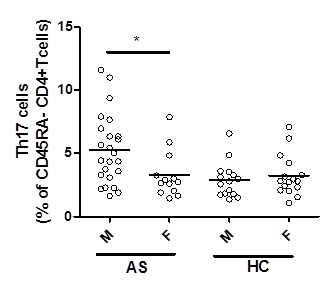Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose : Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is an inflammatory arthritis of the spine, which has a major impact on function and quality of life. AS is known to have a sex-bias with a M:F ratio of 3:1. In addition, females have a delayed onset and reduced radiographic severity compared to males. Genetic and immunologic studies have implicated the Th17-axis in AS pathogenesis, and recent clinical trials suggest efficacy of anti-IL-17A therapy. Prior studies have demonstrated a suppressive effect of vitamin D3 on Th17 cells. In the present study we examine whether there is a sex-bias in the Th17-axis, and its possible relationship to vitamin D metabolism in AS.
Methods: Serum IL-6 and IL-17A were measured by ELISA and 25(OH) vitamin D3 by mass-spectrometry in a cohort of 39 male AS patients, 36 female AS patients and 34 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Whole blood gene expression for vitamin D3-associated and Th17-associated genes was measured by RT-PCR. Th17 cells were measured by flow cytometry of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in a second, overlapping cohort of 14 female AS patients, 24 male AS patients and 30 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Data was analyzed by Mann-Whitney tests and correlations with Spearman tests.
Results: AS patients had an elevated Th17-axis when compared to healthy controls as demonstrated elevated IL-6 (p<0.01), IL-17A (p=0.06) and Th17 cell levels (p<0.05). When stratified for sex, the elevated Th17-axis was restricted to male patients, as exemplified by higher Th17 cell levels in male AS vs female AS (Figure 1). A trend was seen for lower serum 25(OH) vitamin D3 in male AS patients and healthy controls relative to their respective female counterparts. Gene expression of VDR and CYP27B1 (vitamin D3 activating enzyme) were equivalent in male and female AS patients, whereas CYP24A1 (vitamin D3 degrading enzyme) expression was significantly elevated in male AS patients. This was not seen in male vs female healthy controls. In male AS patients, serum 25(OH) vitamin D3 was inversely proportional to whole blood IL23R expression (r=-0.43, p<0.05) and Th17 cell level (r=-0.014, p=0.085).
Conclusion: This is the first demonstration that elevated levels of Th17 cells in AS are restricted to male patients, which could inform targeted therapy with anti-IL17 agents. This may be due to a sex-related alteration in the biochemistry of vitamin D3 which functions as an important inhibitory factor to the Th17 axis. This work demonstrates a biological basis for the observed sex-bias in incidence and in disease expression in AS.
Figure 1: Male AS patients have higher circulating Th17 levels than female AS patients and healthy controls (HC). Results displayed as scatter plot with mean and analyzed by Mann-Whitney test.
Disclosure:
E. Gracey,
None;
B. Green,
None;
P. Yip,
None;
R. Ayearst,
None;
A. Anton,
None;
A. Lin,
None;
R. D. Inman,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-immunological-basis-of-the-sex-bias-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-th17-expansion-is-restricted-to-male-patients-and-correlates-with-sex-related-alteration-in-vitamin-d-metabolism/