Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: Respiratory infections are among the leading causes of hospitalization in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and Streptococcus Pneumoniae (SP) is one of the most frequent pathogens involved. For these patients, the CDC recommends a combined vaccination scheme (CVS) using two types of vaccines but evidence on its effectiveness in this specific population remains insufficient.
Objectives: To assess the impact of the combined vaccination scheme on the incidence of SP infections in patients with RA treated with bDMARD and tsDMARD.
Methods: A cohort was nested in a register including patients with RA who were prescribed a bDMARD or tsDMARD (either naïve or switch) from October 1999 to November 2018. The stem register, BIOBADASER 3.0, is a national multicenter prospective register established in 1999 which recruits patients from 28 tertiary Spanish centers with an estimated national coverage of bDMARD and tsDMARD treatment in RA of 25%.
Vaccination Status assessment
Each center informed about the date when they implemented a systematic SP vaccination protocol and whether they were using the CVS. Those not adopting the latter were excluded from the analysis.
Outcomes
Invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) and all-cause community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) were the main outcomes. However, since it is estimated that in a significant proportion of lower respiratory tract infections, SP presence is underdiagnosed, we also included all events reported using relevant MedDRA® codes related to this type of infection. Demographic and clinical features were also retrieved.
Statistical Analysis
Crude incidence rates (IR) were calculated for each outcome and its combination (“All SP-related infections”). Exposure was split into two periods, pre and post-vaccination, considering the date when the CVS was officially recommended in Spain (May 2015).
Poisson regression modelling was carried out to estimate the incidence rate ratio (IRR) comparing both periods. Models were adjusted for potential confounders available such as sex, age, smoking and burden of comorbidity assessed with the Charlson Index which includes conditions such as diabetes mellitus, chronic respiratory diseases, chronic kidney disease, etc.
Results: Study population baseline features
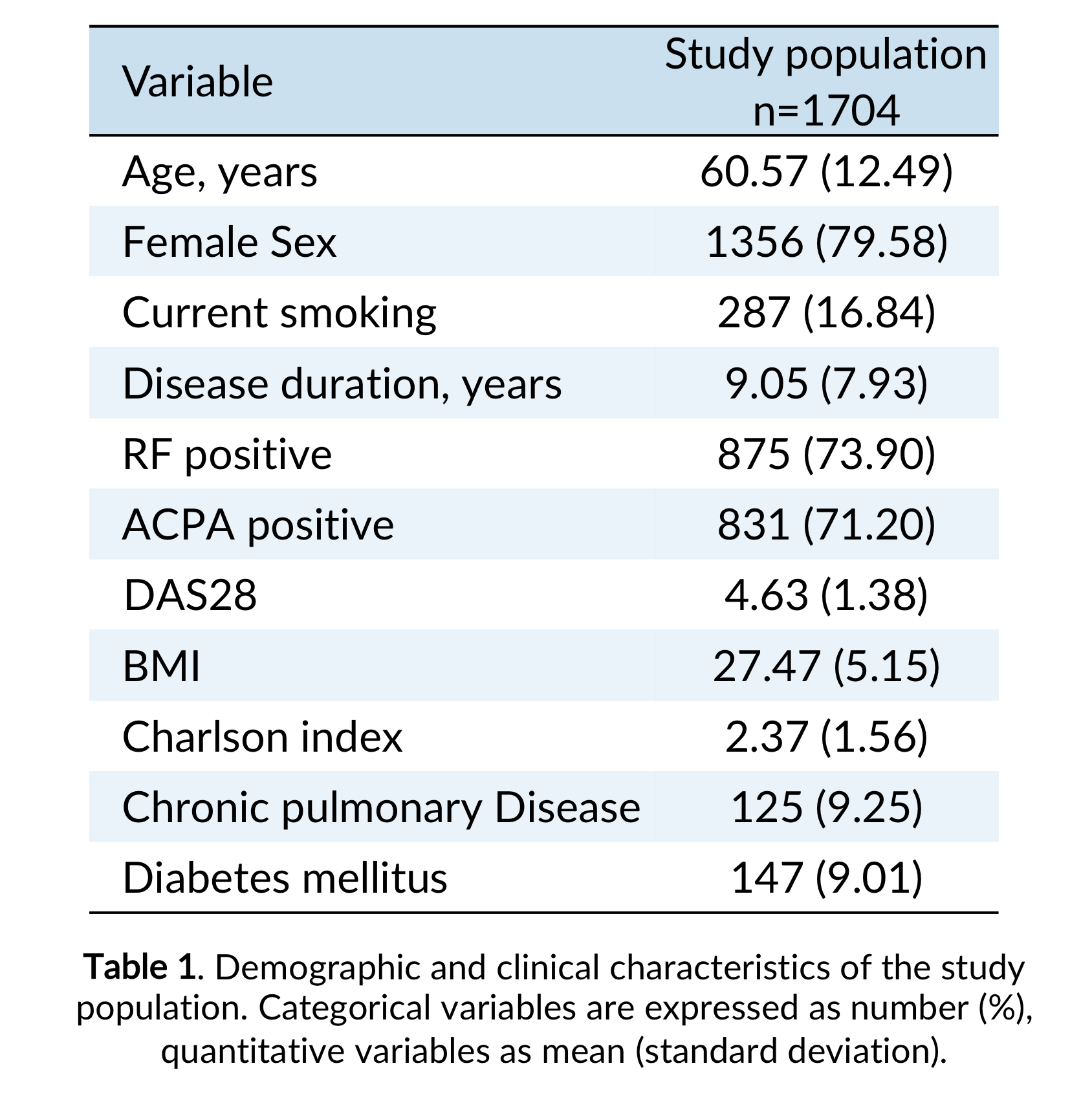
A total of 1704 patients were included, their main features are shown in table 1. All participating centers reported using the CVS except for one that was, therefore, excluded from the analysis.
Incidence Rates
One-hundred and sixty-seven events were found; 2 for IPD, 136 for CAP and 29 for other lower respiratory tract infections. No IPD events were found in the pre-vac period. The IRs were higher in the pre-vac period for the remaining outcomes. Results are shown in Table 2
Crude and adjusted Incidence Rate Ratios
The IRR for all SP-related infections in the post- vac period was 0.25 (95% CI: 0.13 – 0.47) in the multivariable analysis. (table 3).
Conclusion: The incidence of infections due to SP experienced a decrease in RA patients taking bDMARD or tsDMARD after the introduction of the stepwise combined vaccination scheme that was independent of age, sex, smoking or comorbidities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodriguez-Garcia S, Sanchez-Piedra C, Castellanos-Moreira R, Ruiz-Montesinos D, Hernandez V, Pombo-Suarez M, Sanchez-Alonso F, Carmona L, Gómez-Reino J. The Impact of the Combined Vaccination Scheme Against Streptococcus Pneumoniae on the Incidence of Related Infections in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Biologic or Targeted Synthetic DMARD: Data from BIOBADASER 3.0 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-the-combined-vaccination-scheme-against-streptococcus-pneumoniae-on-the-incidence-of-related-infections-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-or-targeted-synthetic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-the-combined-vaccination-scheme-against-streptococcus-pneumoniae-on-the-incidence-of-related-infections-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-biologic-or-targeted-synthetic/