Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is the most common primary vasculitis of the elderly causing blindness if left untreated. However, its hallmark treatment with glucocorticoids (GCs) can lead to significant toxicity including psychiatric manifestations. Few studies have investigated the association between these symptoms and GCA, mainly using Short Form 36 (SF-36), a generic patient-reported outcome (PRO) with a mental health component. Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) is a validated PRO to assess depression and anxiety and to the best of our knowledge has never been evaluated in patients with GCA. We aimed to assess the prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with GCA using HADS and compare its results to SF-36.
Methods: HADS and SF-36 questionnaires were prospectively collected from patients with biopsy- or imaging-proven GCA evaluated from July 2018 to January 2020 in a tertiary centre. An age- and gender-matched control group was retrieved from a population-based dataset – the EpiReumaPT (the largest Portuguese epidemiologic study on rheumatic diseases). HADS-A and -D ≥8 defined possible and HADS-A and -D ≥11 defined probable anxiety and depression, respectively. Univariate analysis was performed using Chi-Square, Mann-Whitney and Fischer’s exact tests, as appropriate. Multivariate analysis was performed using binary logistic regression. Association between values of HADS and SF-36 was assessed using Spearman’s correlation coefficient.
Results:
We included 72 patients diagnosed with GCA, 52 (72.2%) females, with a mean ± SD age of 78.3 ± 7.7 years. The control group consisted of 288 individuals. Table 1 shows the comparison between groups. Patients with GCA had higher median [IQR] HADS-A than controls (7 [7] vs. 5 [5], p< 0.001), as well as a higher prevalence of HADS-A ≥8 and ≥11 (48.6% vs. 26.4%, p< 0.001; 30.6% vs. 12.2%, p< 0.001; respectively). Patients with GCA had higher median [IQR] HADS-D (7 [7] vs. 5 [5], p=0.013) and prevalence of HADS-D ≥11 (33.3% vs. 18.1%, p=0.004) than controls, but prevalence of HADS-D ≥8 did not differ between groups (48.6% vs. 37.2%, p=0.075). Multivariate analyses adjusted for neoplastic disease, hyperuricemia/gout, GCA and history of mental disease showed that GCA and history of mental disease were independent predictors of HADS-A ≥8 (OR 2.0 95%CI: 1.1-3.5, OR 4.4 95%CI: 2.3-8.7; respectively) and HADS-A ≥11 (OR 3.8 95%CI: 2.0-7.4, OR 2.5 CI95%: 1.1-5.5; respectively), but only GCA was an independent predictor of HADS-D ≥11 (OR 2.6 95%CI: 1.4-4.7). Patients with HADS-A or -D ≥8 or ≥11 had inferior levels of SF-36 in all categories except for physical role limitation in HADS-A ≥8 (Table 2). Moreover, values of HADS and mental health component of SF-36 showed significant correlation (HADS-A: r=-0.780, HADS-D: r=-0.742; both p< 0.001).
Conclusion:
Patients with GCA showed a higher prevalence of anxiety and depression when compared to the general population. HADS appeared to be an efficient screening tool for these psychiatric manifestations in GCA, correlating well with SF-36. Future replication of these results in independent cohorts are warranted; however, they currently raise awareness for the fact that mental health should not be overlooked when managing GCA.
 Table 1: Clinical features of patients with giant cell arteritis and matched controls.
Table 1: Clinical features of patients with giant cell arteritis and matched controls.
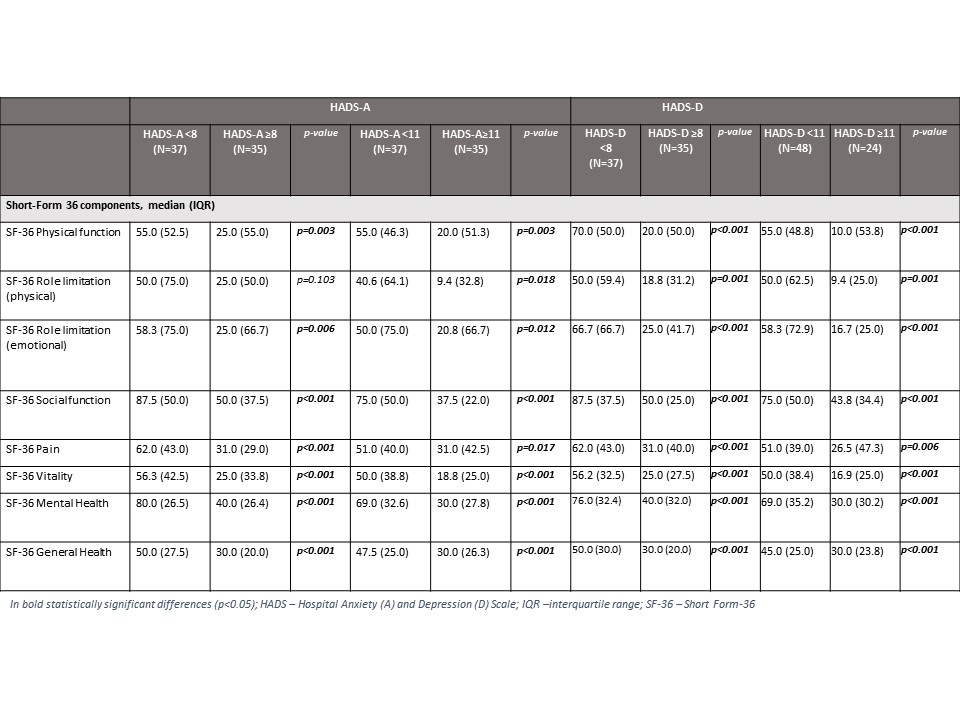 Table 2. Differences between the values of SF-36 in patients with HADS ≥8 and < 8 and HADS ≥ 11 and < 11.
Table 2. Differences between the values of SF-36 in patients with HADS ≥8 and < 8 and HADS ≥ 11 and < 11.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martinho J, Ponte A, Dourado E, Khmelinskii N, Dias S, Barreira S, Cruz-Machado A, Macieira C, Teixeira V, Rodrigues A, Telles-Correia D, Fonseca J, Ponte C. The Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-prevalence-of-anxiety-and-depression-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-prevalence-of-anxiety-and-depression-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis/
