Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 11, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects VII: Disease Activity and Updates in Measurement
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose:
Antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides
(anti-CCP) associate with a more severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) disease
course, and therefore have influence on therapeutic decisions. By comparing two
early RA cohorts enrolled 10 years apart, we wished to determine whether the
predictive value of anti-CCP has changed in contemporary early RA.
Methods:
Two Swedish multicenter prospective observational
early RA cohorts (denoted ‘TIRA’) enrolled patients with symptom duration
<12 months and fulfilling either the 1987 American College of Rheumatology
criteria or suffering from morning stiffness >60 min, symmetrical arthritis,
and small-joint engagement. TIRA-1 enrolled patients 1996-1999, i.e. when
neither anti-CCP tests nor biological therapy were used in clinical routine.
TIRA-2 enrolled patients 2006-2009 using the same inclusion criteria as TIRA-1.
Both cohorts were followed prospectively over 3 years. Anti-CCP tests (CCP2,
EuroDiagnostica AB, Sweden) were performed on baseline serum samples. In
TIRA-2, radiological damage was determined by Larsen score.
Results:
Baseline anti-CCP occurrence was similar in
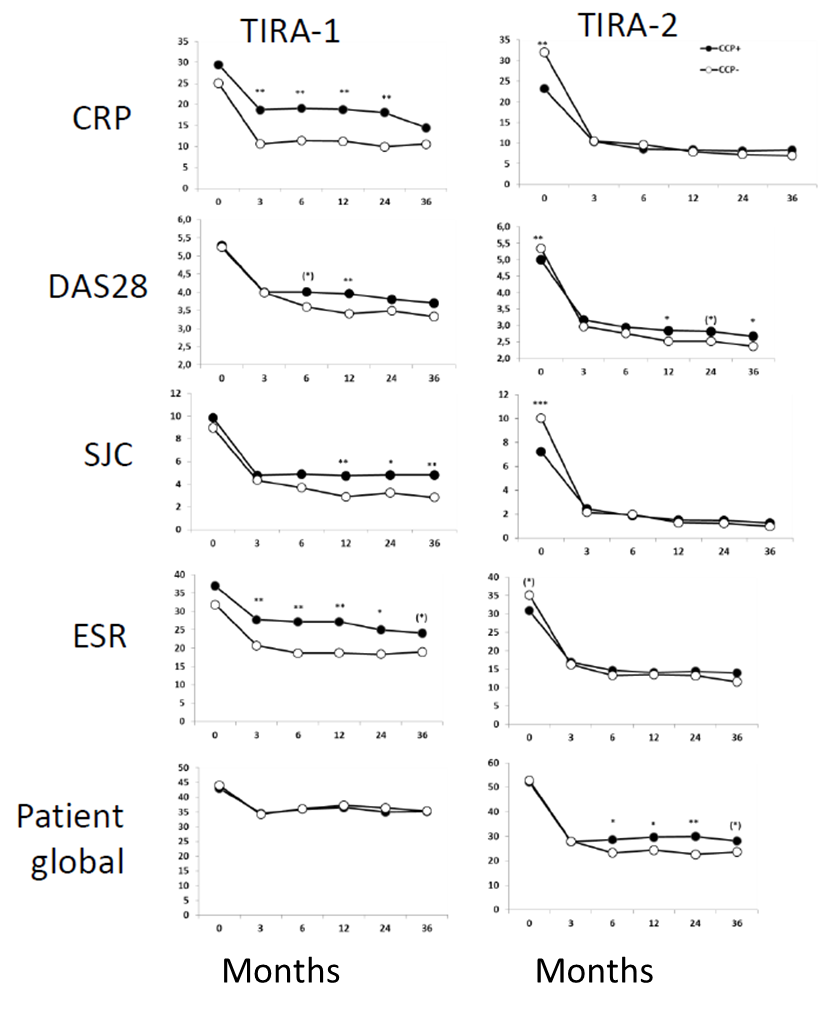
TIRA-1 (156/239, 65%) and TIRA-2 (303/444, 68%). In TIRA-1, follow-up disease
activity measures related to inflammation (ESR, CRP, swollen joint count (SJC))
were higher among anti-CCP positive patients compared with anti-CCP negative
patients (fig 1). In TIRA-2, anti-CCP positive patients had significantly lower
28-joint disease activity score (DAS28), CRP, and SJC at baseline compared with
anti-CCP negative patients, while the 3-year follow-up revealed no significant
differences regarding ESR, CRP or SJC (fig 1). In both cohorts, anti-CCP
positive patients were treated more aggressively. In TIRA-2, baseline anti-CCP
occurrence associated with more radiological damage over time (p = 0.001
regarding 3-year Larsen score; p=0.006 regarding progression). Anti-CCP
remained associated with radiological progression also after adjusting for age,
sex, baseline DAS28, and baseline Larsen score (p=0.024).
Conclusion:
Modern management of early RA attenuates
the association between baseline anti-CCP status and disease activity over
time, but the radiological progression remains increased. Thus, despite early
aggressive therapy, anti-CCP occurrence remains predictive of erosive disease. This
supports pathogenetic properties of antibodies to citrullinated proteins with
regard to bone destruction, regardless of inflammatory responses reflected by
swollen joints or raised CRP/ESR levels.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kastbom A, Ziegelasch M, Thyberg I, Arge B, Martinsson K, Svernell O, Häggström , Salomonsson P, Nyhäll-Wåhlin BM, Transö S, Jacobs C, Skogh T. The Predictive Value of Antibodies to Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide in Two Prospective Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohorts 10 Years Apart [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-predictive-value-of-antibodies-to-cyclic-citrullinated-peptide-in-two-prospective-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohorts-10-years-apart/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-predictive-value-of-antibodies-to-cyclic-citrullinated-peptide-in-two-prospective-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohorts-10-years-apart/