Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical III
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The therapeutic options for systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) have evolved rapidly, with recent guidelines released by the ACR and American Thoracic Society (ATS). Mycophenolate (MMF) has replaced cyclophosphamide (CYC) in most cases of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease after the results of the Scleroderma Lung Study II (SLS-II). The focuSSed trial found benefit of tocilizumab (TCZ) in SSc-ILD as well. Combination immunosuppressive therapy (CI) with rituximab (RTX) and mycophenolate (MMF) over MMF monotherapy has also gained evidence since the EVER-ILD trial publication. The antifibrotic nintedanib has also shown benefit in the SENSCIS trial. We sought out to better understand prescribing patterns of therapy for SSc-ILD internationally, examine treatment trends overall to help examine guideline penetrance, and better understand what drives clinical practice decisions by international SSc experts.
Methods: A survey polling international SSc experts was conducted from October 2023 through March 2024. This survey was filled out by experts at member institutions of the Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium (SCTC) and the European Scleroderma Trials and Research Group (EUSTAR). Members were invited to complete the survey by mass email to all members and/or by newsletters.
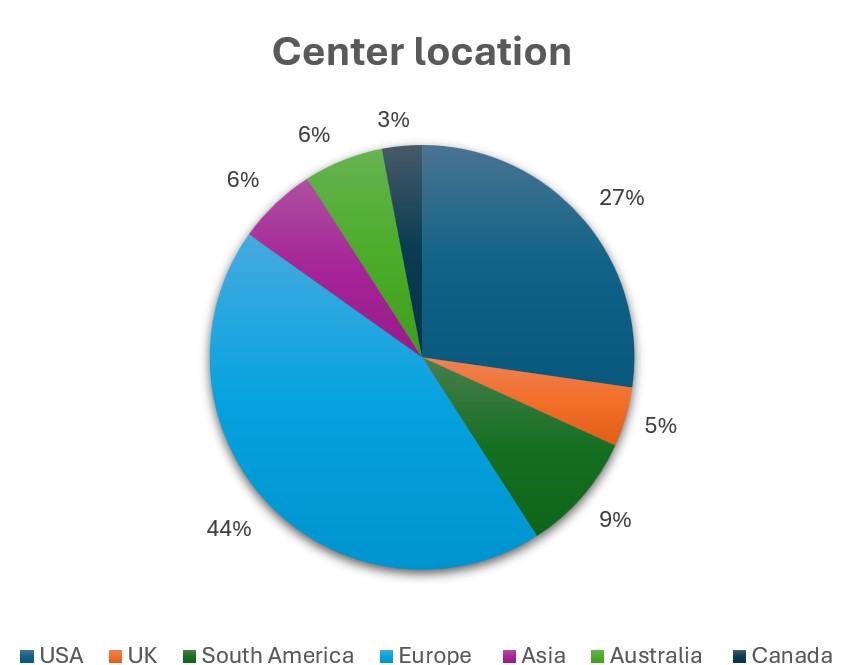
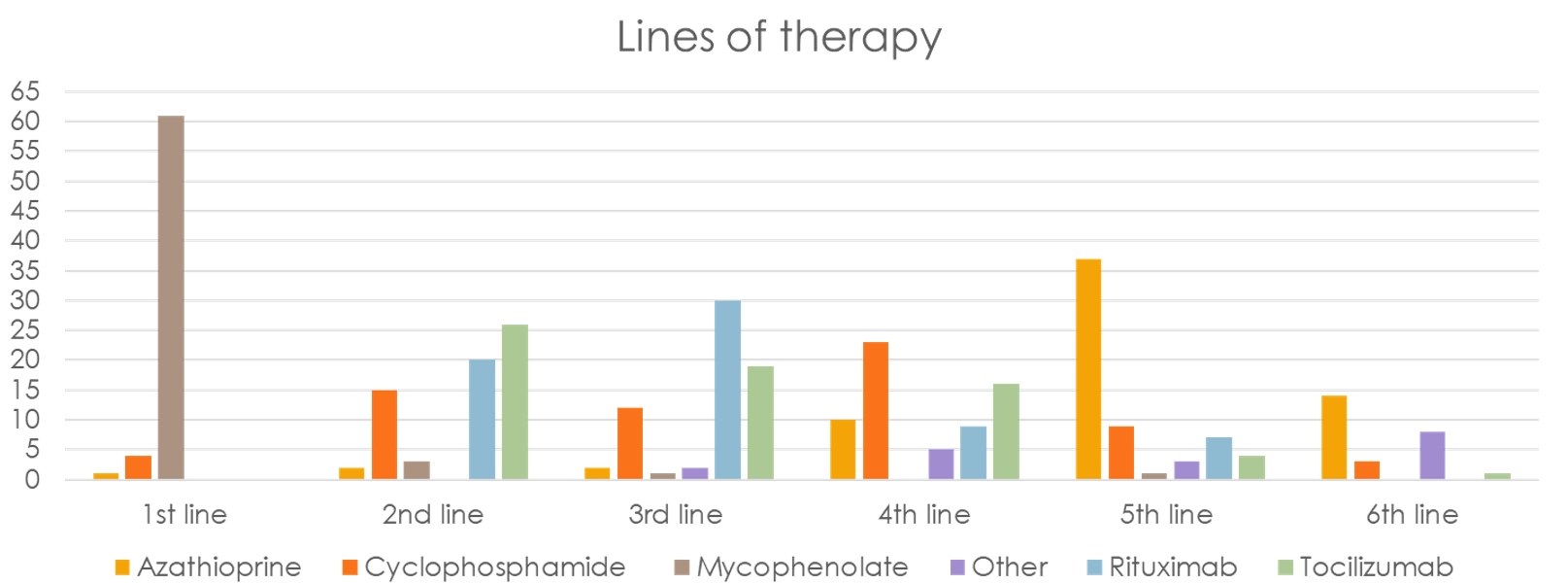
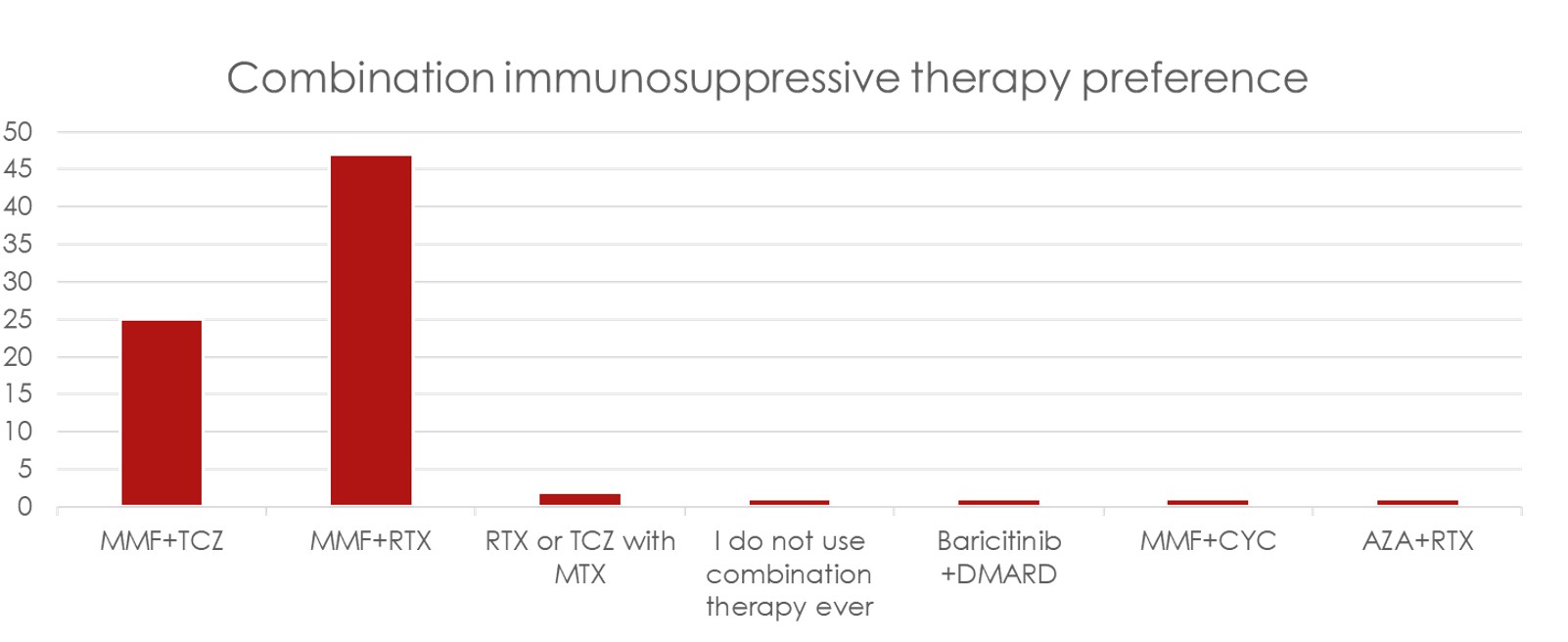
Results: There were 69 total responses of which 3 were excluded due to incomplete surveys. Respondents were mainly at European (44%), followed by USA (27%) locations (Figure 1). MMF was the most common 1st line treatment (61/66) for SSc-ILD, followed by a roughly split preference for RTX or TCZ for 2nd/3rd line treatment with CYC and AZA being less preferred options (Figure 2). Stem cell transplant referral was the most common “other” treatment preference for SSc-ILD (36%). Most experts add an antifibrotic (57%) or use CI therapy (24%) with failure of initial therapy. When CI is used, MMF/RTX is used most (47/66), followed by MMF/TCZ (25/66) (Figure 3). Patients having a systemic inflammatory profile as defined by the focuSSed trial (elevated CRP or ESR or platelets) drove preference for TCZ over MMF as initial monotherapy (51/66) and adding TCZ to MMF (25/66). Steroids were used for SSc-ILD treatment by 36% of experts, with 12% of these respondents using greater than 20 mg of prednisone equivalent.
Conclusion: First line treatment preferences are in line with the ACR ILD treatment guideline. CI is still not typically used, though the EVER-ILD trial appears to have influenced prescribing patterns with RTX/MMF combination therapy more typical than TCZ/MMF. A significant proportion of experts still use prednisone in SSc-ILD, though the upcoming ACR ILD guidelines advise against this. Further studies, specifically evaluating combination MMF/TCZ vs MMF/RTX and whether TCZ is effective for SSc-ILD outside of the inflammatory laboratory profile in the inclusion criteria of the focuSSed trial are necessary to help guide this dynamic field. Further adoption of the ACR ILD guideline may also change prednisone use patterns in SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Macklin M, Bauer Ventura I, Khanna D. Therapeutic Choices in Systemic Sclerosis Associated Interstitial Lung Disease, a Survey of International Experts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-choices-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-a-survey-of-international-experts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-choices-in-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-a-survey-of-international-experts/