Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) is a screening tool used in patients with different medical conditions. However, its validity, reliability and responsiveness to change in systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients have not been evaluated yet.
Our objectives were to evaluate the feasibility, validity, reliability, and responsiveness of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and to analyse its model structure in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc).
Methods: In this study, 307 systemic sclerosis patients were included, of these, 90 participated in the responsiveness analysis. Psychometric properties were tested in analogy to the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology (OMERACT) filter and an exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis was performed to examine the structure of HADS.
Results: The HADS showed adequate feasibility, validity, reliability, and responsiveness to clinically relevant worsening of the disease (table 1). For our population of SSc patients, the HADS model with two sub-scales, HADS-A and HADS-D, and a general scale HADS-S, measuring anxiety, depression, and distress, respectively, was most appropriate (figure 1). The rates of anxiety, depression, mixed anxiety-depressive disorder (MADD) and distress identified by HADS in our cohort were 32.7%, 26.1%, 18.6%, and 49.7%, respectively (figure 2).
Conclusion: The psychometric properties of the HADS make it useful for screening in SSc, where anxiety, depression, MADD, and distress represent a significant burden to patients.
 Table 1: HADS assessed by OMERACT filter criteria
Table 1: HADS assessed by OMERACT filter criteria
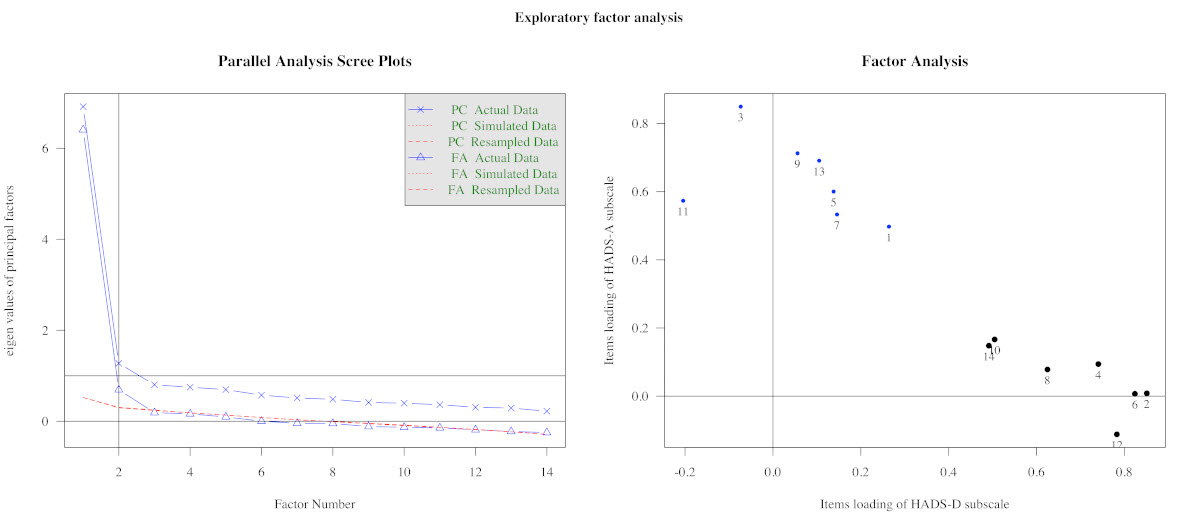 Figure 1: Exploratory Factor Analysis. Parallel analysis scree plot: the solid line shows eigenvalues of actual data, while the dotted and dashed lines (placed on top of each other) show simulated and resampled data. The point of inflection – the point where the gap between simulated data and actual data tends to be minimum – occurs at a number of factors supported by our model (n=2) (left panel); Factor analysis: item loadings of the model sub-scales (right panel).
Figure 1: Exploratory Factor Analysis. Parallel analysis scree plot: the solid line shows eigenvalues of actual data, while the dotted and dashed lines (placed on top of each other) show simulated and resampled data. The point of inflection – the point where the gap between simulated data and actual data tends to be minimum – occurs at a number of factors supported by our model (n=2) (left panel); Factor analysis: item loadings of the model sub-scales (right panel).
 Figure 2: Cases and rates of anxiety, depression, distress and MADD stratified by gender and SSc subset Legend: dcSSc, diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; lcSSc, limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis
Figure 2: Cases and rates of anxiety, depression, distress and MADD stratified by gender and SSc subset Legend: dcSSc, diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis; lcSSc, limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garaiman A, Mihai C, Dobrota R, Jordan S, Maurer B, Flemming J, Distler O, Becker M. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis – A Psychometric and Factor Analysis in a Monocentric Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-hospital-anxiety-and-depression-scale-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-psychometric-and-factor-analysis-in-a-monocentric-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-hospital-anxiety-and-depression-scale-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis-a-psychometric-and-factor-analysis-in-a-monocentric-cohort/
