Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The aim of the study was to elucidate antibody responses after vaccination with two doses of COVID-19 vaccines in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD) treated with biologic and targeted disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (b/ts DMARDs) as monotherapy or together with conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs).
Methods: Antibody levels to antigens representing spike full length protein, spike S1 and a nucleocapsid C-terminal fragment were measured in serum obtained before and 2-12 weeks after second vaccination using multiplex bead-based serology assay. Cut-off for reactivity was defined as mean signal intensity +6SD across 12 pre-pandemic samples for spike and +12SD for nucleocapsid. Patients with IRD receiving b/ts DMARDs and controls from five Swedish regions participated. Percentage (%) responders, defined as antibody levels over cut-off for both spike proteins, in each treatment group was compared to percentage responders among controls. Predictors of antibody response were determined using logistic regression analysis.
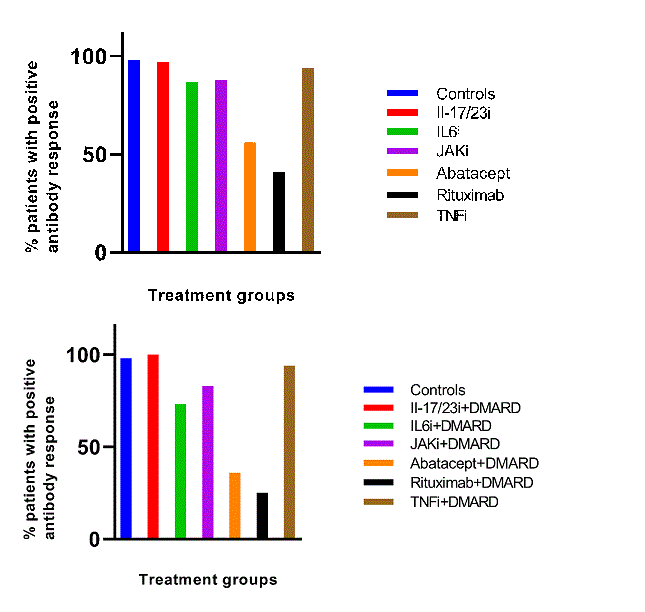
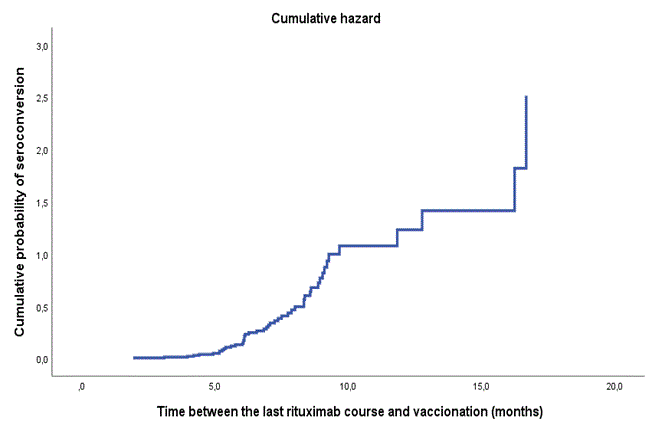
Results: In total, 414 patients and 61 controls participated. Of these, 323 had RA/JIA/psoriatic arthritis/spondylarthritis, 60 systemic vasculitis and 31 other autoimmune diseases. The following treatments were studied: rituximab (n=145), abatacept (n=22), IL6-inhibitors (n=79), JAK-inhibitors (n=58), TNF-inhibitors (n=68), IL12/23/IL17-inhibitors (n=42) and healthy individuals (controls; n=61). Patients receiving rituximab (40.7%), abatacept (55.6%), or IL6-inhibitors (87.0 %) had lower antibody response rate compared to controls (98.4%) which was more pronounced when b/ts DMARD was given in combination with csDMARDs (p< 0.001). There was no difference in response between patients receiving IL12/23/IL17-inhibitors, TNF-inhibitors or JAK-inhibitors and controls. Older patients, those receiving concomitant csDMARDs, prednisolone, and with vasculitis had lower proportion of responders (p< 0.0001). After adjustment in regression analysis, higher age, rituximab, shorter time between rituximab course and vaccination, abatacept and concomitant csDMARD remained significant predictors of impaired antibody response. An increased activity in IRD was reported by 14 (3.4%) patients.
Conclusion: In this large Swedish study including IRD, impaired immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines was observed in patients receiving rituximab or abatacept. Concomitant csDMARD further decreased this response. Older patients had an impaired antibody vaccine response regardless the immunomodulating treatment. Older patients on rituximab and abatacept should be strongly encouraged and prioritized for booster doses of COVID-19 vaccine.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Frodlund M, Chatzidionysiou K, Södergren A, Klingberg E, Bengtsson A, Hansson M, Ohlsson S, Pin E, Klareskog L, Kapetanovic M. The Impact of Immunomodulating Treatment on the Immunogenicity of COVID-19 Vaccines in Patients with Immune-mediated Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Compared to Healthy Controls. a Swedish Nationwide Study (COVID19-REUMA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-immunomodulating-treatment-on-the-immunogenicity-of-covid-19-vaccines-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-compared-to-healthy-controls-a-swedish-nationwide/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-immunomodulating-treatment-on-the-immunogenicity-of-covid-19-vaccines-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-compared-to-healthy-controls-a-swedish-nationwide/