Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-4:30PM
Background/Purpose: Ultrasonography has been validated as a diagnostic tool for giant cell arteritis (GCA). Due to the urgent need for glucocorticoid treatment in acute GCA and the fact that ultrasound detected inflammation normalizes rapidly upon start of treatment, it is challenging to identify patients with pathological vessels for educational purposes. The construction of realistic training model would therefore be a significant advance in GCA ultrasound training.
We have developed a phantom of axillary (AA) and temporal arteries (TA) of GCA patients and controls using high-resolution 3D printing techniques. The aim of this study was to test the reliability of ultrasound findings using these models among experts of the large vessel vasculitis of the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) ultrasound working group.
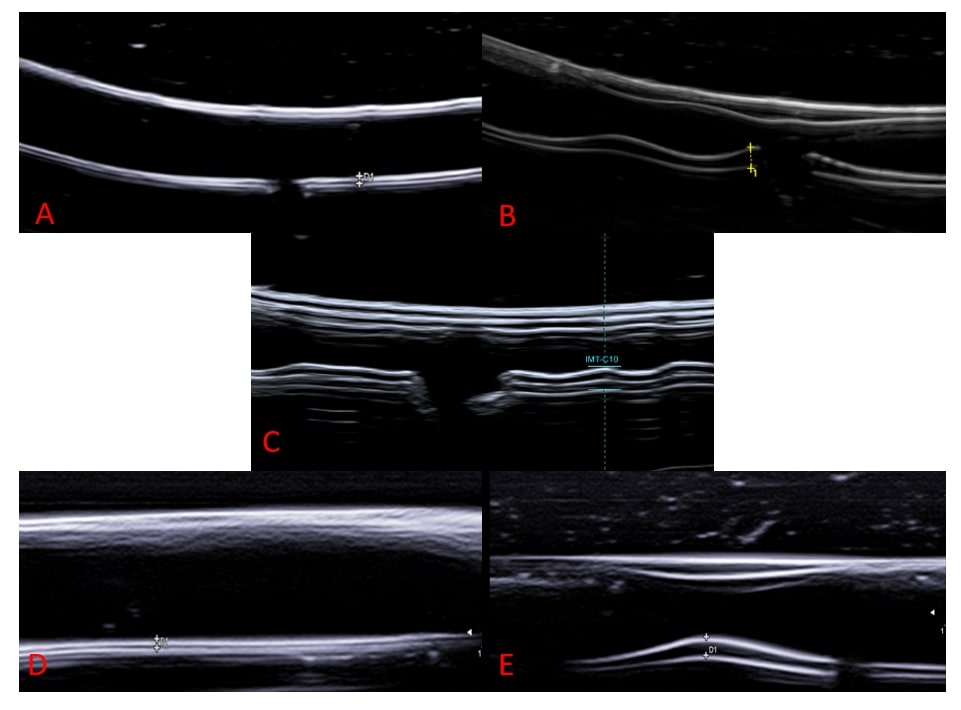
Methods: Phantoms (see Figure 1 for examples) were produced using a Formlabs SLA 3D printer and embedded in a special gelatine as a set, consisting of 3 AA or 2 TA phantoms. Participants from twelve European countries received eight sets of AA and TA phantoms. The phantoms were examined in a blinded fashion according to a predefined protocol and evaluated individually based on the OMERACT GCA definitions valid for ultrasound. In addition, the intima-media thickness (IMT) was measured. The phantoms were categorized as normal (AA&TA) / acute pathology (AA&TA) / chronic pathology (only AA) / none of the above (AA & TA). Due to wider differing results of IMT measurements and classification from the designed IMT and classification in the parietal branch of the temporal artery, TA phantoms were technically adapted and examined in a second round.
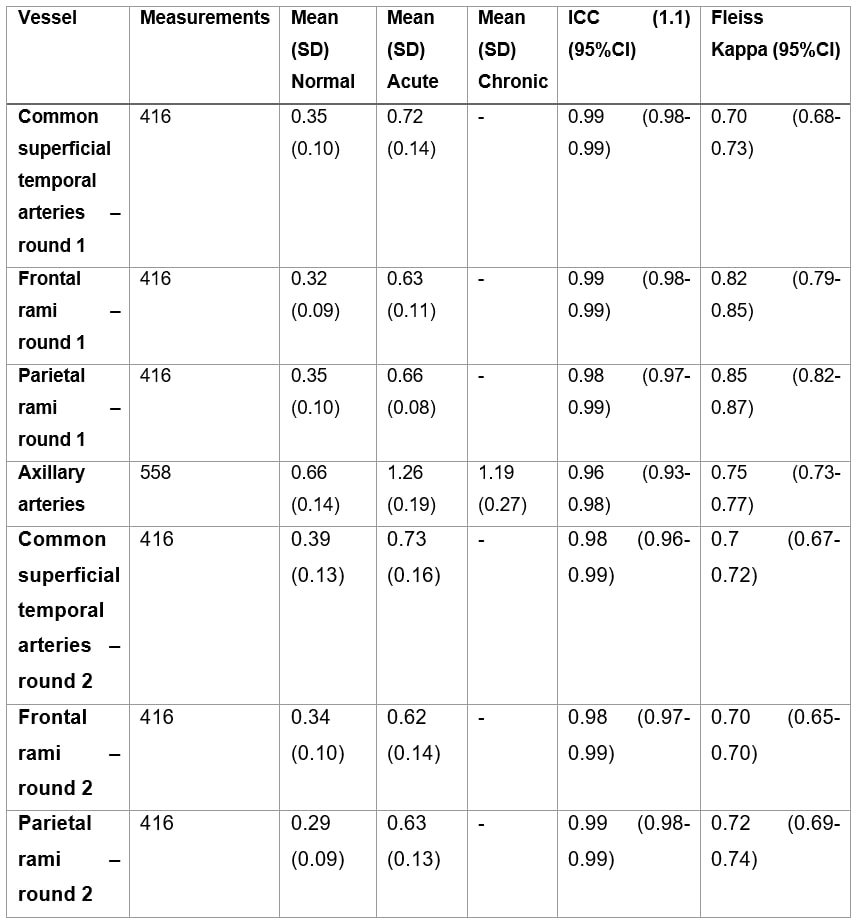
Means and standard deviations were calculated. Interrater-reliability of the classification was calculated using Fleiss-Kappa. Interrater-reliability of the IMT measurements was calculated using the one way random intra-class coefficient (ICC 1.1).
Results: Except for the parietal branch, the published cut-off values for normal and pathological IMT were met. In both rounds the phantoms were correctly classified to their designated classification in over 81% of cases yielding a Fleiss’ kappa of 0.80 (95% CI 0.78-0.81) in round 1 and 0.74 (0.72-0.75) in round 2 (see Table 1). IMT measurements revealed an intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC 1.1) of 0.98 (95% CI 0.98-0.99) in both rounds.
Conclusion: The classification of normal/abnormal phantom vessels as well as measurement of artificial IMT revealed a high reliability of GCA ultrasound among experts. It showed high agreement in correctly classifying the models and demonstrated almost perfect interrater reliability in measuring artificial IMT.
This is the first functional phantom of the temporal and axillary artery designed to train physicians in ultrasound diagnosis of GCA.
A= Normal axillary artery; B=Axillary artery with acute GCA pathology; C=Axillary artery with GCA chronic pathology; D=Normal temporal artery; E=Temporal artery with acute GCA pathology
Note there are no chronic phantoms of temporal arteries. (SD: standard deviation; ICC: intra-class correlation coefficient of IMT measurement; Fleiss Kappa: Fleiss Kappa for classification; CI: confidence interval)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schäfer V, Schremmer T, Recker F, Hartung W, Duftner C, Monti S, Hocevar A, Karalilova R, Iagnocco A, macchioni p, Germano G, NAREDO E, De Miguel E, Seitz L, Daikeler T, Boumans D, Mukhtyar C, Smith K, Wakefield R, Diamantopoulos A, Chrysidis S, Nielsen B, Keller K, Moller Dohn U, Terslev L, Milchert M, Schmidt W, Bruyn G, Juche A, Dejaco C. The OMERACT GCA Phantom Project: Validation of 3D Printed Ultrasound Training Models for Giant Cell Arteritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-omeract-gca-phantom-project-validation-of-3d-printed-ultrasound-training-models-for-giant-cell-arteritis-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-omeract-gca-phantom-project-validation-of-3d-printed-ultrasound-training-models-for-giant-cell-arteritis-2/