Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by abnormalities in vascular pathways and lymphatic vessels with pulmonary hypertension as a major complication. Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C), acting through its cognate receptor VEGFR3 is a major growth factor for lymphatic vessels under physiological conditions. Recent studies have shown that patients with SSc have altered levels of two VEGF-C regulating proteins; the angiogenic factor Ang-2 and the chemokine CCL21, also found to be associated with PAH development.
We assessed the characteristics of VEGF-C in SSc patients and investigated serum levels of VEGF-C, CCL21 and Ang-2 segregated by pulmonary arterial pressure.
Methods: SSc patients from the Oslo University Hospital (n=371) and controls (n=100) were included; and sera analyzed for VEGF-C, CCL21 and Ang-2 by Luminex kits from Millipore. SSc patients with clinically suspect PH were referred to right heart catheterization. Mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) ≥25mmHg in the absence of significant interstitial lung disease (ILD) was defined as PAH; mPAP of 20-24mmHg in the absence of significant ILD borderline PAH. Descriptive statistics and logistic regression analysis were performed and tested by the goodness-of-fit with area under the curve (AUC).
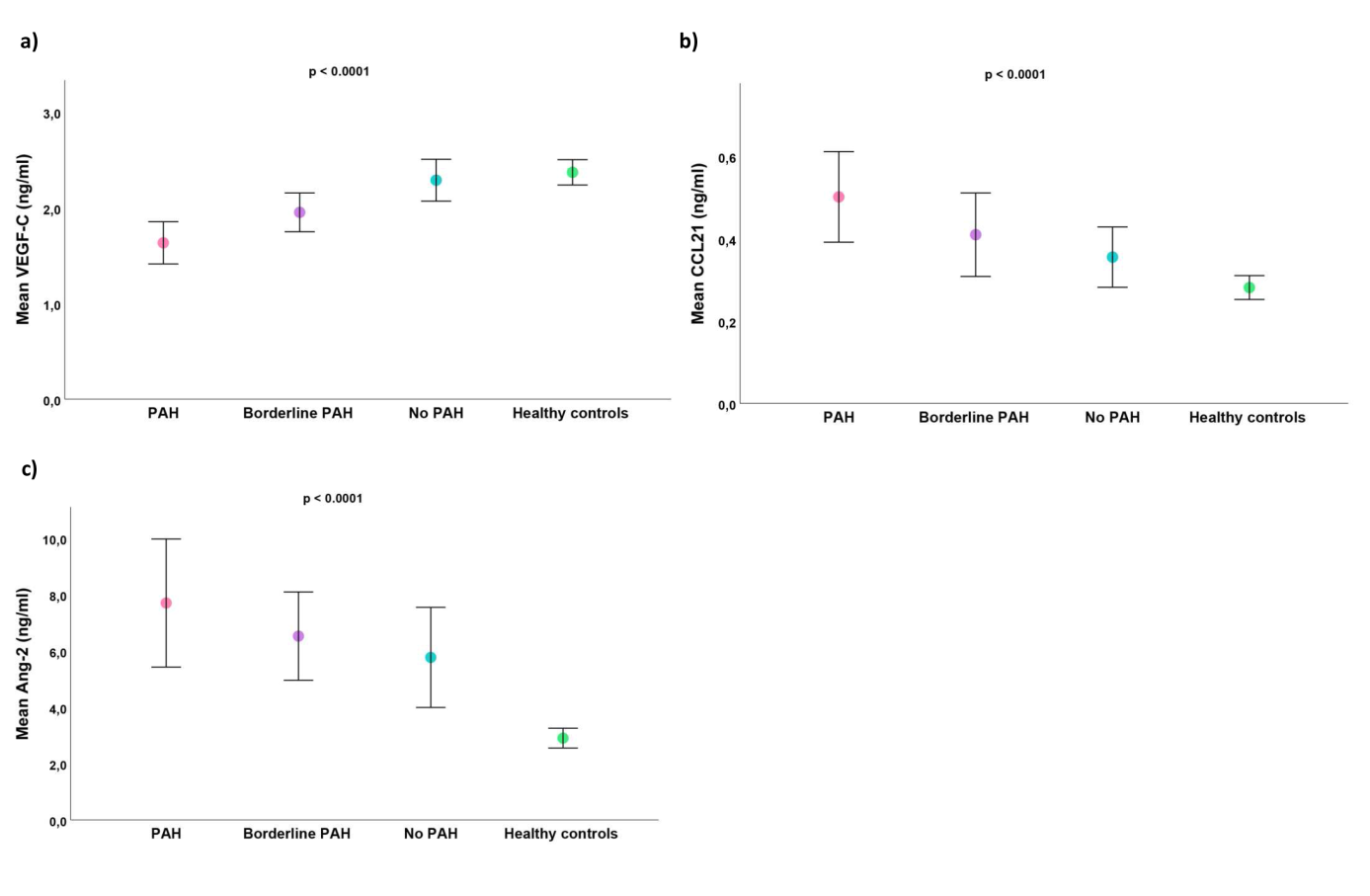
Results: The mean age of SSc patients was 54±14.1 years, 80% were female and 74% had limited cutaneous SSc. Serum levels of VEGF-C were lower in SSc than in controls (2.0±0.7 ng/ml vs. 2.4±0.7 ng/ml, p<0.001)(Table 1). In patients with low levels of VEGF-C (<2.3 ng/ml) PAH was 3.5-fold more frequent than in patients with high levels of VEGF-C (14.7 % vs 4.2 %, p=0.005). 167 patients were assessed by RHC. Patients with PH-ILD (n=27), borderline PH-ILD (n=3) and post-capillary PH (n=14) were excluded from the study, while the remaining 123 patients were included in the investigation of lymphangiogenetic factor expression; including 28 patients with PAH, 45 borderline PAH and 50 with no PAH. CCL21, Ang2 and VEGF-C levels in these groups are shown in Figure 1. VEGF-C (OR 0.99, 95%CI 0.997-0.998, p=0.001, AUC=0.79), CCL21 (OR 1, 95%CI 1-1.003, p=0.050, AUC=0.69) and Ang-2 (OR 1, 95%CI 1-1.0001, p=0.49, AUC=0.67) were associated with PAH compared to no PAH patients.
Conclusion: VEGF-C is associated with ssc-PAH, making it a possible maker for the development of PAH. This study also demonstrates dysregulation of lymphangiogenetic factor expression of multiple targets in sera of SSc-PAH patients.
Table 1: Longitudinal clinical and demographic data
|
|
OUH (n=371) |
PAH (n=28) |
Borderline PAH (n=45) |
No PAH (n=50) |
|
Age at disease onset, yrs |
52 (15.5) |
59 (13.8) |
52 (13.6) |
51 (15.8) |
|
Time from onset to PH, yrs |
7 (8.4) |
7 (8.4) |
10 (10.5) |
n.a. |
|
Females, no (%) |
312 (84.1) |
23 (82.0) |
32 (71.1) |
49 (98.0) |
|
Deceased, no (%) |
91 (24.5) |
14 (50.0) |
11 (24.4) |
10 (20.0) |
|
Limited cutaneous SSc, no (%) |
270 (73) |
26 (92.9) |
23 (57.5) |
44 (88.0) |
|
Anti-Centromere Ab, no (%) |
191 (52.3) |
24 (85.7) |
23 (57.5) |
33 (66.0) |
|
Mean VEGF-C level, ng/ml |
2.0 (0.7) |
1.6 (0.7) |
1.9 (0.7) |
2.3 (0.6) |
Figure 1: VEGF-C (a), CCL21 (b) and Ang-2 (c) serum levels
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Didriksen H, Fretheim H, Palchevskiy V, Andreassen AK, Garen T, Midtvedt O, Gude E, Belperio JA, Molberg Ø, Hoffmann-Vold AM. The Lymphangiogenetic Factors VEGF-C, CCL21 and Ang-2 Are Associated with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-lymphangiogenetic-factors-vegf-c-ccl21-and-ang-2-are-associated-with-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-lymphangiogenetic-factors-vegf-c-ccl21-and-ang-2-are-associated-with-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-in-systemic-sclerosis/