Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Macrophages play an important role in the pathophysiology of Takayasu arteritis (TAK) as granulomatous inflammation is typically found in affected arteries. The expression of the M1 marker (CD86) is increased in the aorta of TAK patients and patients with atherosclerotic disease compared to controls, but the expression of the M2 marker (CD206) overcomes CD86 expression. Thus, this study aims to evaluate in vitro macrophage polarization upon stimulation with sera from TAK patients and healthy controls (HC).
Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed with the inclusion criteria of age ≥ 18 years and fulfillment of the 2022 ACR/EULAR criteria for the TAK group, and age ≥ 18 years plus absence of systemic autoimmune or inflammatory diseases for the HC group. All participants provided written informed consent before entering the study. The human monocytic cell line developed from an acute monocytic leukemia patient (i.e., THP1 cells) was used as macrophage-derived monocytes. The THP-1 cells were cultured and stimulated in vitro to differentiate as M0 macrophages with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA). Then, M0 macrophages were cultured with stimulation with sera from TAK patients presenting active disease (n=12), TAK patients in remission (n=11), and healthy controls (n=23). After 2 days, cells were detached and macrophage subpopulations M0, M1, M2a, M2b, and M2c were identified by flow cytometry. Phenotypes were defined as follows: M0 (CD68+, CD80–, CD86–, CD163– and CD206–), M1 (CD68+, CD80+, CD86+, CD163– and CD206–), M2a (CD68+, CD80–, CD86–, CD163– and CD206+), M2b (CD68+, CD80–, CD86+, CD163– and CD206+) and M2c (CD68+, CD80–, CD86–, CD163+ and CD206+).
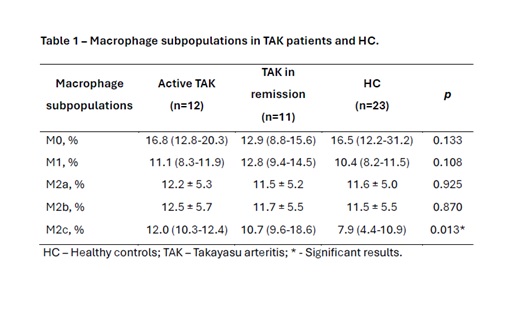
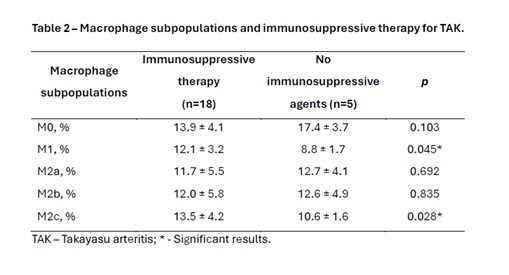
Results: Healthy controls had a higher proportion of M0 macrophages than M1 and M2c macrophages (p < 0.05), while TAK patients had no differences among macrophage subpopulations. Sera from TAK patients induced an increased median percentage of M2c macrophages than HCs’ sera [11.7% (10.1-16.7) vs. 7.9% (4.4-10.9); p = 0.003]. In addition, the proportion of M2c macrophages was higher in both groups: active disease [11.9% (10.3-12.4)] and remission [10.7% (9.6-18.6)] than HC [7.9% (4.4-10.9)]; p < 0.05 (Table 1). The use of immunosuppressive agents (i.e., methotrexate or leflunomide) led to higher proportions of M1 (12.1%±3.2 vs. 8.8%±1.7; p = 0.045) and M2c macrophages (13.5%±4.2 vs. 10.6%±1.6; p = 0.028) compared to those without immunosuppressive therapy, respectively (Table 2). No differences were found in macrophage subpopulations regarding the use of prednisone or biological agents. Daily prednisone dose had a significant correlation with M0 macrophages (r = 0.617; p = 0,043). No correlations were found between disease duration or acute phase reactants and macrophage subpopulations.
Conclusion: The exposure of macrophages to TAK patients’ sera induced higher proportions of M2c macrophages regardless of disease activity status. Immunosuppressive therapy induced a higher proportion of M1 and M2c macrophages. Although daily prednisone dose correlated with M0 macrophages, no impact on macrophage polarization was found with prednisone use or with biological therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
dos Santos J, Orikaza C, Aguiar M, Keppeke G, de Souza A. THP1-derived Macrophage Polarization in Takayasu Arteritis – Impact of Disease Status and Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/thp1-derived-macrophage-polarization-in-takayasu-arteritis-impact-of-disease-status-and-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/thp1-derived-macrophage-polarization-in-takayasu-arteritis-impact-of-disease-status-and-therapy/