Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis that confers significant disease burden. This real-world study described the impact of EGPA on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of patients (pt)s and their ability to work.
Methods: Data were drawn from the Adelphi Real World EGPA Disease Specific Programme™, a cross-sectional survey of physicians and pts in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the United Kingdom (UK), and the United States from July–December 2023. Physicians provided data for 503 pts with EGPA in total, with each physician completing a pt record form for four consecutive pts who they were managing. Physicians reported pt demographics, clinical characteristics, and disease severity. Pts reported HRQoL using the EQ-5D-5L (Dolan 1997 UK tariff; scored from 0 [worst health] to 1 [best health]) and the work productivity and activity impairment questionnaire (WPAI; scored from 0 [no impairment] to 100 [maximum impairment]). Analyses were descriptive.
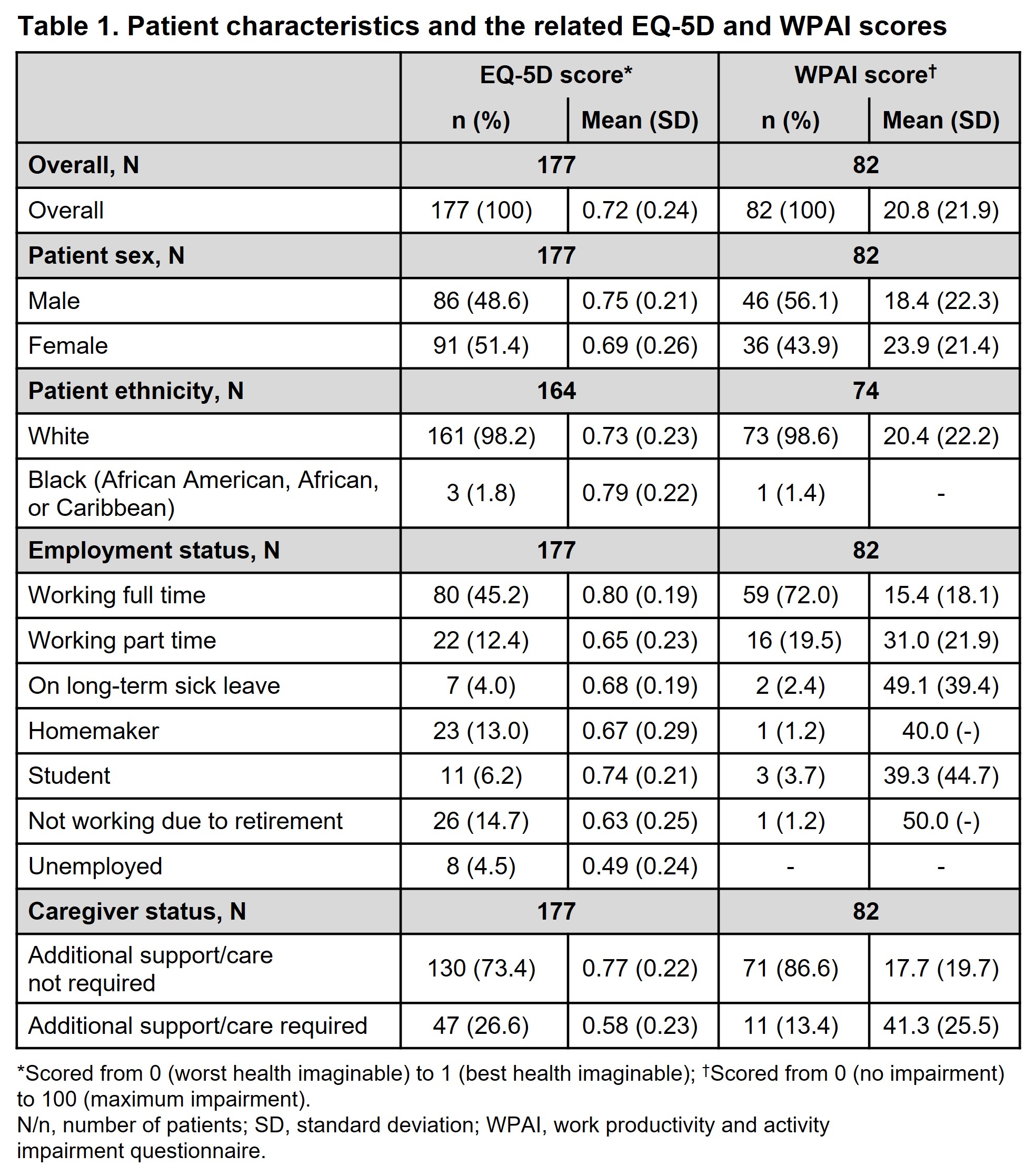
Results: Table 1 summarizes pt characteristics and related EQ-5D and WPAI scores. In all pts (N=503), mean (standard deviation [SD]) age was 49.5 (15.3) years, and 50% were female. In pts who completed the EQ-5D (N=177) and WPAI (N=82) questionnaires, respectively, mean (SD) age was 49.2 (14.2) and 46.0 (10.4) years, and 51% and 44% were female. The majority of pts who completed EQ-5D (n=161/164) and WPAI (n=73/74) questionnaires were White (≥98.2%). Pts had a mean (SD) EQ-5D score of 0.72 (0.24) and a mean (SD) WPAI score of 20.8 (21.9). Pts who did and did not require additional caregiver support had a mean (SD) EQ-5D of 0.58 (0.23) and 0.77 (0.22), respectively. In pts who were employed, unemployed, retired, and on long-term sick leave, mean EQ-5D (SD) was 0.80 (0.19), 0.49 (0.24), 0.63 (0.25), and 0.68 (0.19), respectively.
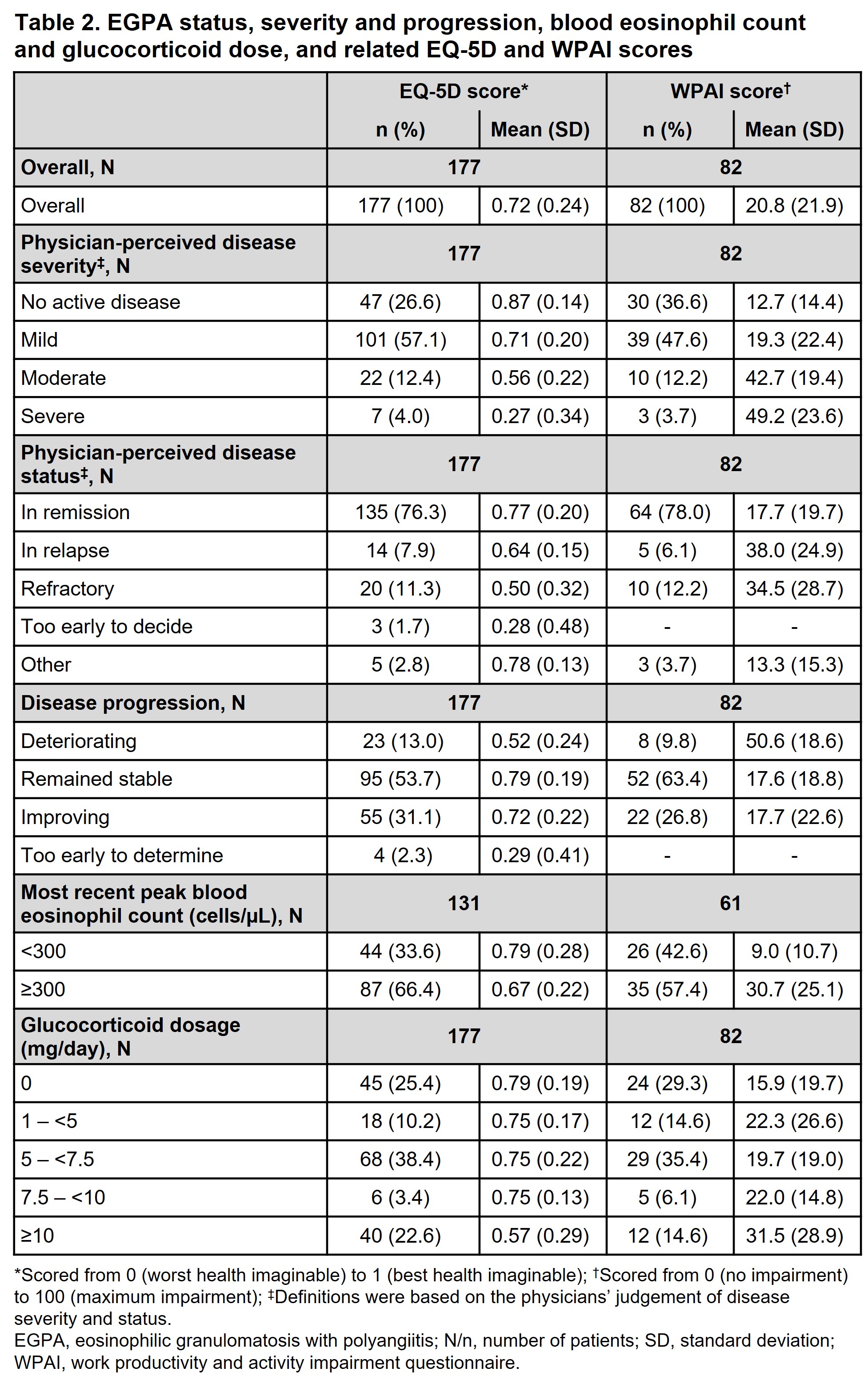
Table 2 summarizes EGPA status, severity, and progression, glucocorticoid dose and blood eosinophil (bEOS) counts, and related EQ-5D and WPAI scores. Based on physician judgement of disease status, over three quarters of pts were in remission and >10% had refractory disease. In pts judged by physicians to have severe, moderate, or deteriorating disease, respectively, mean (SD) EQ-5D was 0.27 (0.34), 0.56 (0.22), and 0.52 (0.24), and mean (SD) WPAI was 49.2 (23.6), 42.7 (19.4), and 50.6 (18.6). Pts with a most recent peak bEOS count (n=131) of < 300 cells/μL and ≥300 cells/μL had a mean (SD) EQ-5D of 0.79 (0.28) and 0.67 (0.22), respectively. Mean (SD) EQ-5D of pts on a glucocorticoid dose of 10 mg/day or greater was 0.57 (0.29).
Table 3 summarizes EGPA-related organ damage and symptoms, and related EQ-5D and WPAI scores. Pts with and without EGPA-related organ damage had a mean (SD) EQ-5D of 0.69 (0.24) and 0.86 (0.20), respectively. Mean (SD) EQ-5D of pts experiencing 1–2 or ≥3 symptoms at survey completion was 0.80 (0.18) and 0.61 (0.25), respectively.
Conclusion: Taken collectively from physician and pt responses, EGPA was associated with poor HRQoL and work impairment, highlighting an unmet need for improving HRQoL. Provision of better targeted therapies during earlier stages of the pt journey could address the burden experienced by pts with EGPA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Spiera R, Dolin P, Shavit A, Rowell J, Edmonds C, Persson J, Kielar D, Mascia D, Siddall J, Pennant T, Hennessy F, Chen S. The Impact of Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis on the Health-Related Quality of Life of Patients and Their Ability to Work: Evidence from a Real-World Survey in Clinical Practice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-on-the-health-related-quality-of-life-of-patients-and-their-ability-to-work-evidence-from-a-real-world-survey-in-clinical-practice/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-eosinophilic-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-on-the-health-related-quality-of-life-of-patients-and-their-ability-to-work-evidence-from-a-real-world-survey-in-clinical-practice/