Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: TNFα inhibition is a cornerstone of therapy for rheumatologic disease, yet there is no orally administered TNFα inhibitor available. A novel oral TNFα inhibitor (SAR441566) which specifically inhibits TNFR1 signaling is currently in clinical development. In contrast to biologic TNFα inhibitors, this compound preserves homeostatic TNFR2 signaling. Using SAR441566 in a mouse model of RA (collagen induced arthritis), disease improvement similar to biologic TNFα inhibition was observed*. Based on safety, PK and PD characteristics in first-in-human studies, a phase 1 proof-of-mechanism (POM) trial in psoriasis was conducted. The primary objective was to evaluate tolerability and safety, with secondary/exploratory objectives to assess clinical and biomarker response over 4 weeks of treatment.
Methods: The clinical trial was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-center study with SAR441566, an oral TNFα inhibitor. All participants had dermatologist-diagnosed mild-moderate psoriasis. Peripheral blood biomarkers were assessed by ultra-sensitive immunoassay platform.
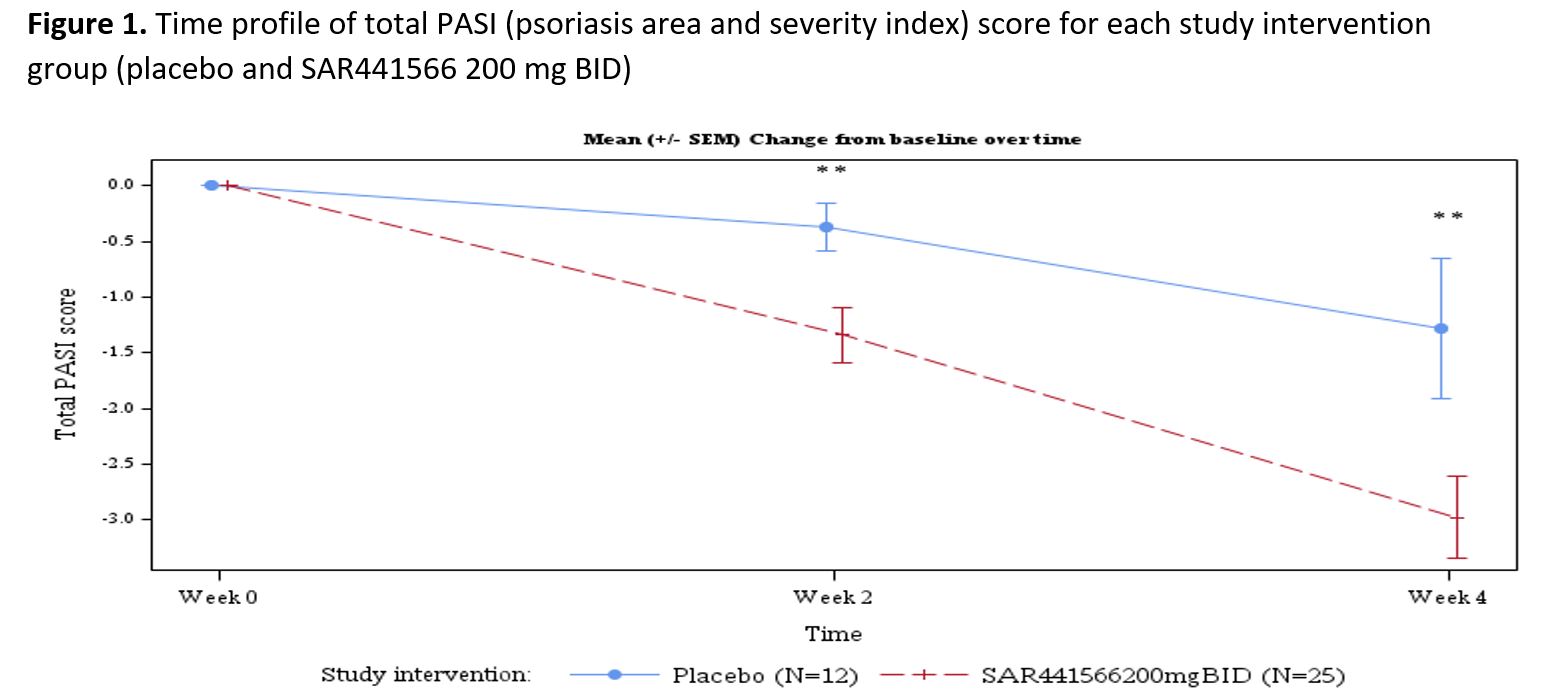
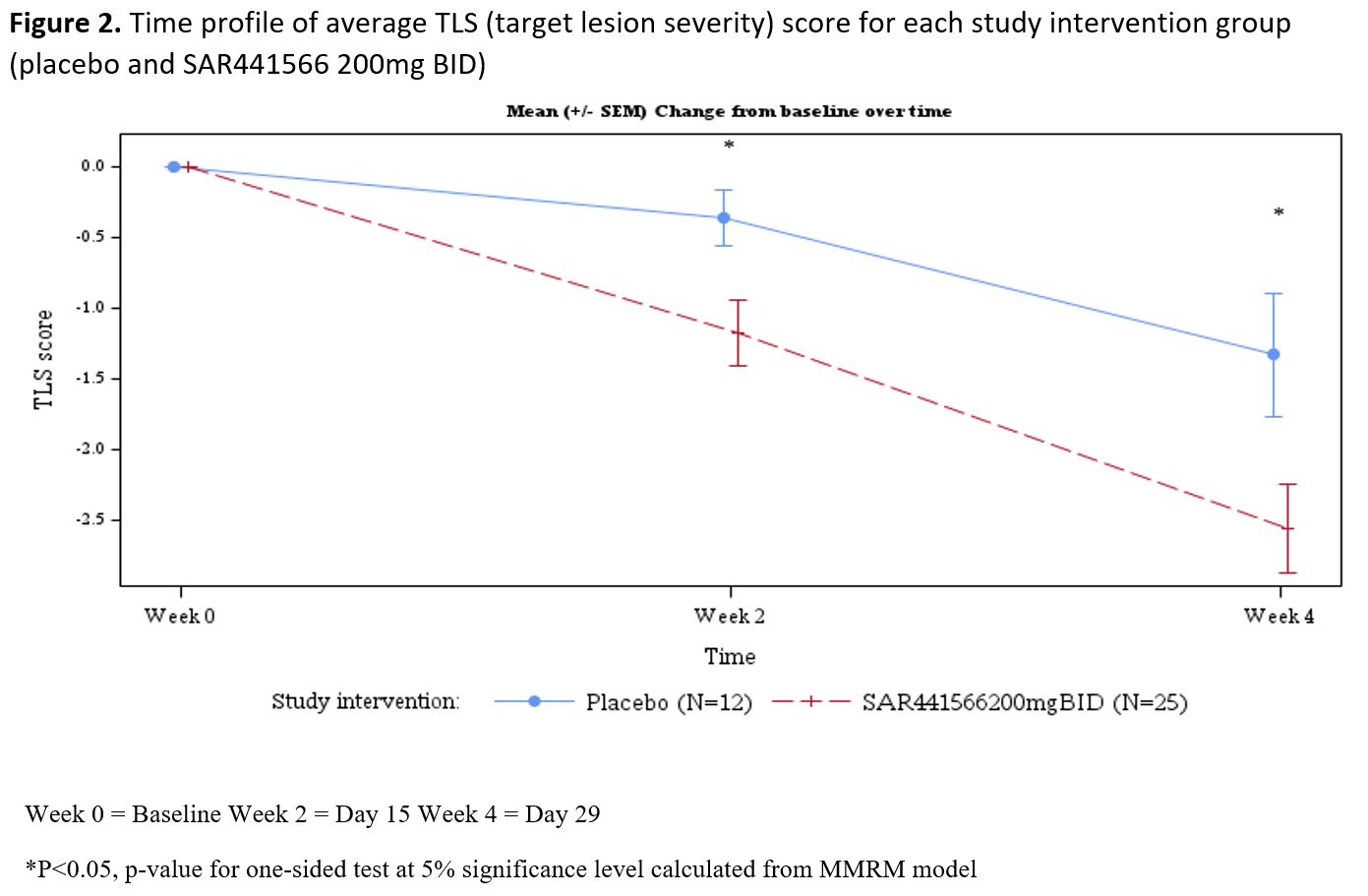
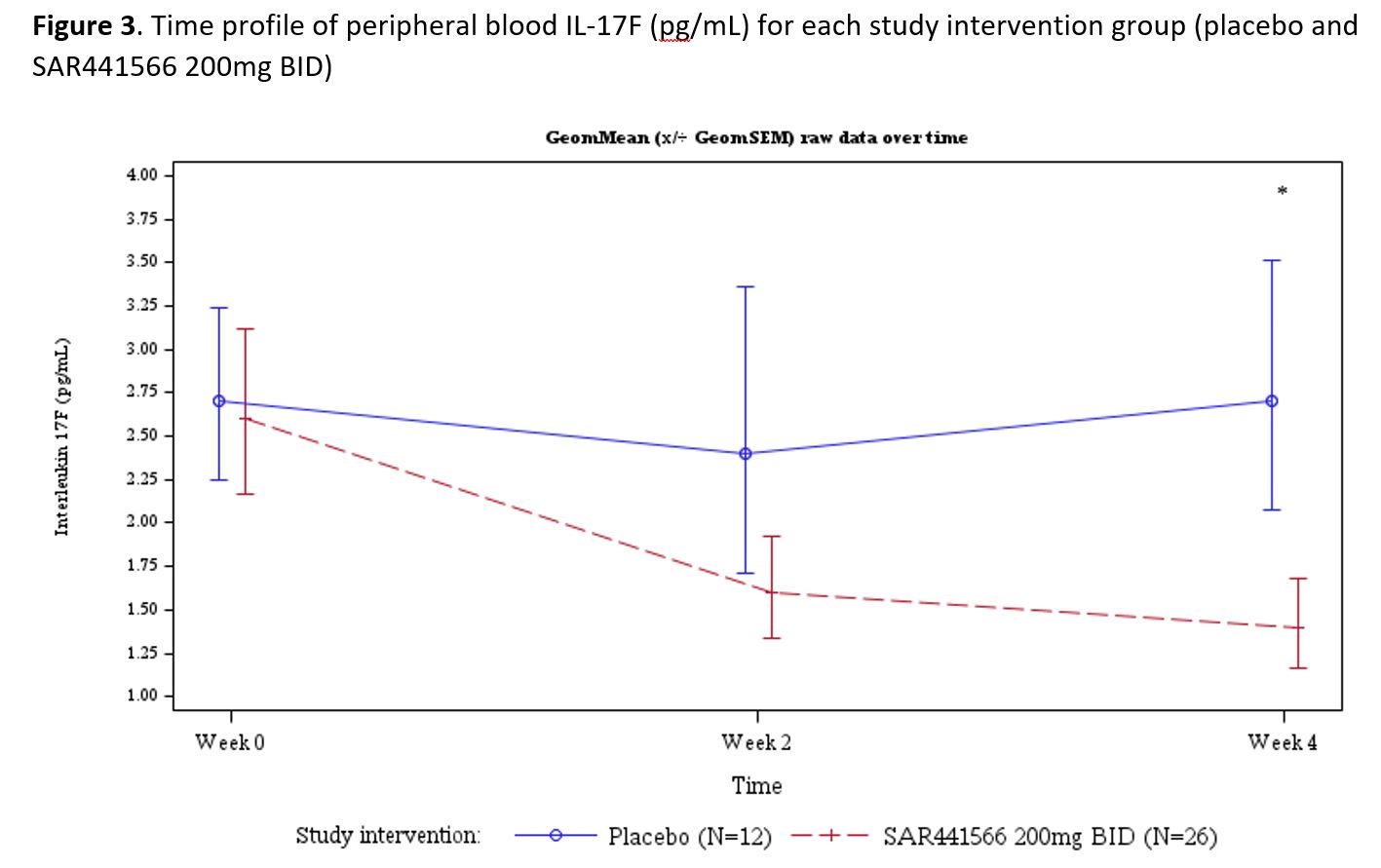
Results: Psoriasis patients recruited to the study randomized to oral TNFα inhibitor (n=26) vs placebo (n=12) were similar in age (µ±SD: 44.2±9.7 vs 40.5±12.5 yrs, p=0.332), race (proportion in %: 96.2 vs 91.7 Caucasian p= 0.565), BMI (26.45±2.97 vs 25.98±2.92 kg/m2, p=0.650), baseline disease severity Investigator Global Assessment (IGA) score (2.42±0.64 vs 2.25±0.45, p=0.407), psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score (8.91±3.73 vs 7.86±2.53, p=0.382), and target lesion severity (TLS) score (6.83±1.60 vs 7.42±1.40, p=0.280). With regards to safety and tolerability, there were no serious adverse events (SAEs), severe treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) or AE of special interest (AESI). All observed TEAEs were grade 1/2 and participants fully recovered. There were few potentially clinically significant abnormalities for vital signs, ECG and laboratory parameters scattered across groups. All were considered not clinically meaningful by the investigator. With regards to clinical response by week 4, patients (N=37) were noted to have significant adjusted mean % improvement in PASI (LSM±SE, 35.09±4.47 vs 15.71±6.33, p=0.009) and TLS (% change 38.18±4.33 vs 20.44±6.18, p= 0.012). The proportion of patients achieving improvement by at least 1 severity level in IGA was 58.3 vs 0%, p=0.003. In addition to improvement in disease severity (PASI and TLS score change from baseline, Figures 1 and 2), Figure 3 depicts improvement in IL-17F.
Conclusion: This phase 1 study demonstrated that this novel oral TNFα inhibitor was safe, well tolerated, and clinically effective, to be further confirmed in larger trials. Limitations include the sample size and homogeneous population. A computational disease platform is being applied to translate psoriasis results to estimate the efficacy of SAR441566 for RA. A phase 2b dose ranging intervention proof-of-concept trial testing efficacy and safety for RA is planned.
*Vugler et al, An orally available small molecule that targets soluble TNF to deliver anti-TNF biologic-like efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2022
Continuous data were summarized using the number of observations available, mean, Standard Deviation (SD), median, standard error of mean (SEM), minimum, and maximum. Categorical and ordinal data were summarized using the count and percentage of participants. Time profile plots and statistical modeling (Mixed model for repeated measures [MMRM]) were used to compare intervention vs placebo. Statistical significance differences between active drug and placebo were reported as a p-value and were calculated either from MMRM model (adjusted mean percentage improvement from baseline) or two-sample t-test for comparing means between the two groups on continuous data or chi-square test for comparing proportions between the two groups on categorical data. p-values <0.05 were considered significant.
Statistical significance calculation based on adjusted mean percentage improvement from baseline modeling using Mixed Models for Repeated Measures (MMRM).
Comparisons for SAR441566 vs placebo at week 2 demonstrated change from baseline in SAR441566, with geometric mean IL17-F levels of 1.65±2.55 vs. 2.39±2.71 pg/mL, p= 0.292, and significant improvement at week 4 1.35±2.55 vs. 2.73±2.44 pg/mL, p= 0.038.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fishbein A, Nguyen M, Chow O, Matos T, Dreis C, Zhang H, Poirel M, Gassenhuber J, Dufault M, Frank-Dietrich W, Perrin L, Rehberg M, Kohlmann M, Nassr N. The Potential of an Oral TNFα Inhibitor with TNFR1 Specificity: Results of a Phase 1b Proof-of-mechanism Trial in Psoriasis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-potential-of-an-oral-tnf%ce%b1-inhibitor-with-tnfr1-specificity-results-of-a-phase-1b-proof-of-mechanism-trial-in-psoriasis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-potential-of-an-oral-tnf%ce%b1-inhibitor-with-tnfr1-specificity-results-of-a-phase-1b-proof-of-mechanism-trial-in-psoriasis/