Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To date, information about the impact of the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) pandemic on rheumatology practice and on rheumatologists is limited.
The primary objective of the study was to evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on rheumatology practice in the Arab countries. Secondary objectives were to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on the rheumatologists and to develop recommendations to improve the rheumatology practice.
Methods: A cross-sectional 21-items web survey was designed by members of the Arab League of Associations for Rheumatology (ArLAR) and validated by its scientific committee in English and in French. The survey was disseminated by e-mail and on social media to all rheumatologists in the 15 ArLAR countries. It comprised 19 close-ended questions about demographic characteristics, impact of the pandemic on the activities (in percentage, where 100% corresponds to complete suspension), attitude towards telemedicine, and two open-ended questions about the unmet needs and the ways to improve the practice. Recommendations were developed to improve practice during the pandemic.
Results: Between May 9 and May 24, 2020, 858 rheumatologists were included in the analysis (27.3% of registered rheumatologists in the ArLAR countries), 37% were in the 35-44 years age category, 60% were females and 48% worked in the private sector (Table 1). The impact of COVID-19 on the rheumatology practice was significant (Figure 1), with a decrease of 69% on hospitalization, 65% on outpatient clinic, 56% on infusion centers and 43% on income. A higher impact on the outpatient clinic activity was associated with the region (highest impact in North Africa, lowest in the Levant), using telemedicine, and impact on income, The higher impact was negatively associated with working in the private sector (compared to the public sector and university teaching hospitals) (Tabl2 2). Telemedicine was used in 70% of cases, but mostly based on traditional telephone contacts and e-mails, and was reimbursed in only 12%. The mental impact related to the stress caused by COVID-19 was reported in 77% of the respondents (minor in 60.4%, major in 16.7% of cases). Fifteen rheumatologists (1.8%) were personally infected. The participants reported 156 cases of COVID-19 among their patients, of whom 22% died. The top-cited unmet needs were: access to drugs and a telemedicine platform.
Conclusion: The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant negative impact on the rheumatology practice in the Arab countries. Accordingly, better access to drugs and providing telemedicine platforms are recommended to improve rheumatology practice in the region.
 Table 1. Characteristics of the 858 rheumatologists
Table 1. Characteristics of the 858 rheumatologists
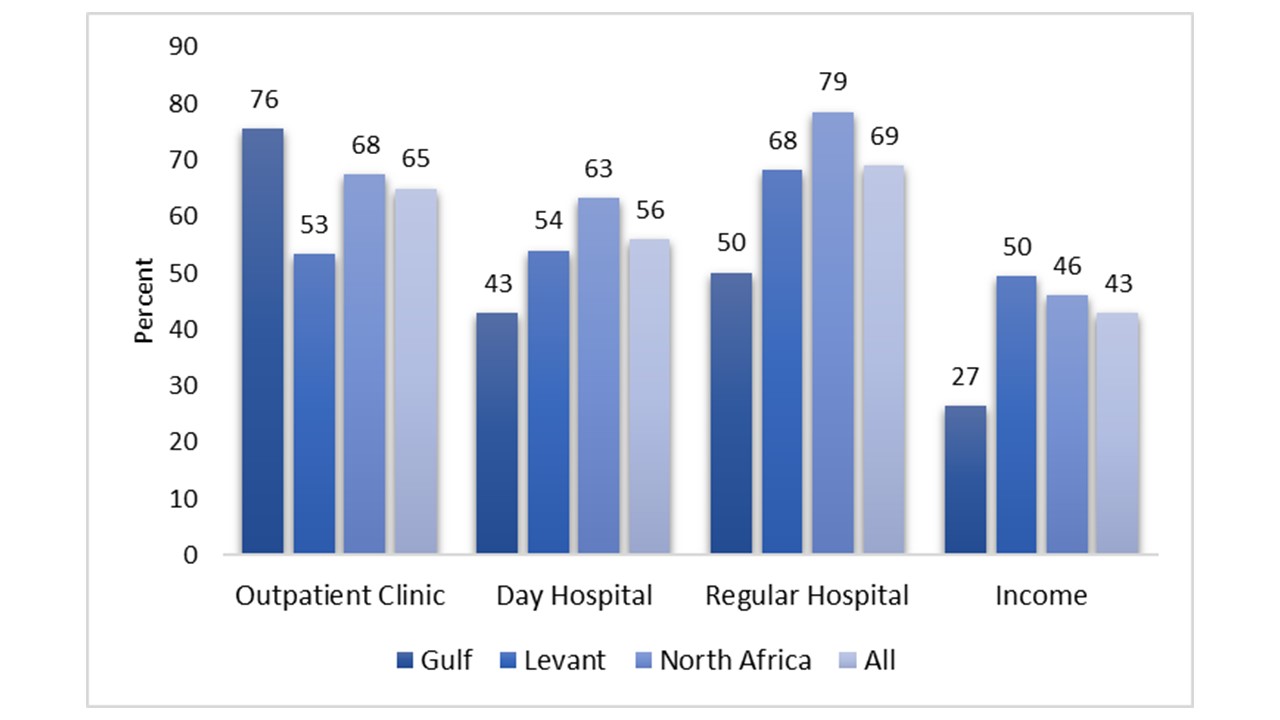 Figure 1. Impact of the COVID-19 on the rheumatology practice (outpatient clinic, day hospital, hospital and income).
Figure 1. Impact of the COVID-19 on the rheumatology practice (outpatient clinic, day hospital, hospital and income).
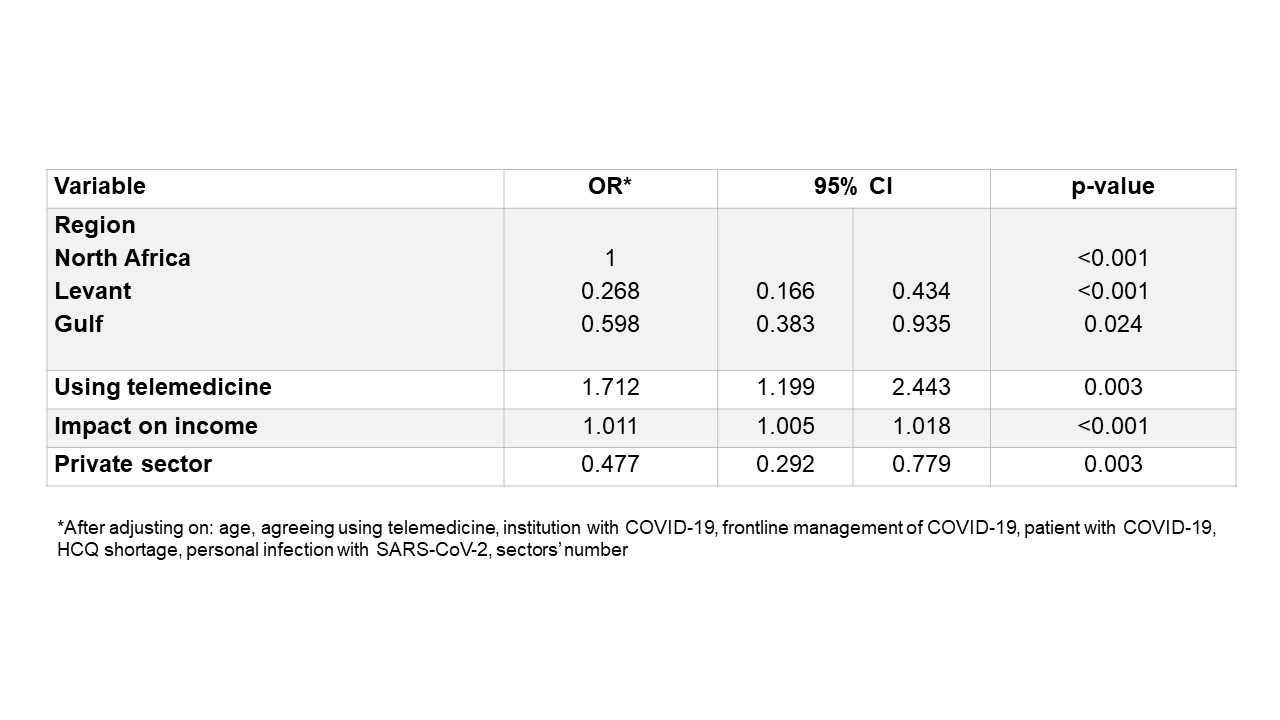 Table 2. Factors associated with a higher impact on the outpatient clinic activity
Table 2. Factors associated with a higher impact on the outpatient clinic activity
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ziade N, Hmamouchi I, El Kibbi L, Abdulateef N, Halabi H, Abutiban F, Hamdi W, el Rakawi M, Eissa M, Masri B. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Rheumatology Practice: A Study in 15 Arab Countries [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-rheumatology-practice-a-study-in-15-arab-countries/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-the-covid-19-pandemic-on-rheumatology-practice-a-study-in-15-arab-countries/
