Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: Biomarkers
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus Nephritis (LN) confers a poor prognosis, and there is a lack of effective non-invasive tests to assess disease activity and treatment response. We previously showed that a set of six urinary biomarkers (NGAL, KIM-1, MCP-1, adiponectin, hemopexin, ceruloplasmin) is sensitive and specific in adult patients with active LN, using renal biopsy as reference. In pediatric patients, Renal Activity Index for Lupus (RAIL) can differentiate LN treatment responders from non-responders and even anticipate the future achievement of complete renal remission (CRR). The objective of this study is to validate the utility of RAIL using clinically and/or histologically confirmed response to induction therapy-based data and urine sample collected from a large randomized controlled trial (RCT; NCT01714817).
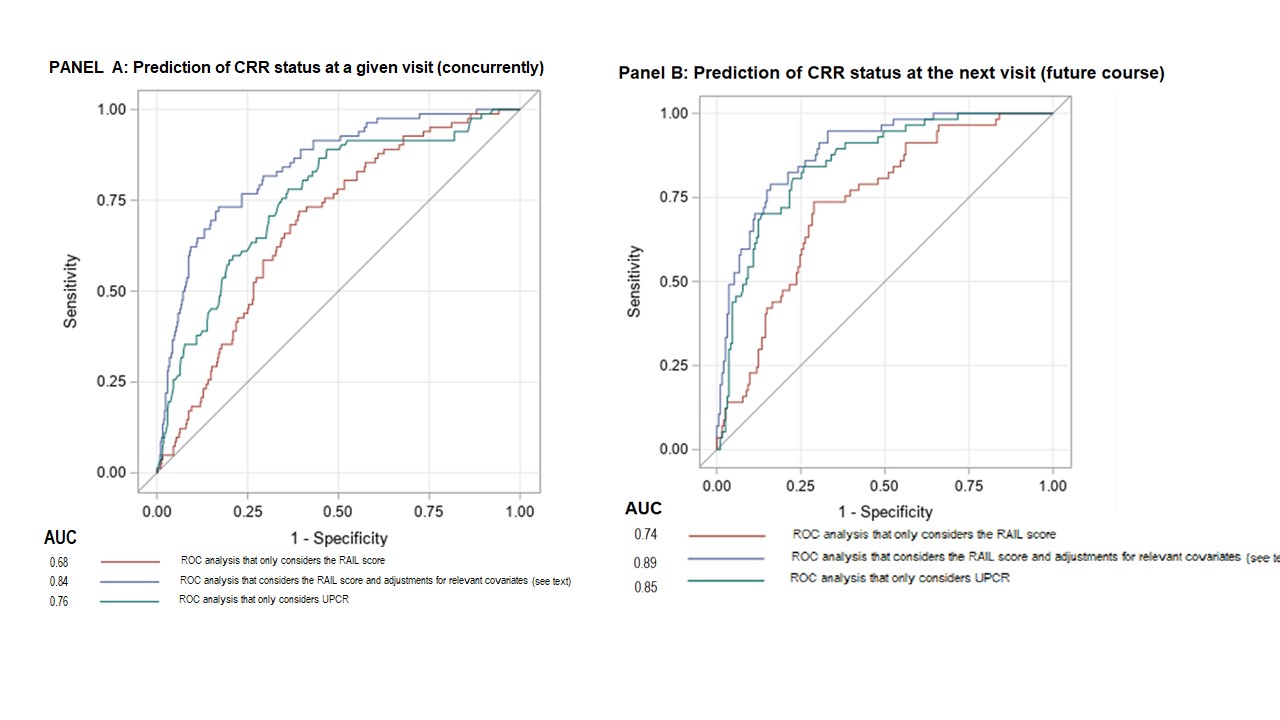
Methods: Random urine samples from 240 patients (pts), treated in a RCT using MMF and high dose corticosteroids with or without abatacept, were used in this exploratory analysis. Pts fulfilled ≥4 of 11 ACR SLE 1997 classification criteria, had biopsy-proven Class III or IV ( with/without Class V overlap) and urine-protein-creatinine ratio (UPCR) > 1, kidney biopsy within 12 mo plus signs of active LN within 3 mo of baseline. After collection, urine samples were stored frozen prior to assaying of the RAIL biomarkers using single-plex assay. RAIL scores were calculated after correction of urine creatinine as previously described (Gulati et al. Lupus 2017). Presence of complete renal remission (CRR+) was defined as a UPCR < 0.5 mg/mg, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or a decrease <15%, and an inactive urine sediment (red blood cells < 5 cells/ HPF). Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve analyses evaluated the ability for RAIL to discriminate by CRR status (CRR+ vs. CRR-) concurrently; and to predict the CRR status at the next visit.
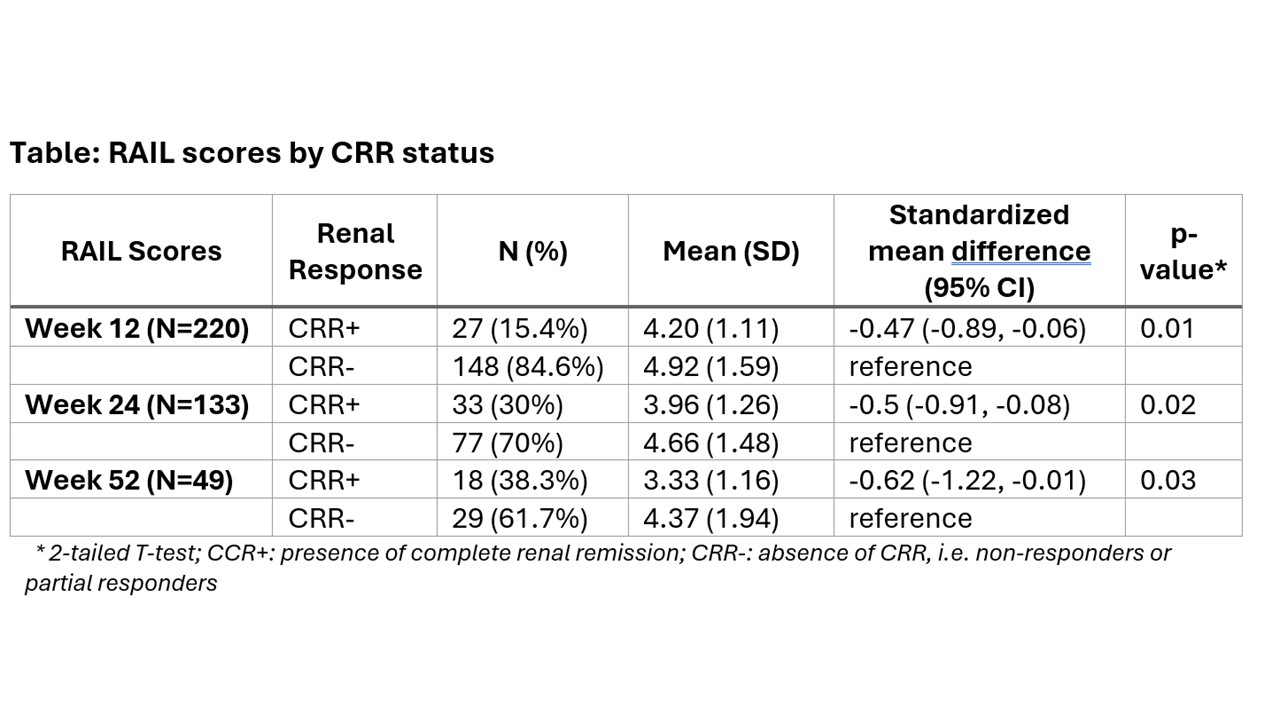
Results: Among 240 LN pts, 41% were white, and 89 % were female with a median age of 32 years (range 17-72). At baseline, median (interquartile range [IQR]) was for: UPCR 2.4 (1.2, 4.6) mg/dL, eGFR 101.8 (75.4, 124.66) mL/min/1.73 m2. While all pts had baseline urine samples, only 190,127 and 43 had samples collected at week (wk) 12, 24 and 52. There were 27 (15%), 64 (31%) and 73 (44%) pts with CRR+ at wk 12, 24 and 52, respectively. RAIL scores of pts with CRR+ were significantly lower than of pts with CRR- at wk 12, 24 and 52 (see Table). ROC analyses showed that RAIL scores are highly effective in discriminating CRR status, and RAIL scores remained significant predictors after adjustment for the intervention arm, UPCR, previous CRR status, weight, and age. After adjustment, the area under the curve (AUC) was 0.84 (p< .001) for detecting CRR status and 0.88 (p< .001) to predict CRR status at the next visit. ROC curves for detecting CRR-status concurrently at a visit (Panel A) and at a subsequent visit (Panel B), with and without adjustment for covariates, along with UPCR are depicted in the Figure.
Conclusion: Longitudinal RAIL scores differentiate patients who achieved CRR from others. Higher RAIL score also seem to anticipate the future course of LN. RAIL has novel clinical utility as a non-invasive biomarker signature to monitor treatment response over time.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aundhia M, Liu J, Cody E, Rose J, Merritt A, Quinlan-Waters M, Sproles A, Thornton S, Devarajan P, Huang B, brunner h. The Renal Activity Index for Lupus (RAIL) Identifies Active Renal Disease in SLE Patients and Its Longitudinal Score Associates with Achievement of Renal Responses in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-renal-activity-index-for-lupus-rail-identifies-active-renal-disease-in-sle-patients-and-its-longitudinal-score-associates-with-achievement-of-renal-responses-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-renal-activity-index-for-lupus-rail-identifies-active-renal-disease-in-sle-patients-and-its-longitudinal-score-associates-with-achievement-of-renal-responses-in-lupus-nephritis/