Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Cytokines, Mediators, Cell-Cell Adhesion, Cell Trafficking and Angiogenesis - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The polarization of macrophages was the expressed to M1/M2 phenotype by various stimuli or environment signals. The M1 macrophage was pro-inflammatory phenotype and was key effector cells in the immune response of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). So, M1 macrophage influenced the inflammation of RA synovial membrane and joint destruction in RA, whereas M2 macrophage was anti-inflammatory phenotype and could down-regulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in RA. The SIRT1 attenuated the RA inflammation via dawn-regulation of NF-¥êB signaling. However, the effect of SIRT1 on macrophages polarization remained unclear. So we aimed to check out that activated SIRT1 modulated macrophages polarization into M1 phenotype and controlled the inflammation of RA.
Methods: Monocytes from synovial fluid of RA patients, bone marrow–derived monocytes (BMDCs) from mice were studied. monocytes were cultured with M-CSF for 7days to differentiate into M0 macrophages (monocyte-derived mature macrophages M0 phenotype). M0 macrophages were incubated with LPS and IFN-gamma in order to obtain M1 macrophages. M1 macrophage markers were detected by real-time PCR.
Results: Activation of SIRT1 was achieved by Resveratrol, activated SIRT1 attenuated M1 macrophage phenotypes and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. macrophages obtained from SIRT1-tg mice, which were overexpression of SIRT1, exhibited decreased M1 markers in association with enhanced activation of AMPK/ACC compared with macrophage from control C57BL/6 mice. In addition to SIRT1 activation, M1 polarizing signal, acetylation of NF-¥êB p65, was suppressed. In SIRT1-deficient macrophages, resveratrol fail to increase AMPK activity and to decrease the expression M1 markers owing to enhanced acetylation of NF-¥êB p65.
Conclusion:
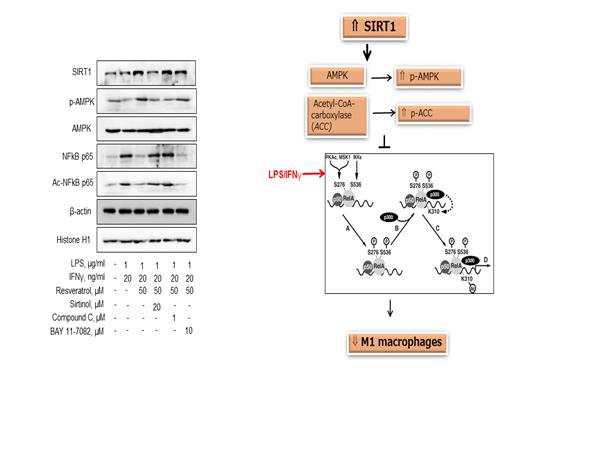 SIRT1 maybe an important modulator of M1 macrophages polarization and increased AMPK activity, that suppressed acetylation of NF-¥êB p65 during inflammation of RA. so, modulation of SIRT1 maybe a new target in RA treatment.
SIRT1 maybe an important modulator of M1 macrophages polarization and increased AMPK activity, that suppressed acetylation of NF-¥êB p65 during inflammation of RA. so, modulation of SIRT1 maybe a new target in RA treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee SY, Chung WT, Lee SW, Park SY, Jae Ho B. The Modulation of Macrophage Polarization By SIRT1 Maybe New Target Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-modulation-of-macrophage-polarization-by-sirt1-maybe-new-target-therapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-modulation-of-macrophage-polarization-by-sirt1-maybe-new-target-therapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
