Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
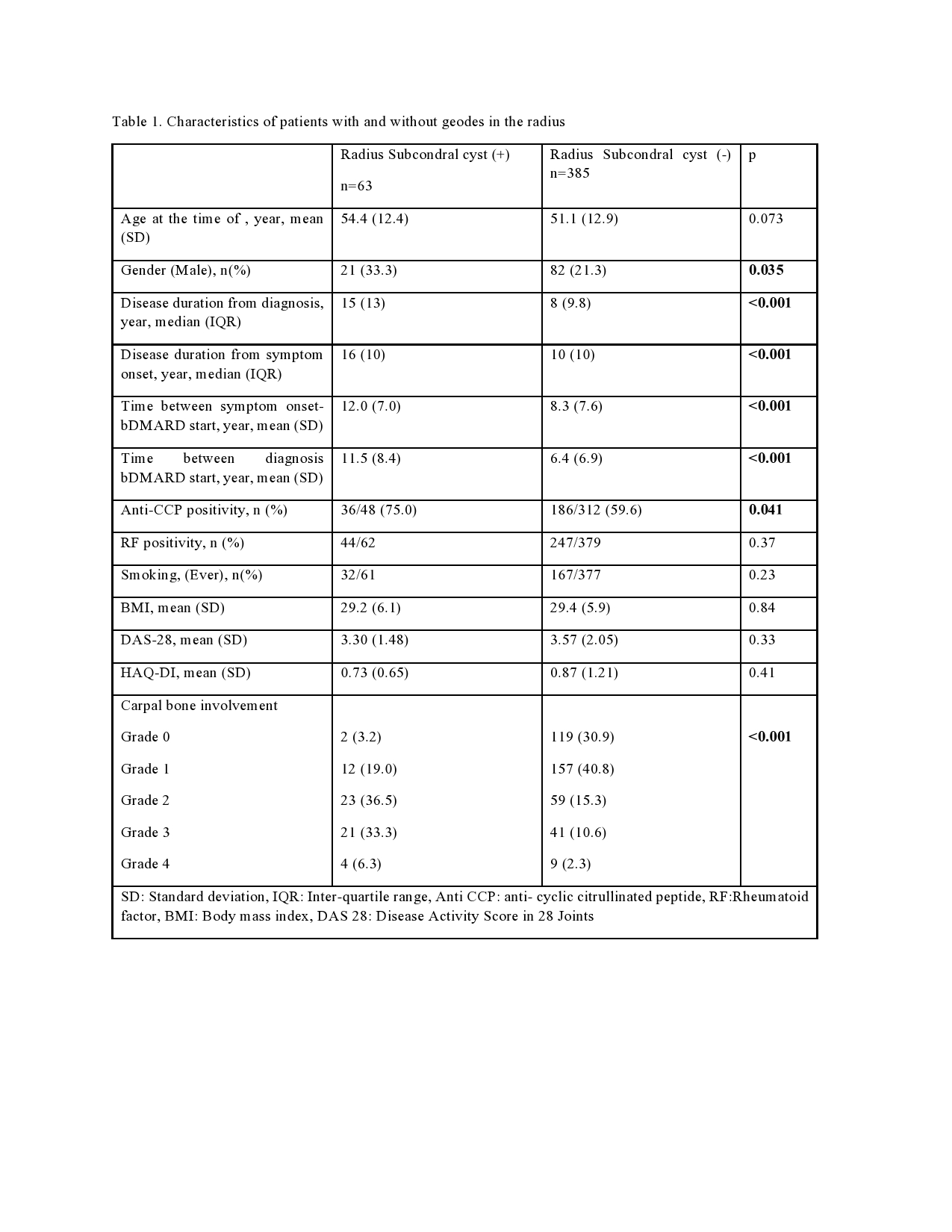
Background/Purpose: The presence of subchondral cysts in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has long been recognised. The concept of geodes used in geology would be the best terminology used to name the latter. In this asessment, we aimed to determine the frequency, distribution and characteristics of geodes in the radius in RA patients in a biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (bDMARD) cohort.
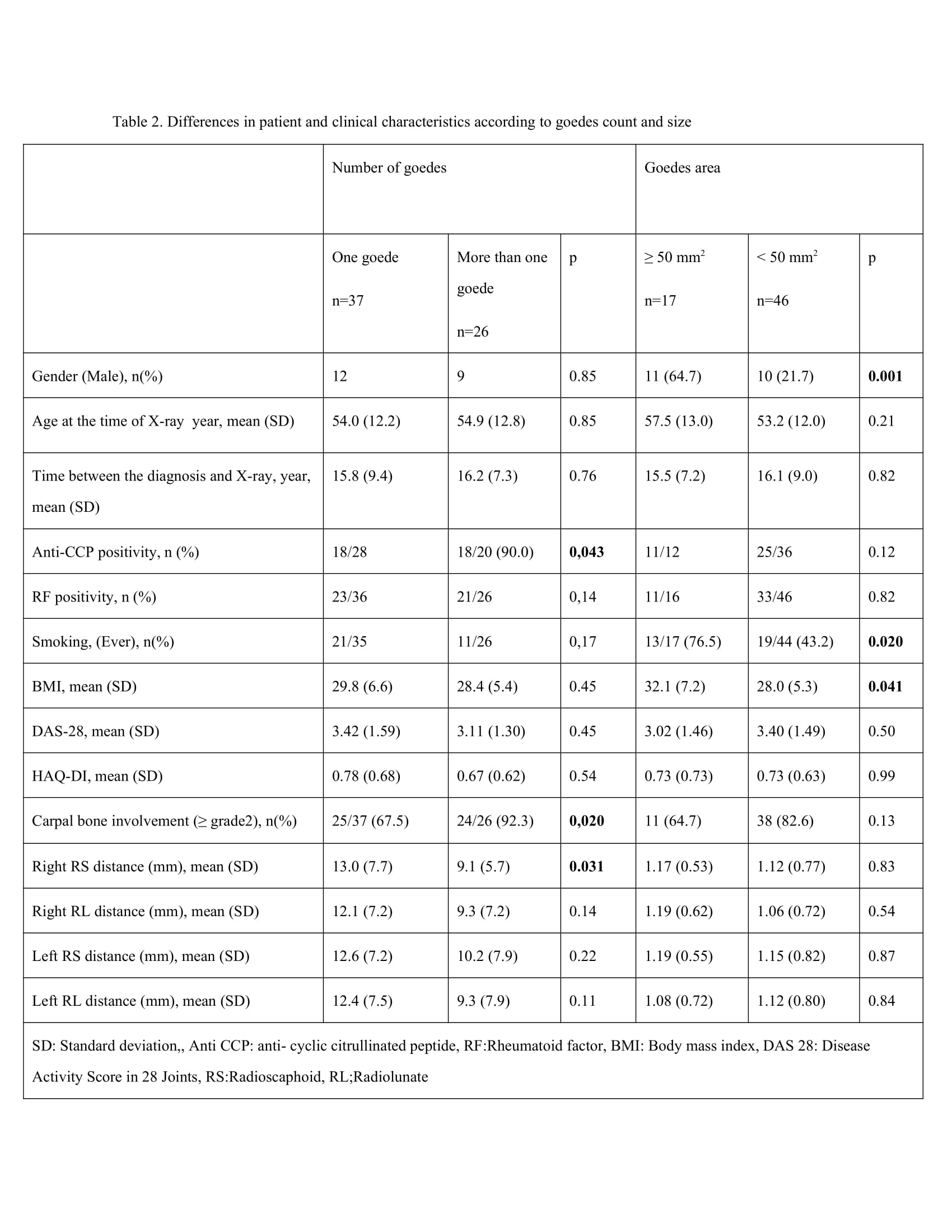
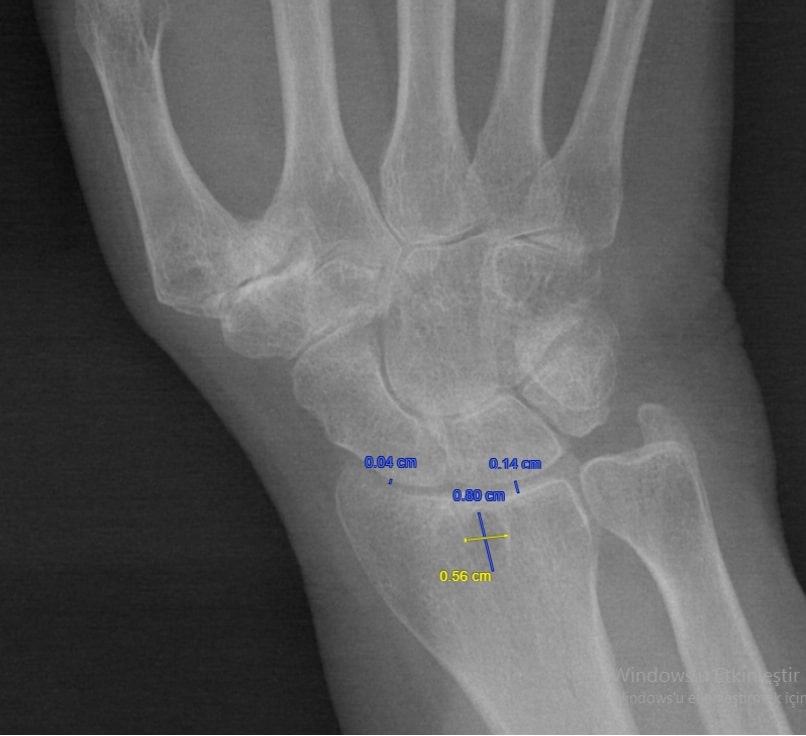
Methods: The HUR-BIO database was established in 2005, 2355 RA patients were registered as of January 2023. Anterior-posterior standard hand X-rays of the first 500 patients in HUR-BIO who had at least one hand X-ray were evaluated. The most recent hand X-ray of the patients was evaluated. From 500 patients in 28 (5.6%) patients, the presence or absence of subchondral cysts on radiographs could not be determined. 24 (4.8%) patients had cystic-erosive changes in the radius, but these patients were not included in the analysis because the bone integrity of the radius cortex was compromised. The localisation and size of the geodes, the distance from the distal part of the radius, the distance from the geodes to the radius, and the distance between the radius and the carpal bone were measured.. The distance between the radius and scaphoid and the distance between the radius and lunate bone were measured at the narrowest point (Figure 1). Involvement of the carpal bones was evaluated according to the modified Larsen score. Demographic, clinic characteristtics were assessed and compared between patients with and without goedes.
Results: Goedes were found in 63/448(14.1%) of these patients. Mean (SD) years of age at the time of hand x-ray was 54.4 (12.4) and 51.1 (12.9) in with/out goedes, respectively In the comparison of patients with/out goedes, there were differences in terms of male gender and anti-CCP positivity and disease duration. Larsen score in carpal bones was worse in patients with subchondral cysts (Table 1). A total of 98 cysts were found in 63 patients; 8 (12.6%) unilateral single cyst 37 (58.7%), unilateral double cyst 14 (22.2%), bilateral 12 (19.0%). The dominant cyst on the right was found in 40 patients and the second cyst in 14 patients, while the dominant cyst on the left was found in 35 patients and the second cyst in 9 patients. The distribution of sclerosis around these cysts was as follows; absent 4 (4.1%), mild 59 (60.2%), moderate 33 (33.7%), marked 2 (2.0%). The mean (SD) distance between the upper end of the cyst and the radius was 1.7 (0.67) mm. In 26 patients with multiple cysts, anti-CCP antibody positivity was more frequent (90.0% vs 64.3%, p=0.043), and Larsen score of grade 2 or higher was more frequent (92.3% vs 67.6%, p=0.020) Patients with subchondral cysts larger than 50 mm2 were more frequently male (64.7% vs 21.7%, p=0.001), smoking was more frequent (76.5% vs 43.2%, p=0.020).(Table 2).
Conclusion: In a cohort of RA patients who were required to use bDMARD, geodes were found in the radius in 14% of patients. These cysts were, usually single but bilateral in one-fifth of the patients. The relation between the diameter and number of geodes, anti-CCP positivity and gender suggests that these patients may represent a subgroup with a more erosive course.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kalyoncu U, Ayan G. The Frequency and Importance of Subchondral Radius Cysts in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Under B/tsDMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-frequency-and-importance-of-subchondral-radius-cysts-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-under-b-tsdmards/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-frequency-and-importance-of-subchondral-radius-cysts-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-under-b-tsdmards/