Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The Latin American Group for the Study of Lupus (GLADEL) 2.0 is an observational prevalent and incident cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in Latin-American countries. Here we evaluated the work productivity and activity impairment (WPAI) in patients with active lupus nephritis (LN) at cohort entry and 12 months after treatment initiation according to their renal response.
Methods: Forty-four centers from Latin-American countries enrolled patients ≥18 years of age who fulfilled the 1982/1997 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and/or the 2012 Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) classification criteria for SLE. Patients from different subsets of LN were enrolled. For this analysis, patients in Group II (prevalent inactive LN), III (prevalent active LN), and IV (incident LN) and 12-month follow-up data were included. Demographic, clinical manifestations, disease activity (SLEDAI-2k) and damage SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI) were examined. At baseline, WPAI scores stratified by the presence of active or inactive LN were compared. At 12 months, absenteeism, presenteeism, global work impairment in employed patients and activity impairment in patients with active LN were compared according to their renal response. Renal responses were defined according to EULAR/Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) – complete clinical response: urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) < 0.5 g/g; partial clinical response: ≥ 50% reduction in UPCR; no response: < 50% reduction in proteinuria. Descriptive analyses were performed.
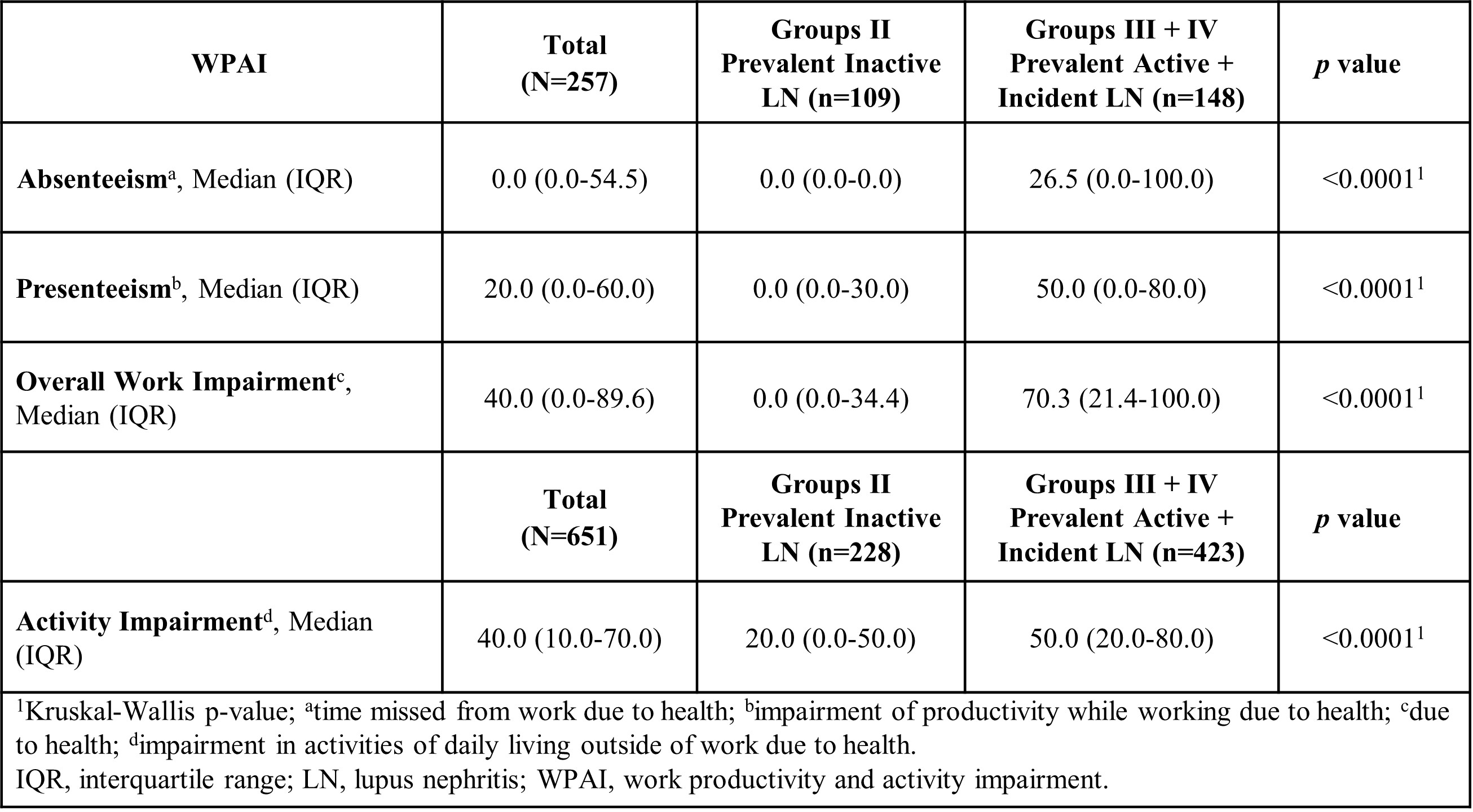
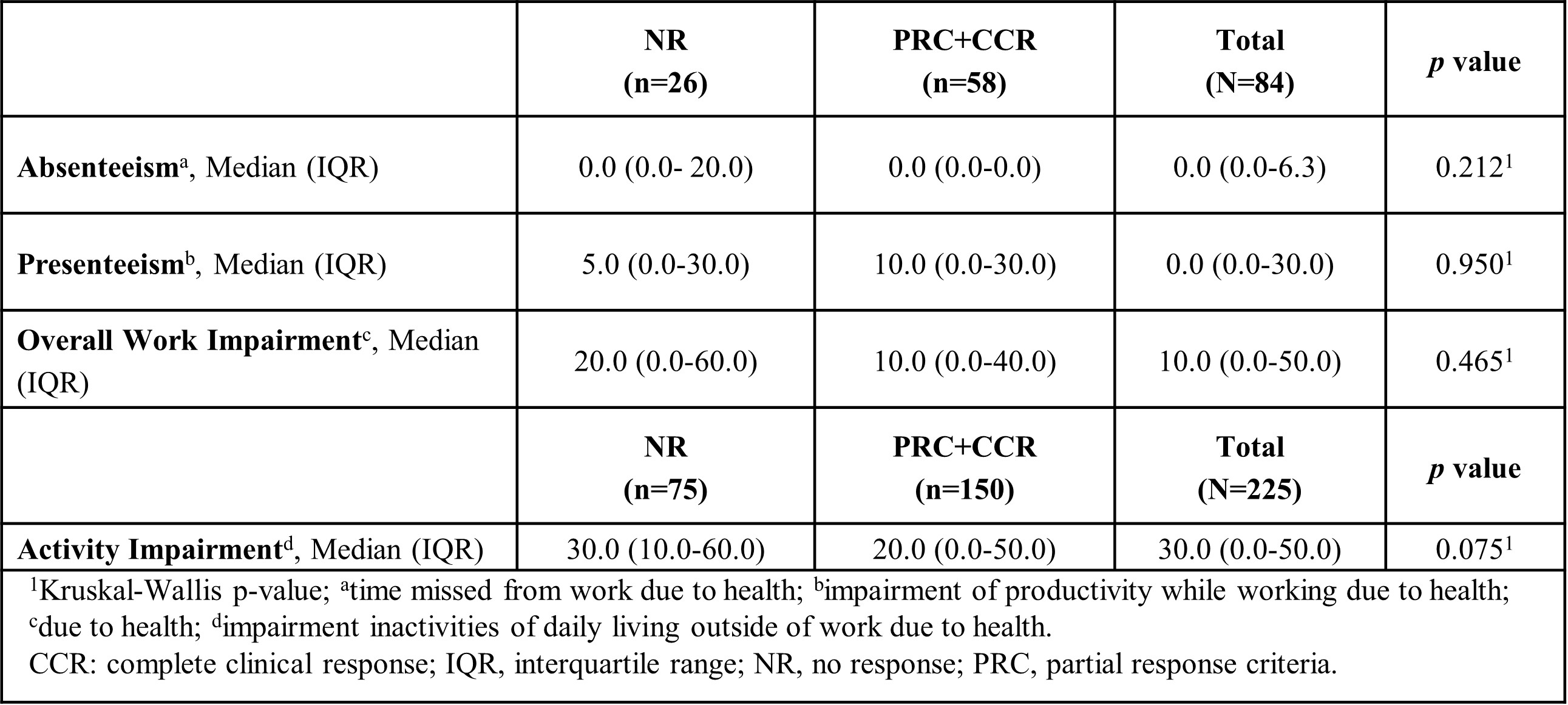
Results: Of the 1081 patients included in the cohort, 651 with history of LN were evaluated (423 with active LN and 228 with inactive LN). Of the active LN patients, 369 (87.4%) were women, were younger at cohort entry, of a lower socioeconomic status, had a higher unemployment rate and a higher SLEDAI than patients with inactive LN. Of the LN patients, 257 (39.5%) were employed (salaried work) at cohort entry and were included in this analysis. Patients with active LN showed higher rates of impairment in the WPAI score with greater impact and lower work productivity in all domains than in patients with inactive LN (Table 1). At 12 months, there was no evidence of a positive impact on work productivity as measured by the WPAI in patients who achieved renal response (Table 2).
Conclusion: Patients with active LN presented a greater impairment on WP compared to patients with inactive LN. There was no evidence of a positive impact on WP in patients who achieved a complete or partial renal response after 12 months of treatment. Future analyses with a larger number of patients being followed up would be necessary to provide more definitive data.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nieto R, Quintana R, Ávila D, Serrano Morales R, Harvey G, Hernandez L, Roberts K, Catoggio L, Subils G, Gobbi C, Juliana B, Ibáñez Peña P, Ariel Berbotto L, Bertolaccini M, Riseni D, De Los Ángeles Gargiulo M, Pisoni C, Serventi J, Buschiazzo E, De Souza Barbosa V, MONTICIELO O, Andrade C, Ribeiro F, Bonfa E, Borba E, Sato E, Peralta A, Donoso S, Aroca Martínez G, Medina H, Echeverri A, Molina-Rios S, Rubio M, López R, Moreno M, Vera Lastra O, Pérez Cristóbal M, Núñez-Álvarez C, Amezcua Guerra l, García-Valladares I, Mendoza C, Galarza-Delgado D, Vázquez M, Paats A, Calderón J, Alva A, Louis R, Pizzarossa C, Carlomagno A, Gamboa-Cardenas R, Alarcon G, Sbarigia U, Zazzetti F, Orillion A, Pons-Estel G, Pons-Estel B. The Impact of Active Lupus Nephritis on Work Productivity in Patients from a Latin American Lupus Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-active-lupus-nephritis-on-work-productivity-in-patients-from-a-latin-american-lupus-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-active-lupus-nephritis-on-work-productivity-in-patients-from-a-latin-american-lupus-cohort/