Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Manual muscle testing (MMT) and Functional index 2(FI-2) are the usual methods in assessing disease activity and functional status in IIM1. Limitations of MMT8 include low sensitivity to change and floor/ceiling effect2 .FI-2 takes a longer time to administer. Several Timed function tests (TFTs) namely 2-minute walk test (2MWT), 30s raise from a chair test and 30s 1kg arm rise test have potential to measure both these aspects2 and needs to be evaluated in IIM.
Our objective was to evaluate the performance of TFT in assessing muscle diseases at baseline and to evaluate the performance of TFTs to detect the longitudinal change in muscle power and endurance at 3 and 6 months.
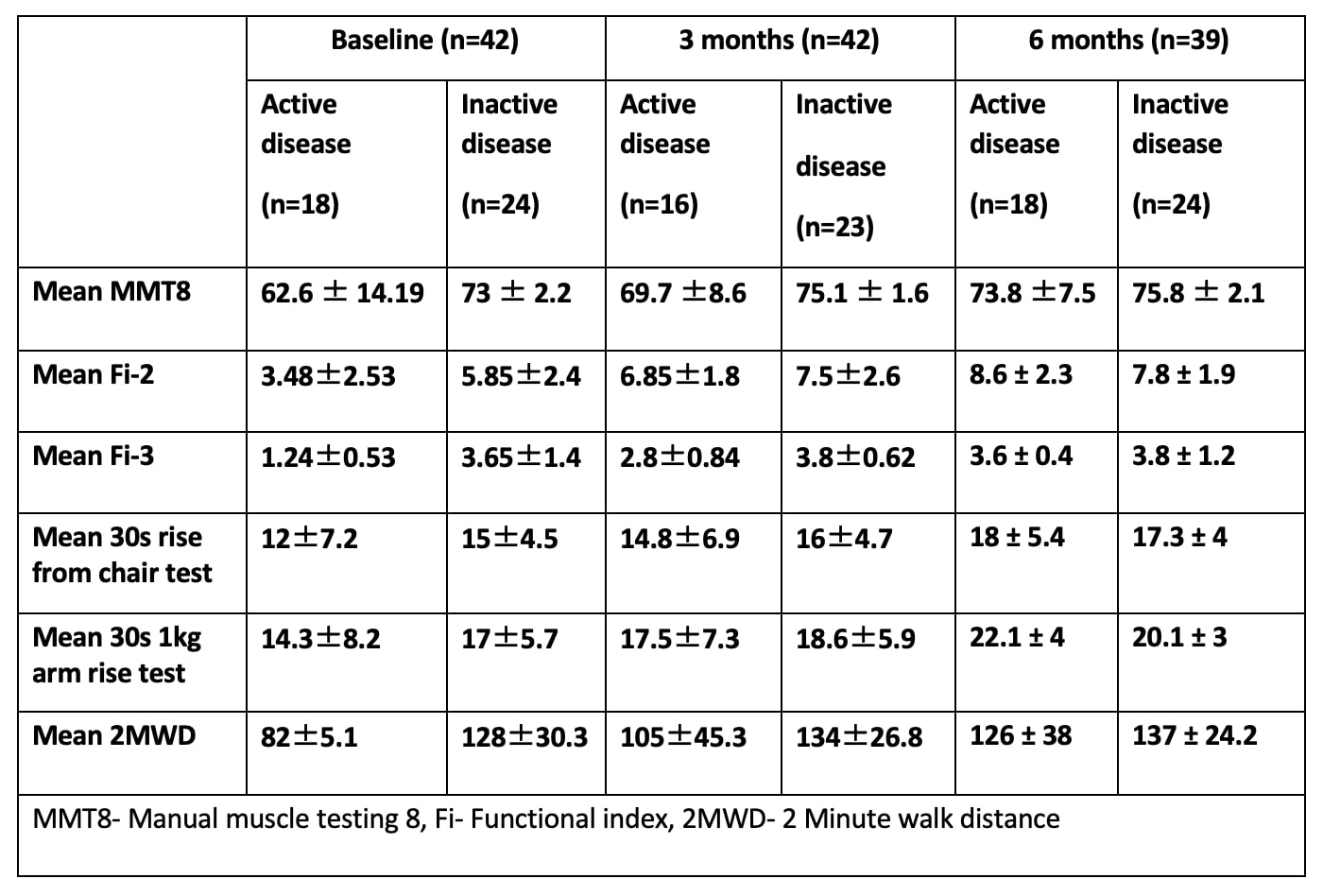
Methods: This was an observational cohort study which included 42 patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis satisfying EULAR/ACR classification criteria. MMT8, FI-2, FI-3 and TFTs were done at baseline, 3 months and 6 months. Individuals with a stable MMT-8 over last 1 month with no evidence of extra muscular disease activity were classified as inactive and the others as active disease.
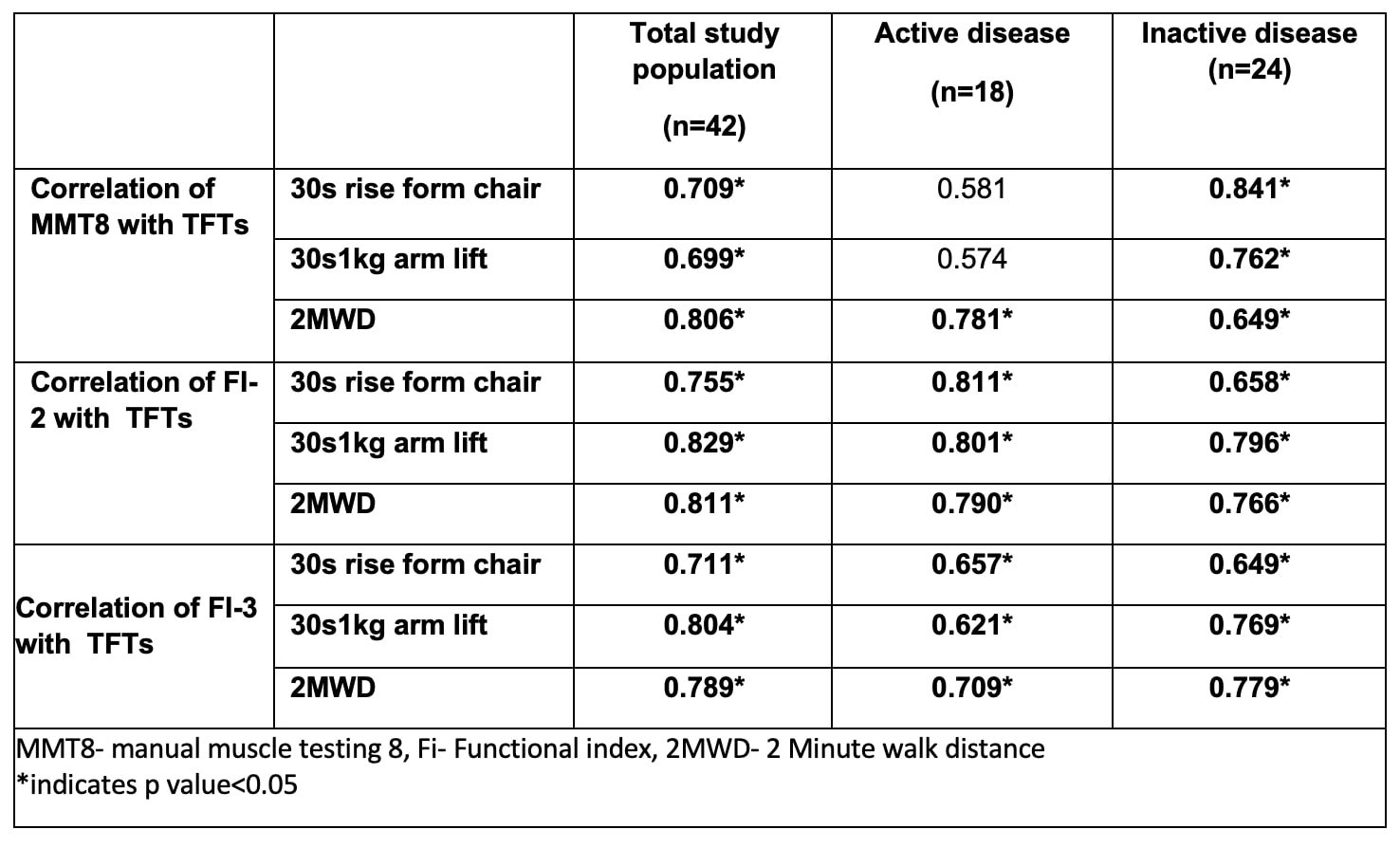
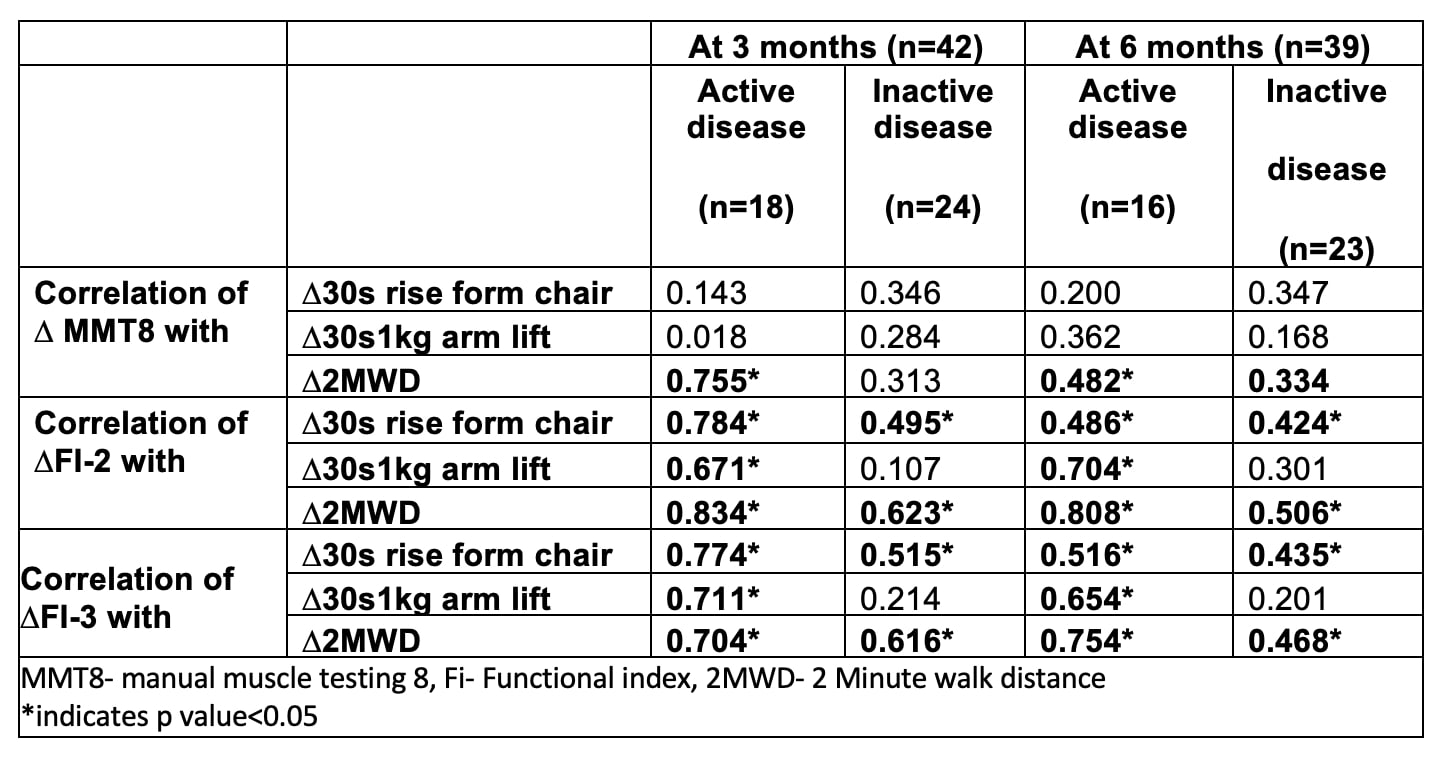
Results: All 42 [11 (27%) polymyositis, and 31 (73%) dermatomyositis] completed three month follow-up assessment and 39 underwent evaluation at 6 months. The mean MMT8 of the total study population at 59±12, 67 ±8 and 71 ± 9 at baseline, 3 and 6 months respectively. In the active disease subgroup the MMT-8 was 62.6 ± 18, 69.7 ± 9 (n=42), 73.8 ± 9.6 (n=39)at baseline, 3 and 6 months respectively. The 3 TFTs had moderate to high correlation with MMT8 and FI-2 adn FI-3 at baseline (Table 2). The change in TFTs showed a moderate to strong correlation with the change in FI-2 as well as FI-3 among the study population at three months and six months (Table 3). Among the TFTs 2MWD had the best performance with moderate correlation with both MMT8, FI-2 and FI-3 in active disease suggesting a role in assessing both disease activity and endurance.
Conclusion: Using timed function tests can be an excellent alternative to FI-2/3 in assessing muscle endurance. 2-minute walk distance could be a better alternative to conventional muscle testing as it measures both power and endurance, is simple to perform and could be a valid patient reported outcome measure.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
dunga s, Kavadichanda C, Negi V. Timed Function Tests as Measures of Disease Activity and Functional Outcome in Inflammatory Myositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/timed-function-tests-as-measures-of-disease-activity-and-functional-outcome-in-inflammatory-myositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/timed-function-tests-as-measures-of-disease-activity-and-functional-outcome-in-inflammatory-myositis/