort of high-risk vaccine-refractory IMID patients undergoing B-cell depletion and/or with primary immunodeficiencies that received PrEP with a single dose of subcutaneous tixagevimab/cilgavimab (150mg/150mg). COVID-19 outcomes and serum anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG were assessed at baseline, day 1, day 14, day 28, month 3, and after at least 6 months. Standardised incidence ratios (SIR) of COVID-19 were compared to (i) a control group of other vaccine-refractory IMID and primary immunodeficiency patients who did not receive prophylactic treatment with tixagevimab/cilgavimab and (ii) the local general population to assess the risk of symptomatic COVID-19. All included patients were attending the outpatient clinic of the Department of Medicine 3 (Rheumatology and Immunology) of the University Clinic Erlangen between March and September 2022. Ethical approval (#157_20 B) to conduct this analysis was granted by the institutional review board of the University Clinic of Erlangen.
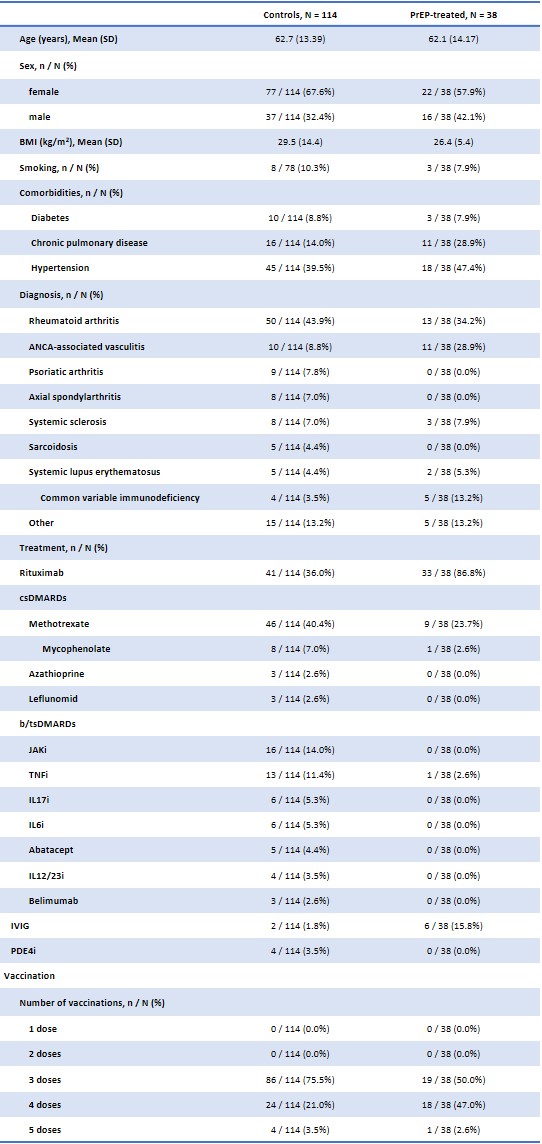
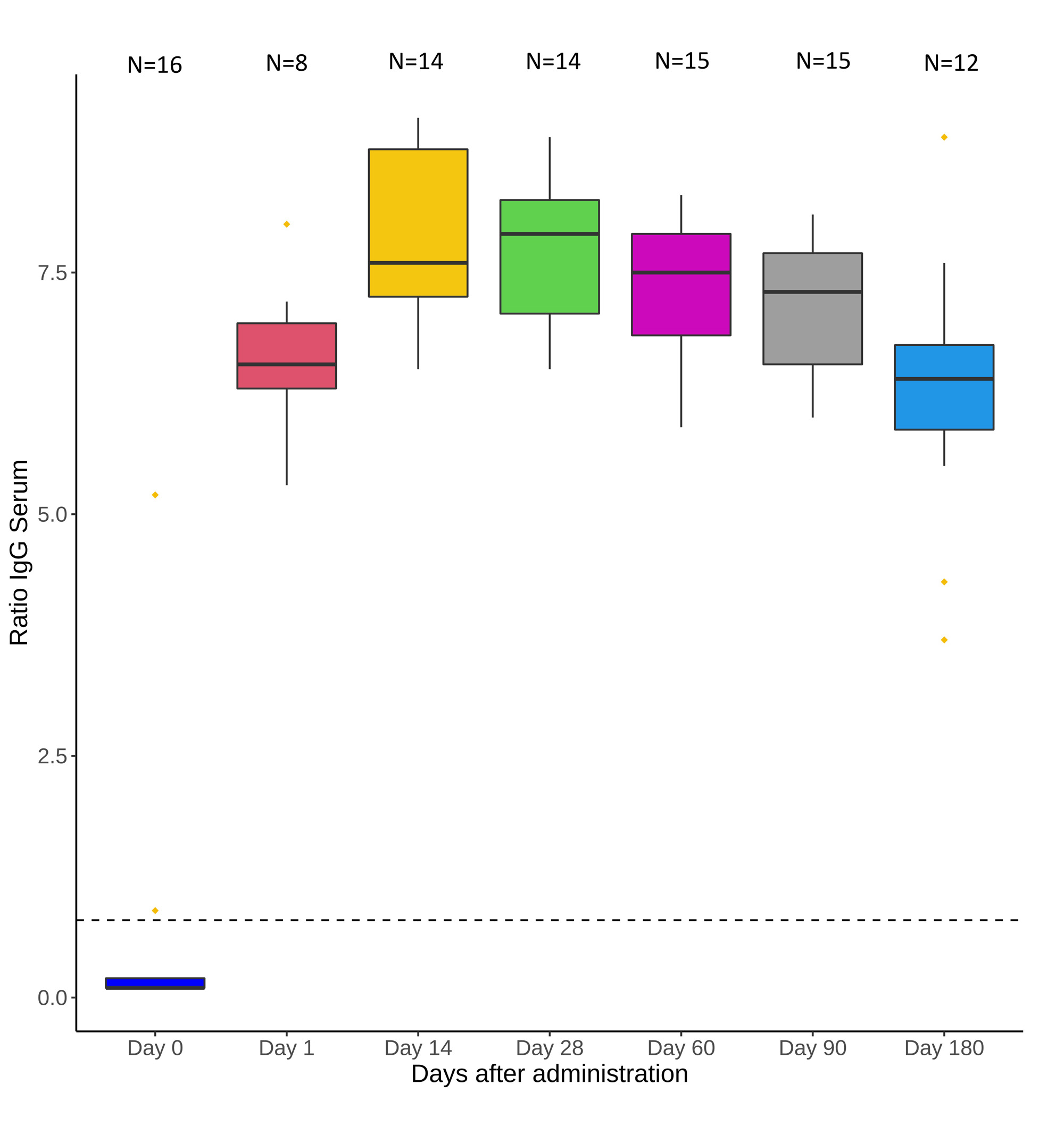
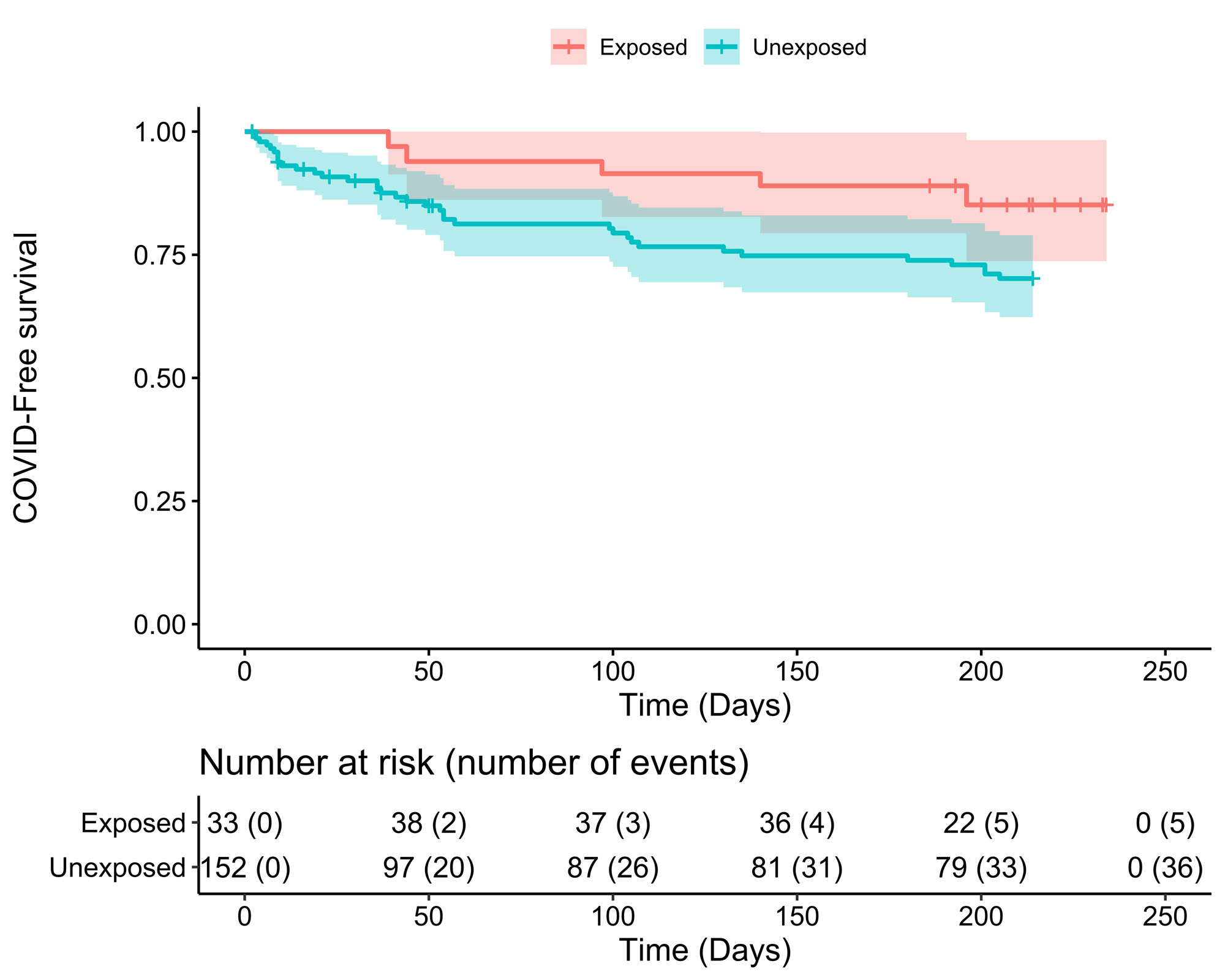
Results: A total of 38 high-risk IMID patients received tixagevimab/cilgavimab and were compared with 114 untreated high-risk IMID controls. Clinical and demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. Serum anti-Spike IgG increased to 6.6 OD (SD: ±0.8) at day one and remained positive up to month 6 (6.3±1.4 OD) (Figure 1). Compared to the general population, the SIR of COVID-19 in treated patients was 0.76 (95% CI: 0.24-1.58) despite the increased risk profile and more frequent use of B-cell-depleting therapies. The SIR of the untreated control group was 1.51 (1.07-2.02), corresponding to a significantly increased incidence of COVID-19. A Kaplan-Meyer curve of infection-free survival throughout the 6-month follow-up period is shown in figure 2.
Conclusion: Passive immunization with tixagevimab/cilgavimab is safe and effective in quicklly inducing anti-SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity and potentially in preventing COVID-19 in high-risk vaccine-refractory IMID patients. These data provide a proof of concept for the use of monoclonal antibodies as a preventative strategy against SARS-CoV-2 in vulnerable populations such as those with inadequate vaccine responses. Thus, the development of new neutralizing antibodies to protect this frail population remains critical.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Minopoulou I, Tascilar K, Corte G, Yalcin Mutlu M, Schmidt K, Bohr D, Hartmann F, Manger B, Kleyer A, Simon D, Harrer T, Schett G, Fagni F. Tixagevimab/Cilgavimab for the Prevention of COVID-19 in Vaccine-refractory Patients with Autoimmune Diseases: A Prospective Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tixagevimab-cilgavimab-for-the-prevention-of-covid-19-in-vaccine-refractory-patients-with-autoimmune-diseases-a-prospective-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tixagevimab-cilgavimab-for-the-prevention-of-covid-19-in-vaccine-refractory-patients-with-autoimmune-diseases-a-prospective-cohort-study/