Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The triglyceride to HDL cholesterol (TG/HDL) ratio, a recognized surrogate marker of insulin resistance, has emerged as a predictor of cardiovascular (CV) risk. However, its clinical relevance in RA remains unexplored. In this study, we aimed to investigate the prognostic value of the TG/HDL ratio in predicting mortality in RA patients.
Methods: RA patients meeting the 1987 ACR criteria were recruited consecutively from rheumatology practices from 1996 to 2011. Patients were invited to return for periodic follow-up evaluations. At each visit, clinical and laboratory variables were recorded, including measures of RA disease activity, CV risk factors and the occurrence of CV events. All deaths were confirmed with a death certificate. Deaths were classified as having a CV cause if the death certificate included conditions with ICD-9 codes 390-459.
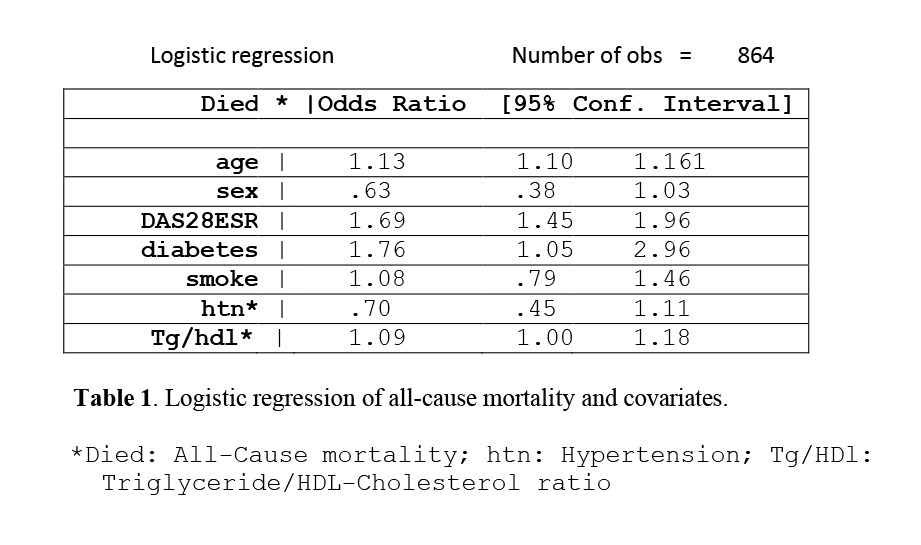
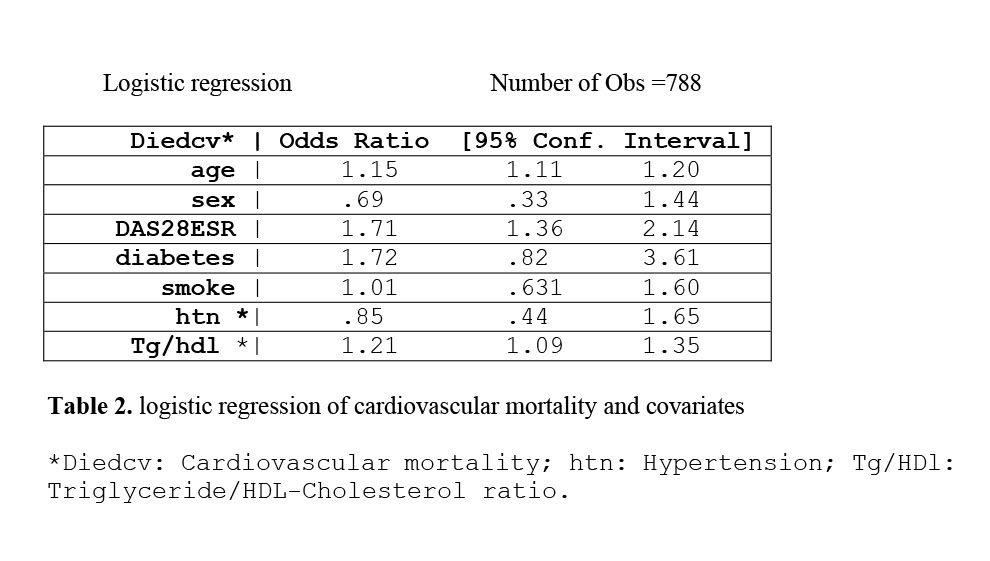
We used logistic regression analysis to examine the association between TG/HDL ratio and all-cause and CV mortality. Results were adjusted for other risk factors including age, sex, smoking status, diabetes, hypertension, and disease activity (measured by DAS28 ESR).
Results: We studied 1211 patients [906 (75%) were women]. The mean follow-up time was 9.959 person-years with 278 deaths (2.7 per 100 person-years) for all-cause mortality. The mean follow-up time for CV mortality was 8745 person-years with 121 deaths (0.3 per 100 person-years).
TG/HDL ratio was associated with an increased risk of both all-cause mortality (OR=1.09, 95% CI 1.00-1.19, p=0.041) (Table 1) and CV mortality (OR=1.21, 95% CI 1.09-1.35, p< 0.001). (Table 2) after adjusting for age, sex, disease activity, diabetes, smoking status, and hypertension.
Conclusion: TG/HDL ratio is an independent risk factor of all cause and CV mortality in RA patients. These findings suggest that the TG/HDL ratio may be a useful biomarker for assessing CV risk among patients with RA, which could lead to improved risk management and reduced CV morbidity and mortality among RA patients. The role of insulin resistance in RA deserves further study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Restrepo Suarez J, Lorenzo C, Del rincon I, Escalante A. The Triglyceride to HDL Ratio, a Surrogate Marker of Insulin Resistance, Predicts All Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-triglyceride-to-hdl-ratio-a-surrogate-marker-of-insulin-resistance-predicts-all-cause-and-cardiovascular-mortality-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-triglyceride-to-hdl-ratio-a-surrogate-marker-of-insulin-resistance-predicts-all-cause-and-cardiovascular-mortality-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/