Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
Background/Purpose: Despite significant progress in understanding the pathophysiology of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA), the availability of tools to accurately predict treatment response remains limited. Our objective was to identify gene expression patterns that may predict treatment response to tofacitnib in patients with polyarticular course JIA.
Methods: Whole blood samples were collected from JIA patients using PAXgene tubes prior to starting tofacitinib treatment as part of the clinical trial NCT02592434. Patients were categorized as treatment responders (TR) if they achieved a JIA-ACR70 response or higher at week 18, while those with a JIA-ACR response of 30 or less were considered poor responders (PR). Bulk RNA sequencing was performed using Illumina Nova-seq, generating 50 million reads per sample. Gene expression levels were measured at baseline. Differential gene expression analyses were conducted using the dream method from variance Partition. Gene ontology overrepresentation analyses were subsequently performed using the dseqr adaptation of the goana function from the limma R package.
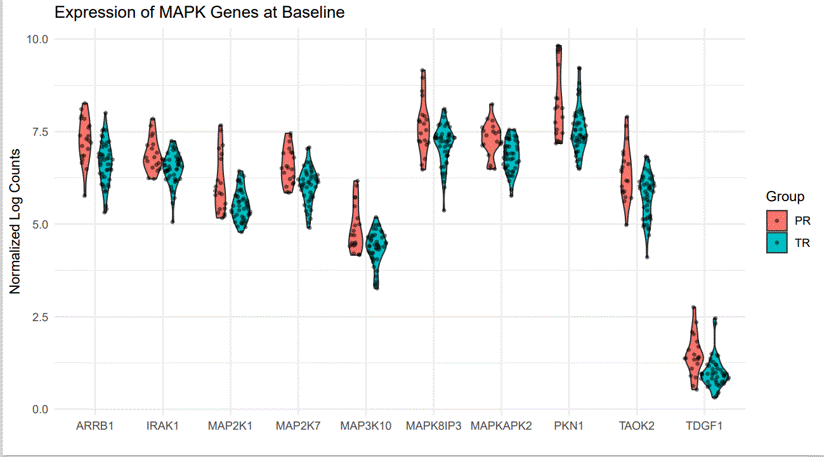
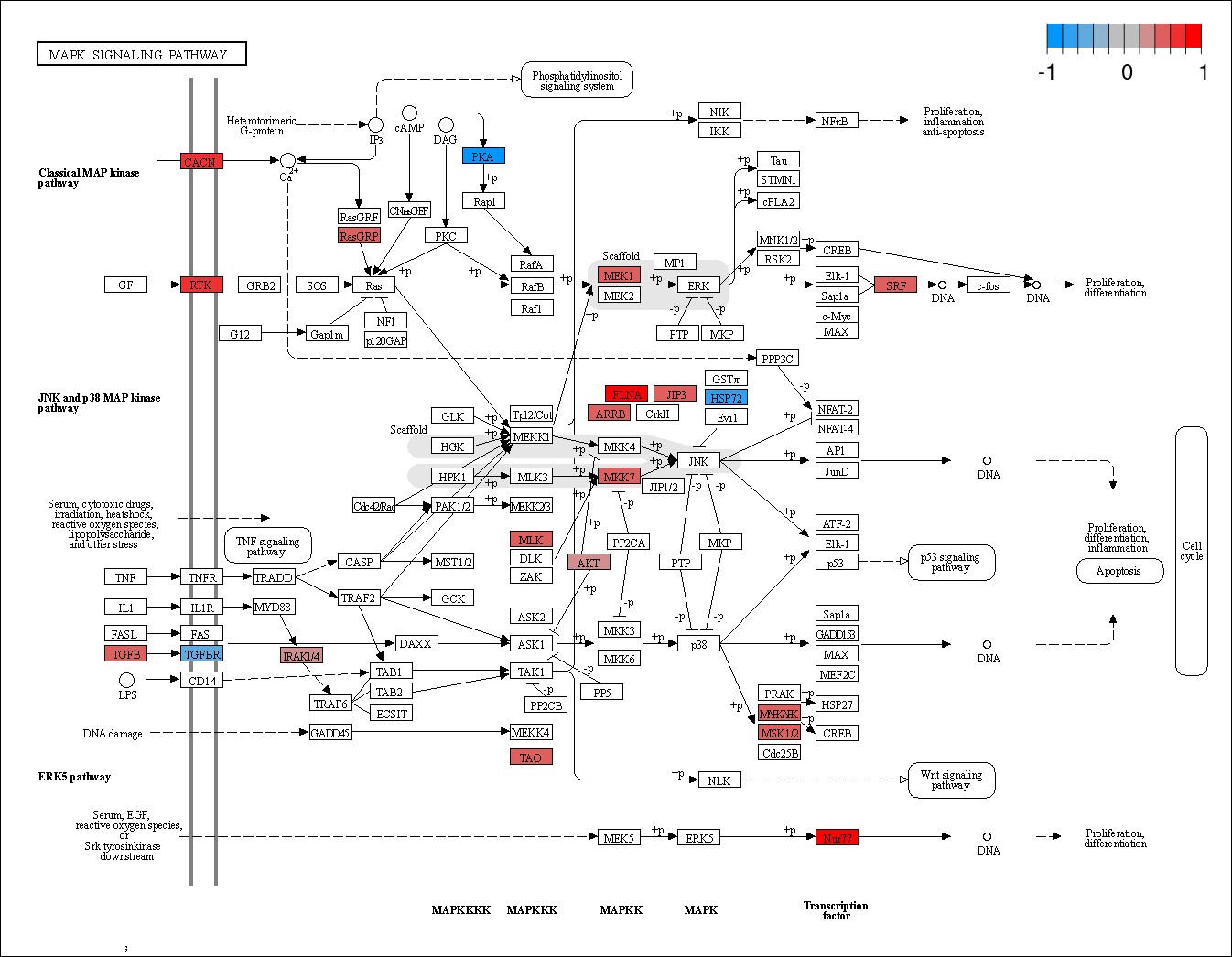
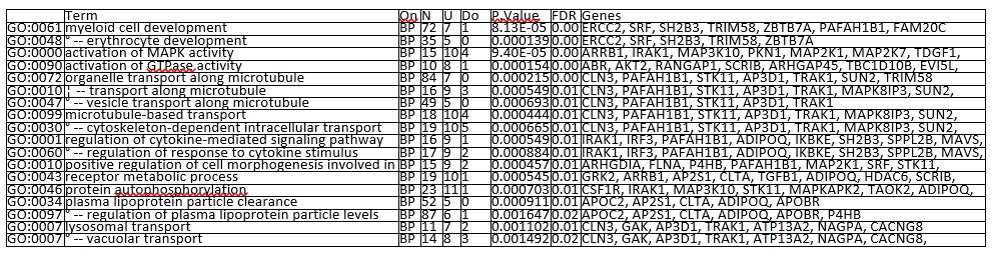
Results: 663 of 31,799 genes assayed were identified as differentially expressed in PR as compared to TR (FDR< 0.05) from samples acquired prior to treatment initiation. Gene ontology analysis revealed a significant upregulation of genes associated with MAP kinase pathway activation in PR (p=9.40E-05) (Figure 1.a &1.b). Other ontologies that were upregulated in PR included myeloid stem cell development (p=8.13E-05), activation of GTPase activity (p=0.00015), and organelle transport along microtubule (p= 0.00021) (Table 1).
Conclusion: Assessment of MAP kinase pathway gene expression prior to treatment may aid in identification of polyarticular course JIA patients that could exhibit poor response to tofacitinib. If confirmed, this finding could be used to personalize treatment of JIA patients for whom tofacitinib treatment is considered.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Eloseily E, Pickering A, Dhakal S, Brunner H, Thornton S, Grom A. The Upregulation of MAP Kinase Pathway Genes Is Associated with Poor Treatment Response to Tofacitinib in Polyarticular Course Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-upregulation-of-map-kinase-pathway-genes-is-associated-with-poor-treatment-response-to-tofacitinib-in-polyarticular-course-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-upregulation-of-map-kinase-pathway-genes-is-associated-with-poor-treatment-response-to-tofacitinib-in-polyarticular-course-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/