Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: RA, Spondyloarthritis, & OA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is a chronic inflammatory rheumatic disease involving the axial skeleton, entheses and peripheral joints, and may occur together with extra-articular manifestations, such as psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease and uveitis. Patients with SpA are experiencing deterioration or bad quality of life. The most common symptoms are: physical limitations and limitations of motor activity, fatigue and sleep disturbances caused by the disease and inflammatory pain. Due to the young age of patients the sexual disorders, limitations or inability to work or to perform other social roles should be put into considerations.Since the last century in medicine it is considered that the regular quality of life assessment should complement the clinical efficacy assessment of the applied treatment. The efficacy of the biological treatment and its superiority to placebo has been proved in the newest research. There is scarcity of the studies which evaluate the efficacy of biological treatment regarding the quality of life. It is worth paying attention that the patients’ satisfaction should be crucial in treatment selection and planning.
The main purpose of this meta-analysis was to evaluate the impact of biological treatment on the quality of life of the patients with ankylosing spondylitis.
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed on PubMed and Web of Science until May 2020 to obtain eligible studies. The used search terms were as follows: (‘‘Quality of Life’’) OR (‘‘patient-reported outcomes’’) OR (“well-being”) OR(“health related quality of life”) AND(“biological treatment ofankylosing spondylitis”) in this meta-analysis.
Results: Twenty-three papers were finally assigned to meta-analysis. Quality of life was evaluated using the questionnaires: SF-36, ASQoLS, FACIT-F: EQ-5D-5L, EQ-5D VAS. The results of the meta-analysis showed thatin baseline study the quality of life of patients with AsS treated with biological drugs and the control group (placebo) did not differ (Q = 3.32, p = 0.854, I2 = 0.00%). However, after 16 weeks of the study the results were statistically different, and the group treated with biological drugs had better improvement in quality of life. The positive direction of the improvement of functioning was observed within the functional efficiency assessed with questionnaire BASFI.What is more, the significant decrease of CRP in the group with biological treatment was revealed, which confirmed the effectiveness of therapy.
Conclusion: (1) The biological treatment significantly improves the quality of life andfunctional efficiency as well as it decreases the inflammation markers in patients with SpA. (2) There is a need for introduction of the uniform study protocol andthe definition of a standard methodology for research tools in the evaluation of quality of life in patients with SpA in order to comparethe different results in differentscientific teams.
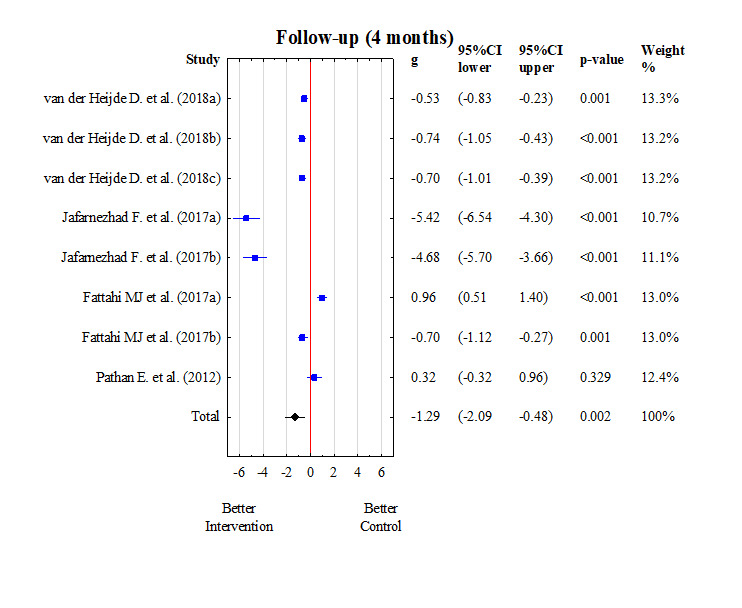 Quality of life in the control and intervention group after 4 months of treatment
Quality of life in the control and intervention group after 4 months of treatment
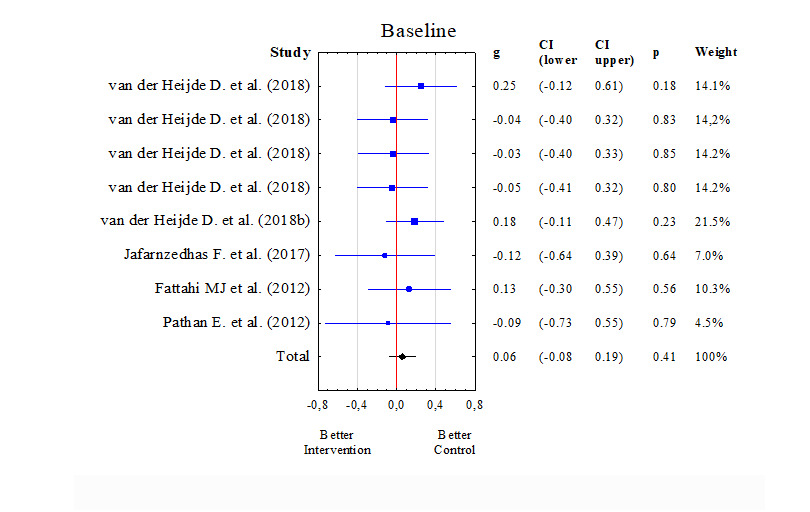 Quality of life in the control and intervention group at the beginning of treatment
Quality of life in the control and intervention group at the beginning of treatment
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tański W, Chabowski M, Świątoniowska-Lonc N, Jankowska-Polańska B. The Role of Biological Treatment in the Health-Related Quality of Life of Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients’ Assessment – Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-biological-treatment-in-the-health-related-quality-of-life-of-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-assessment-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-biological-treatment-in-the-health-related-quality-of-life-of-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-assessment-meta-analysis/
