Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Small RNA (sRNA) sequencing has revealed new classes of sRNAs beyond microRNAs. These sRNAs can regulate genes and are also useful biomarkers of disease. The aim of this study was to determine if the endogenous plasma sRNA landscape of patients with RA is altered compared to control subjects and determine their association with disease-related parameters in RA.
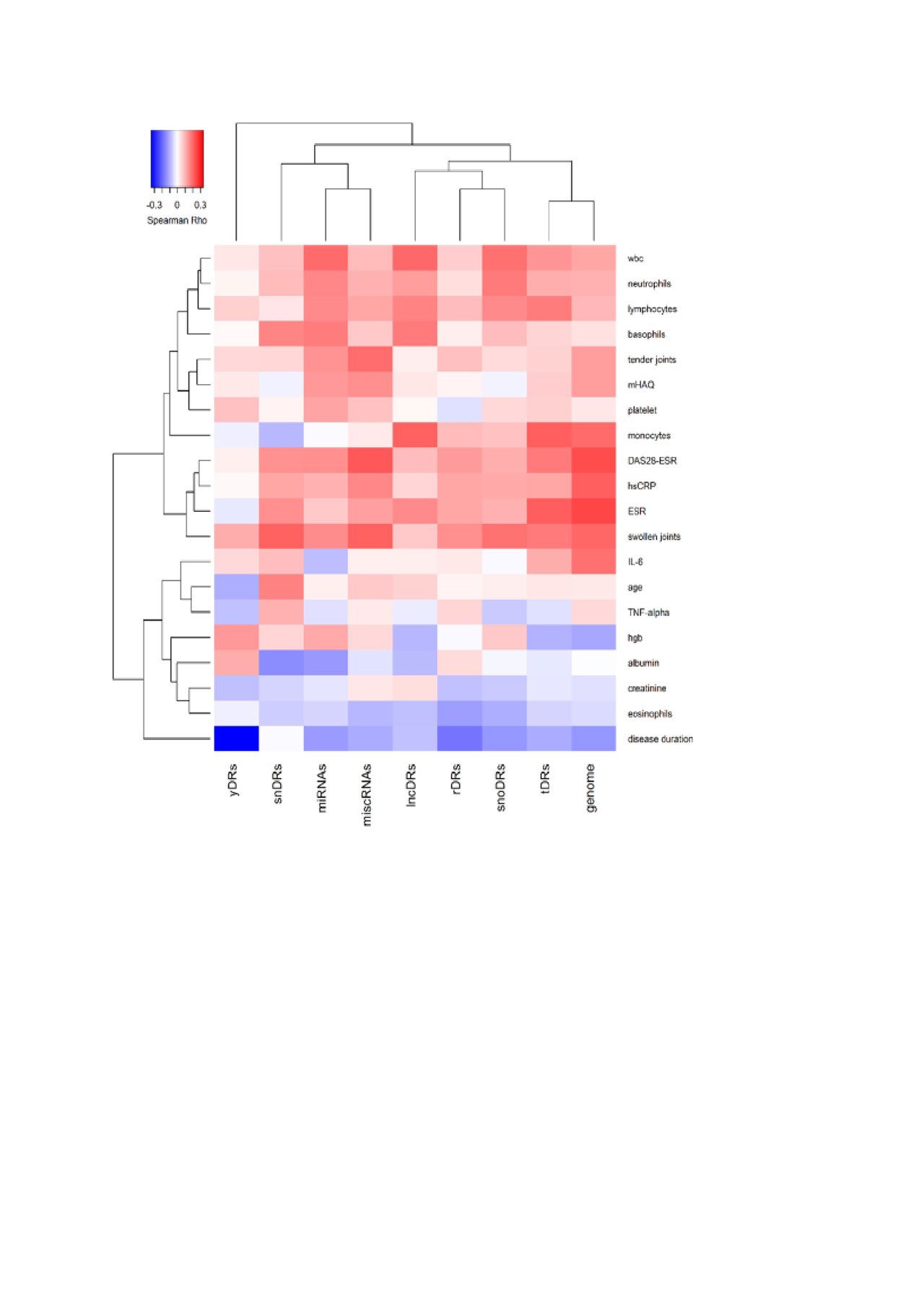
Methods: sRNA sequencing was performed on plasma from 165 RA and 90 control subjects who were frequency-matched for age, race and sex. TIGER pipeline was used to quantify endogenous sRNAs including microRNAs and sRNAs derived from small nuclear RNAs (snDRs), small nucleolar RNAs (snoDRs), YRNAs (yDRs), transfer RNAs (tDRs), long non-coding RNAs (lncDRs), miscellaneous sRNAs (miscRNAs), and sRNAs aligning to the human genome but not annotated sRNAs categories (such as sRNAs aligning to messenger RNAs or precursors such as pre-rRNAs). Sequencing reads were normalized to million total reads. The reads in each sRNA category were compared between RA and control subjects and correlated with disease activity measures and general laboratory measures with Spearman correlation. The correlations were presented using heatmap with hierarchical clustering.
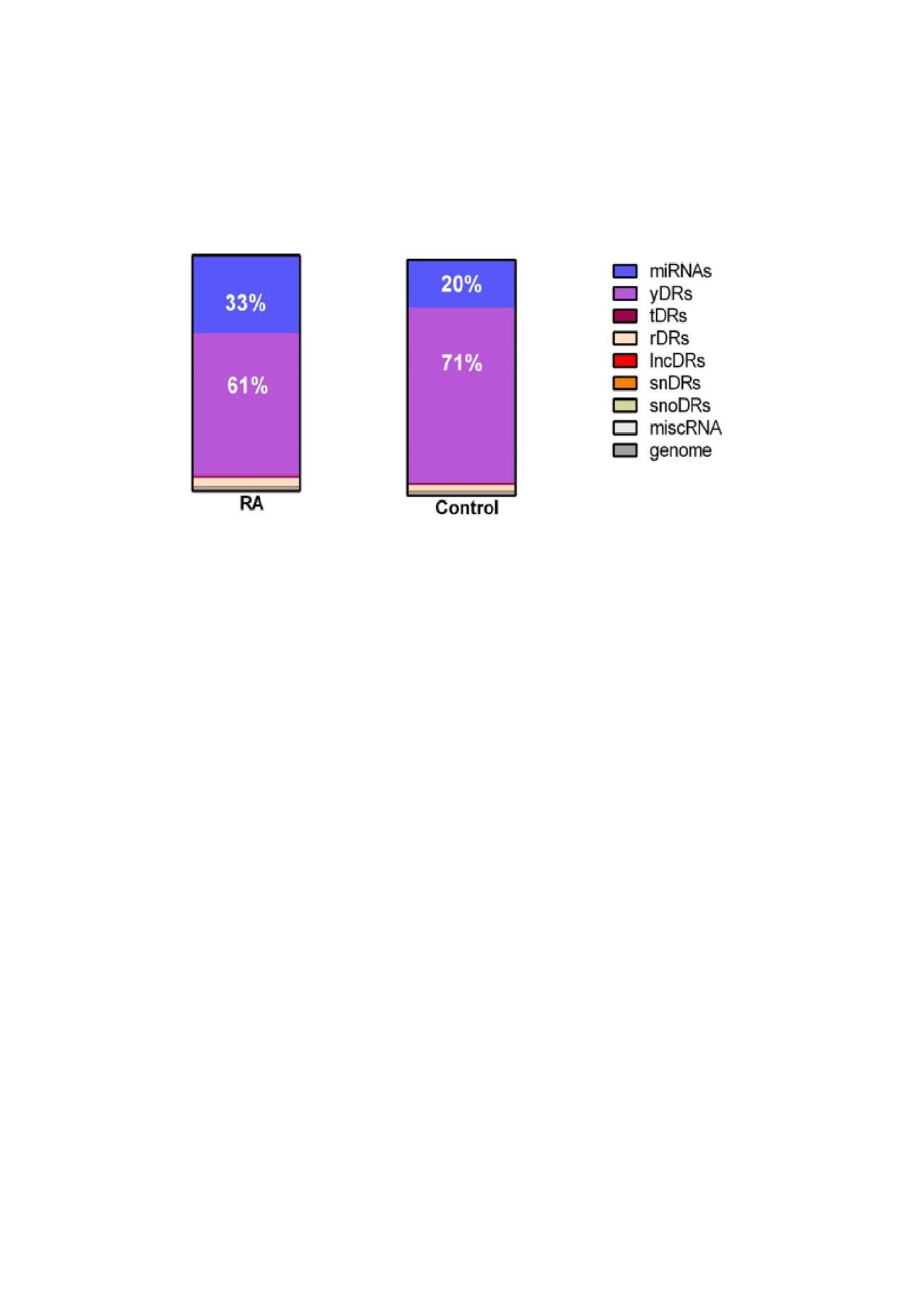
Results: The largest proportion of endogenous plasma sRNAs was yDRs, followed by microRNAs. Patients with RA had more microRNAs (1.42-fold, P=0.01), more tDRs (1.14-fold, P=0.04), and fewer yDRs (-1.41-fold, P=0.009) compared to control subjects (Figure 1), but other sRNAs as classes were not significantly different in RA. Disease duration was inversely associated with yDRs (Figure 2). Disease-related parameters such as DAS28 score, swollen joint count, and inflammatory markers were significantly positively associated with genome reads not classified as a sRNA category, tDRs and miscRNAs (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Endogenous plasma sRNAs are altered in patients with RA compared to control subjects. While individual miRNAs have been well studied and many are excellent biomarkers in RA, non-miRNA sRNA and unclassified sRNAs were significantly associated with disease related parameters as classes and may represent novel biomarkers for RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ormseth M, Solus J, Sheng Q, Ye F, Song H, Wu Q, Guo Y, Oeser A, Allen R, Vickers K, Stein C. The Endogenous Plasma Small RNAome of Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-endogenous-plasma-small-rnaome-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-endogenous-plasma-small-rnaome-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/