Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Neonatal Lupus (NL) is a rare syndrome caused by placental transfer of maternal anti-Ro/SSA and anti-La/SSB autoantibodies to the fetus. Cardiac manifestations may comprise autoimmune congenital heart block (CHB) and dilated cardiomiopathy (DCM). The prevalence of CHB has been estimated as 1-2% in anti-Ro/SSA-positive women while the recurrence rate is 16-19%. The rarity of these conditions requires the establishment of collaborative registries in order to improve our knowledge on the management of CHB. Here we report the preliminary data of the Italian Registry of the autoimmune congenital heart block, which was created in the frame of the Italian Society for Rheumatology in 2016.
Methods:
The aim was to collect retrospective and prospective pregnancies complicated with CHB in patients with anti-Ro/SSA and/or anti-La/SSB antibodies. The study was approved by the Ethic Committee of the Promoting Centre in July 2016 and it has been approved by other eight Italian Institutions. Data regarding demography, maternal treatment before and after CHB detection, neonatal outcome, maternal and neonatal follow-up were collected through an online electronic datasheet prepared in a Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) platform. Two-tailed Student’s t-test for continuous variables, Fisher’s exact test or Yates’s Chi squared test for categorical variables were applied. The statistical software Stata/SE14.2 was used.
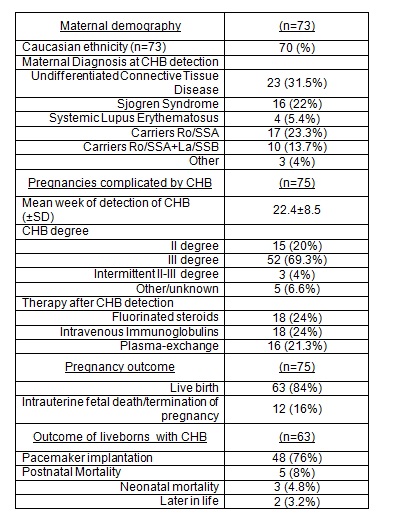
Results:
Seventy-five pregnancies complicated with the detection of CHB were collected in 73 women. CHB was detected in utero in 68 cases (90.6%), 5(6.7%) neonatal cases, 2(2.7%) unknown. Demographic description of the cohort, degree of CHB and treatment are reported in the table. The death of the child was observed in 17 (23.2%) cases: 7 fetal-deaths,5 termination of pregnancy and 5 postnatal death. Maternal and fetal risk factors for fetal mortality were analyzed for possible associations. At univariate analysis, factors associated with death were hydrops (p=0.065) and pericardial effusion (p=0.025).
Conclusion:
The Lu.Ne registry is an ongoing project aiming at collecting all cases of CHB referred to Italian Rheumatology Centres. Our preliminary data confirmed that hydrops and pericardial effusion are risk factors for fetal death. Conversely, we found that the majority of the mothers (58%) whose pregnancy was affected by CHB had a formal diagnosis of systemic autoimmune disease. This is in contrast with other registries showing that usually CHB was incidentally detected in healthy women. Probably such discrepancy is related to the recruiting Centres all belonging to Rheumatology Society. The collection of CHB cases from Gynecological and Pediatric Cardiology Centres, planned in the next months, will complete our analysis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fredi M, Andreoli L, Bertero T, Bortoluzzi A, Breda S, Cappa V, Ceccarelli F, Cimaz R, De Vita S, Di Poi E, Franceschini F, Gerosa M, Govoni M, Hoxha A, Lojacono A, Marozio L, Mathieu A, Minniti A, Muscarà M, Padovan M, Piga M, Priori R, Ramoni V, Ruffatti A, Tonello M, Zatti S, Calza S, Brucato A, Tincani A. The Italian Registry of Autoimmune Congenital Heart Block (Lu.Ne Registry): Report of the First Year of Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-italian-registry-of-autoimmune-congenital-heart-block-lu-ne-registry-report-of-the-first-year-of-activity/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-italian-registry-of-autoimmune-congenital-heart-block-lu-ne-registry-report-of-the-first-year-of-activity/