Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation in many of the body’s tissues, including the skin, joints, lungs, kidneys and heart. This inflammation causes damage to these tissues and produces significant mortality, with most complications of the disease involving direct effects on these organs. SLE affects young women between the ages of 15 and 45 years at a 9:1 rate as compared to men. The etiology is complex and remains elusive, however the susceptibility of women during the years in which estrogen levels are at their highest suggests a significant and critical contribution to the development of SLE. Estrogens are known to have pleiotropic effects on the immune system which is mediated through either estrogen receptor α (ERα), estrogen receptor β (ERβ) or the cell surface G-protein coupled receptor GPER1. ERα has been studied extensively in this context, however ERβ and GPER1 have received much less attention. Previously, our group and others have shown that ERα carrying immune cells are mediators of proinflammatory effects of estrogen more so than cells that lack this receptor. In the pursuit of a drug that is tailored to have a favorable selective estrogenic effect, the OSU Drug Development Institute discovered a novel carborane-based selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM), OSU-ERβ-012. This ERβ agonist exhibits potent binding of human ERβ (Ki = 2.0 nM) and functional selectivity for ERβ over ERα of at least 200-fold. The work presented herein describes the utility of OSU-ERβ-012 in treating SLE in a humanized mouse model of the disease.
Methods: PBMC isolated from patients with active SLE were adoptively transferred into NSG mice and allowed to expand in vivo for one week. The mice were divided into 3 cohorts receiving either vehicle control, prednisone or OSU-ERβ-012 via daily oral gavage for five weeks. Blood samples were taken at baseline, 3 and 5 weeks. Serum was analyzed for circulating cytokines using the MSD human V-PLEX Proinflammatory Panel. At 5 weeks, mice were euthanized, kidneys and hearts were harvested and processed for H&E, Masson’s Trichrome and IHC histology. Lupus patient PBMCs were isolated and stimulated in vitro under various conditions and then flow cytometry was used to identify specific cell types affected by OSU-ERβ-012.
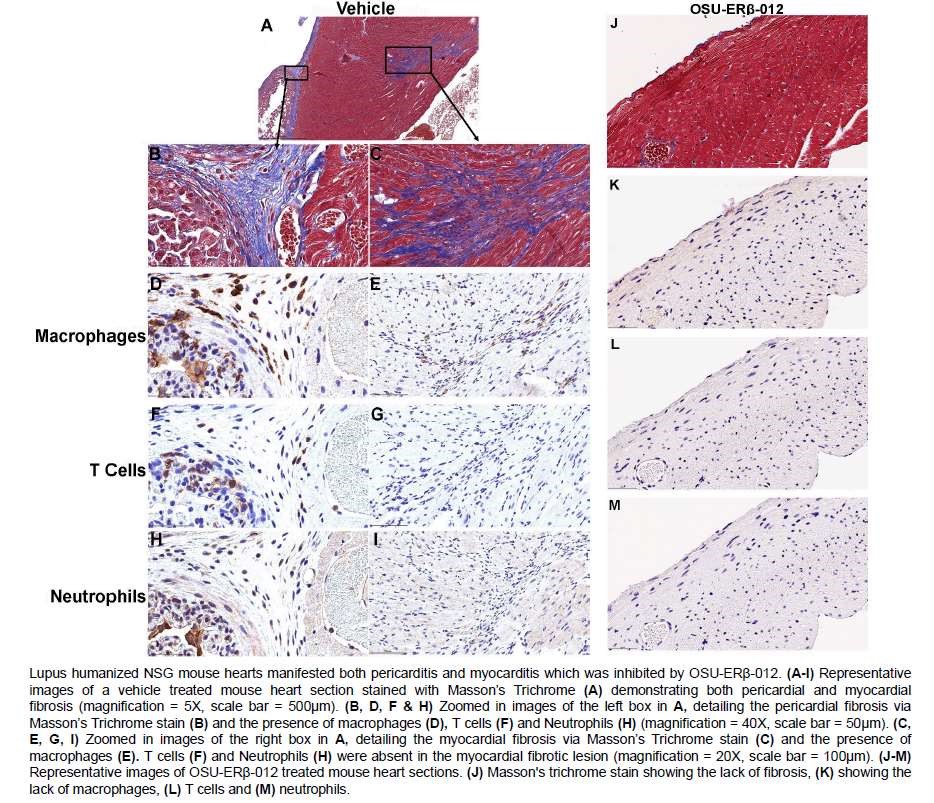
Results: OSU-ERβ-012 was as effective as prednisone in suppressing glomerular inflammation and more effective at inhibiting inflammation of the heart. More specifically, the ERβ agonist was superior to prednisone at inhibiting pericarditis, myocarditis and cardiac fibrosis. OSU-ERβ-012 demonstrated effectiveness in suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines. The in vitro effect of OSU-ERβ-012 confirmed the suppression of IFNγ and TNFα and revealed the cell type specific effects of the drug.
Conclusion: OSU-ERβ-012 is an effective inhibitor of the SLE inflammatory process and warrants additional study as a potential therapeutic in patients with SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zeno B, Alexandrov T, Yuan H, Bruckner S, Jarjour W. The ERβ Agonist, OSU-ERβ-012, Suppresses Systemic, Kidney and Heart Inflammation in a Chimeric Mouse Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-er%ce%b2-agonist-osu-er%ce%b2-012-suppresses-systemic-kidney-and-heart-inflammation-in-a-chimeric-mouse-model-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-er%ce%b2-agonist-osu-er%ce%b2-012-suppresses-systemic-kidney-and-heart-inflammation-in-a-chimeric-mouse-model-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/