Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1264–1307) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) is a heterogenous condition encompassing multiple subtypes with varying histopathology, prognosis, and potential treatment options. The most common RA-ILD subtypes are usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) and nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). RA-UIP is characterized by fibrosis and portends the worst prognosis but may be treated with antifibrotic therapy. RA-NSIP is more likely to have inflammatory features on lung imaging. Despite these differences, most prior research studied RA-ILD as a single entity rather than examining individual subtypes. Therefore, we investigated differences in demographic, serologic, and lifestyle risk factors for RA-ILD and major RA-ILD subtypes.
Methods: We systematically identified RA-ILD cases and RA-noILD controls from two established RA cohorts. RA-ILD and subtypes (including UIP, NSIP, and other/indeterminate) were determined by clinical imaging reports and research review of clinically-indicated chest high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) by at least two thoracic radiologists using a sequential reader method. RA-ILD cases met criteria for definite/probable RA-ILD (Bongartz, A&R, 2010). RA-noILD controls had no evidence of ILD on clinical review of medical records AND research HRCT review. Demographics, RA-related autoantibody testing, and smoking were extracted from study questionnaires or electronic health records. We investigated associations between RA-ILD and subtypes with demographic, serologic, and lifestyle factors using multivariable logistic regression, pooling both cohorts due to limited sample size.
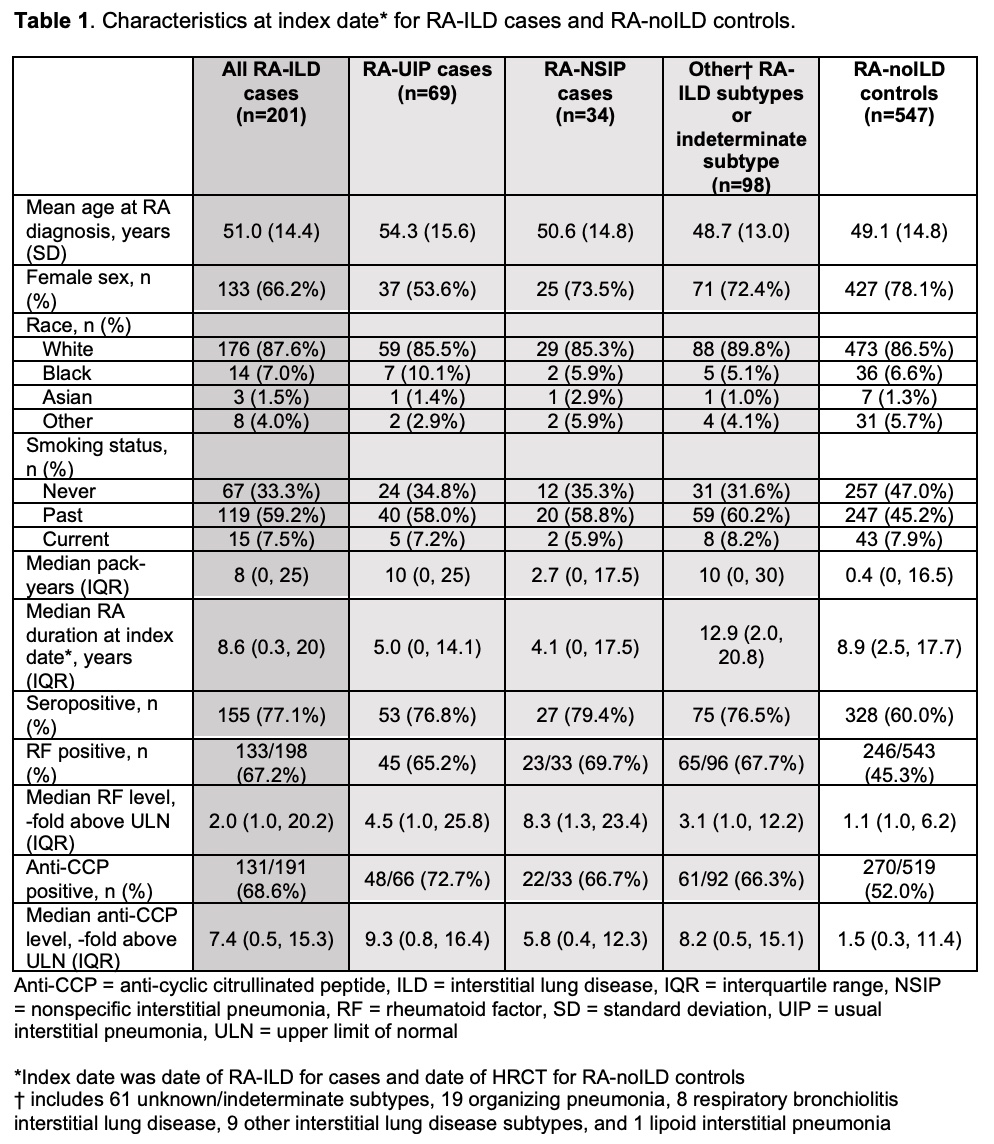
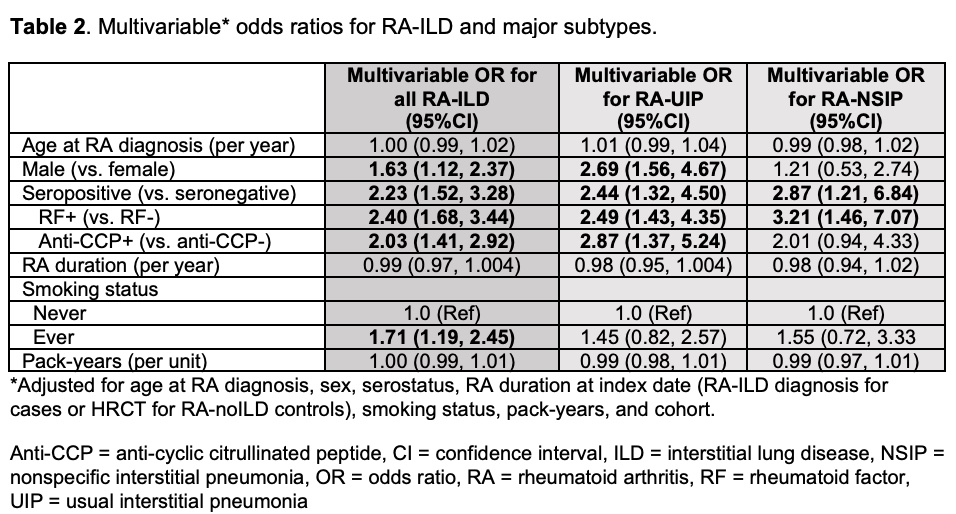
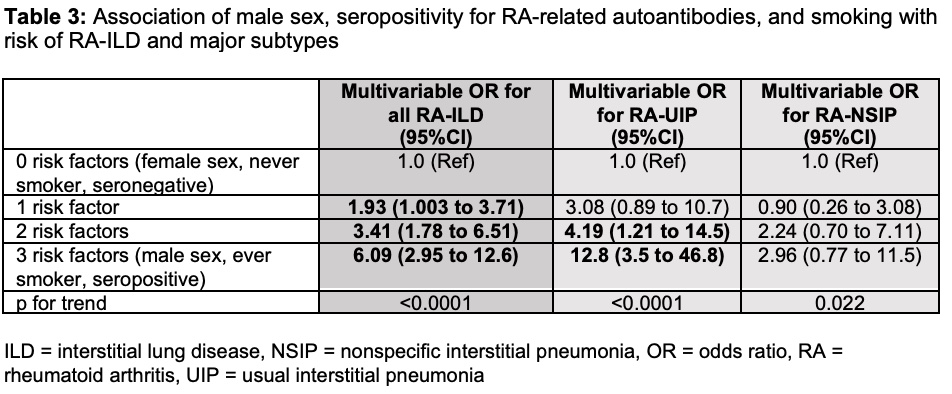
Results: From 3328 RA patients, we identified 201 RA-ILD cases (mean age 51 years, 66.2% female) and 547 RA-noILD controls (mean age 49 years, 78.1% female). Of the RA-ILD cases, 69 (34.3%) had RA-UIP, 34 (16.9%) had RA-NSIP, and 98 (48.8%) had other subtypes or were indeterminate (Table 1). RA-ILD was associated with male sex (OR 1.63, 95%CI 1.12 to 2.37), seropositivity for RF and/or anti-CCP (OR 2.23, 95%CI 1.52 to 3.28) and ever smoking (OR 1.71, 95%CI 1.19 to 2.45, Table 2). Having all three risk factors (male, seropositive, smoking) was strongly associated with RA-ILD (OR 6.09, 95%CI 2.95 to 12.58, Table 3) and particularly with RA-UIP (OR 12.8, 95%CI 3.50 to 46.8) compared to RA-NSIP (OR 2.96 95%CI 0.77 to 11.56). RA-UIP was associated with male sex (OR 2.69, 95%CI 1.56 to 4.67) and positive anti-CCP (OR 2.23, 95%CI 1.52 to 3.28, Table 2). RA-NSIP was associated with positive RF (OR 3.21 95%CI 1.46 to 7.07) but not male sex (OR 1.21, 95%CI 0.53 to 2.74).
Conclusion: In this study comparing systematically phenotyped RA-ILD cases with RA-noILD controls confirmed by HRCT, we found distinct risk factor profiles for RA-UIP and RA-NSIP. Male sex and elevated anti-CCP were strongly associated with RA-UIP, the most severe RA-ILD subtype. The combination of male sex, seropositivity, and smoking conferred nearly 13-fold increased risk of RA-UIP. These findings suggest that RA-ILD sex differences are specific to RA-UIP and may help clarify RA-ILD heterogeneity to optimize screening and treatment approaches.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McDermott G, Hayashi K, Juge P, Gill R, Byrne S, Gagne S, Vanni K, Kowalski E, Qian G, Bade K, Saavedra A, Kawano Y, Diiorio M, Wolfgang T, Kim E, Dellaripa P, Weinblatt M, Shadick N, Doyle T, Sparks J. The Impact of Sex, Serostatus, and Smoking on Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Interstitial Lung Disease Subtypes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-sex-serostatus-and-smoking-on-risk-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-subtypes/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-sex-serostatus-and-smoking-on-risk-for-rheumatoid-arthritis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-subtypes/