Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Clinical Manifestations
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is a severe manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) that leads to significant morbidity and mortality. Therefore, it is essential to identify biomarkers that predict incident LN in a newly diagnosed SLE patient. Anti-double stranded DNA antibodies (dsDNA) serve as a standard of care disease activity marker in patients with LN. However, the evidence for a predictive role of anti-dsDNA for incident LN is limited. To fill these knowledge gaps, we performed a case-control study to look at the association of anti-dsDNA in newly diagnosed SLE for future incident LN. We determined that the presence of and high titers of anti-dsDNA in newly diagnosed SLE are a significant predictor of future incident LN. Additionally, we found that the presence as well as the titers of anti-dsDNA at the time of SLE diagnosis predict earlier onset of LN. These results provide a roadmap for the use of anti-dsDNA levels to risk stratify newly diagnosed SLE patients. This stratification could guide disease activity monitoring to diagnose LN at an earlier stage.
Methods: In a prospective, observational case-control study, patients with the diagnosis of SLE were divided into cases (SLE patients with a biopsy proven LN) and controls (without LN). A logistic regression model was utilized to identify the predictive value of the presence of and high titers of anti-dsDNA for future incident LN. A survival analysis was performed to identify the time to new development of LN in relation to the presence of and high titers of anti-dsDNA.
Results: Of 394 SLE patients included in this study, 300 had LN, and 94 did not have LN. In univariate logistic regression analysis, the presence of and high titers of anti-dsDNA were associated with a significantly higher risk for incident LN. In a multivariate logistic regression model, the risk of incident LN was 2-fold with the presence of anti-dsDNA antibodies at the time of SLE diagnosis, adjusting for age, gender and sex (OR 2.1, CI 1.2- 3.4, p 0.005). In comparison to Caucasians the African Americans had a 5-fold risk of developing LN. In a multivariate Cox proportional hazard model, the adjusted risk for the early development of LN was 44% higher in those with anti-dsDNA. The adjusted risk was about 5-fold for other races in comparison to Caucasian race. By utilizing titers as a continuous variable in the multivariate model, the adjusted risk for early development of LN increased by 8.3% for each doubling of anti-dsDNA. In Kaplan Meier analysis, the median time(month) to development of LN among patients who had a positive anti-dsDNA with new onset SLE was much shorter than patients who did not have anti-dsDNA with new onset SLE (14.4 vs 34.4, p 0.003).Similarly, the median time to incident LN among patients with high anti-dsDNA titers (≥2 times the upper limit of normal) was significantly lower compared to those with lower anti-dsDNA titers (12.3 vs 39.0,p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Younger age, African American race, presence of anti-dsDNA and high titers of anti-dsDNA at the time of SLE diagnosis are significant predictors for the incident LN.
Younger age, Hispanic ethnicity, non-Caucasian race, and presence of anti-dsDNA antibody at the time of SLE diagnosis increased the likelihood of a more rapid progression to LN.
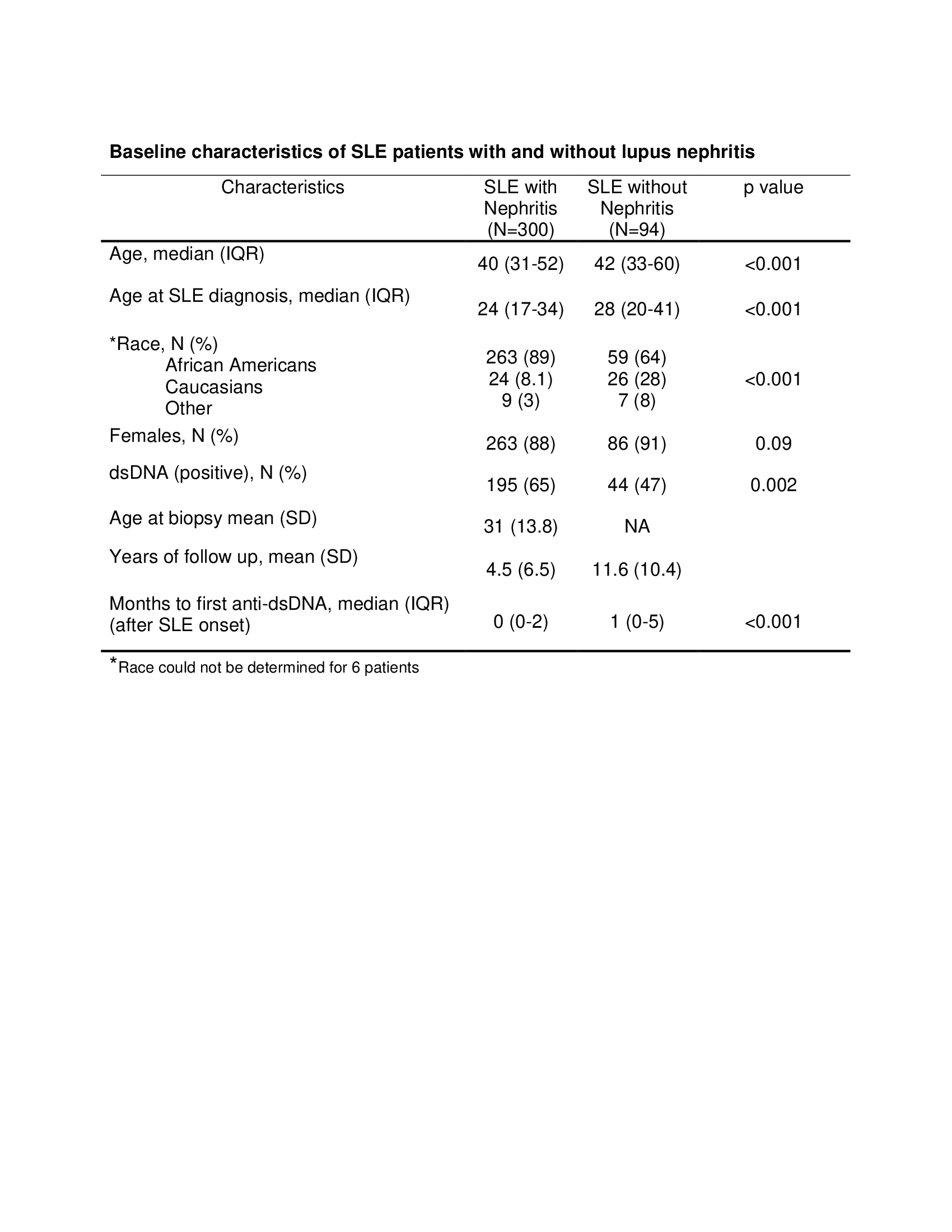 Baseline characteristics of SLE patients with and without lupus nephritis
Baseline characteristics of SLE patients with and without lupus nephritis
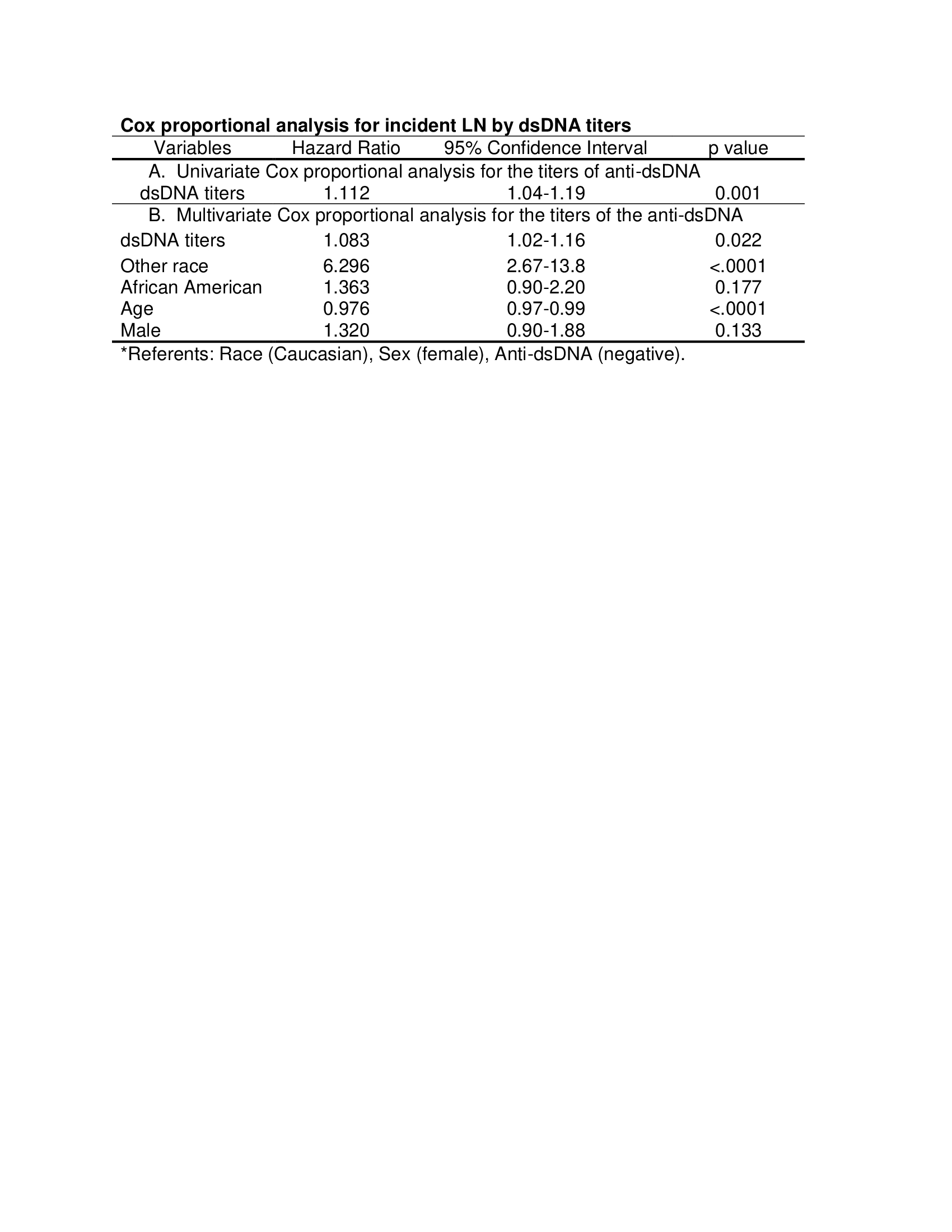 Cox proportional analysis for incident LN by dsDNA titers
Cox proportional analysis for incident LN by dsDNA titers
 Kaplan-Meier survival curve for the incident lupus nephritis based on the titers of anti-dsDNA at the time of SLE diagnosis
Kaplan-Meier survival curve for the incident lupus nephritis based on the titers of anti-dsDNA at the time of SLE diagnosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumari P, Ramakrishnan V, Obeid J, Kamen D, Oates J. The Role of Anti-dsDNA Antibodies in Predicting Incident Lupus Nephritis in Newly Diagnosed Lupus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-anti-dsdna-antibodies-in-predicting-incident-lupus-nephritis-in-newly-diagnosed-lupus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-role-of-anti-dsdna-antibodies-in-predicting-incident-lupus-nephritis-in-newly-diagnosed-lupus/
