Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:In Japan, oral tacrolimus (TAC) was approved for the treatment of RA in 2005 and the improvement of symptoms thorough the use concomitant with disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), including MTX has been reported. On the other hand, the efficacy and tolerance of biological agents therapy concomitant with TAC are unknown. The objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy and tolerance of biological agents concomitant with TAC in Japanese patients with RA using retention rate analysis.
Methods: Total patients (n=1541) who underwent 4 biological agents (etanercept: ETN, adalimumab: ADA, tocilizumab: TCZ, abatacept: ABT) treatment between 2003 and 2011 at Nagoya University Hospital and 12 other institutes (Tsurumai Biologics Communication Study Group) were enrolled. In each biologics analysis, patients were divided into three groups: (1) concomitant only MTX (MTX group) (2) concomitant only TAC (TAC group) (3) monotherary (mono group). In TAC or MTX group, these drugs were only ones which concomitant with biologics. Patients who underwent biologics combined with other DMARDs were excluded. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to estimate retention rate in each biologics group. To estimate the tolerance of concomitant biologics with TAC, cumulative hazard function was performed in each biologics group.
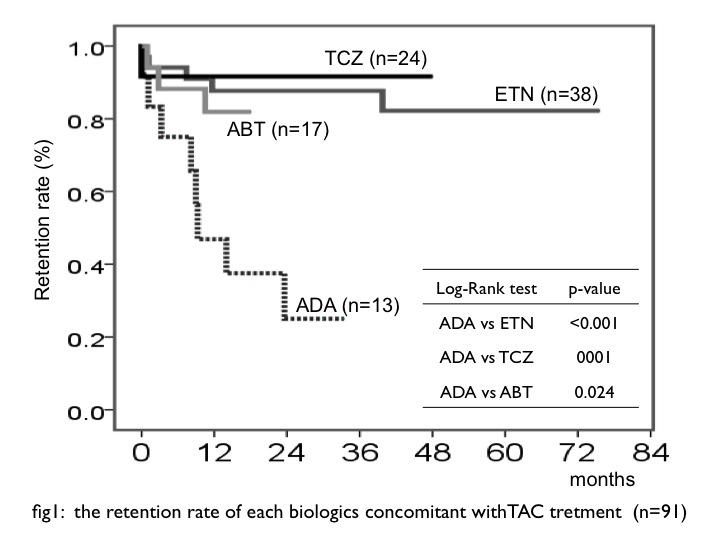
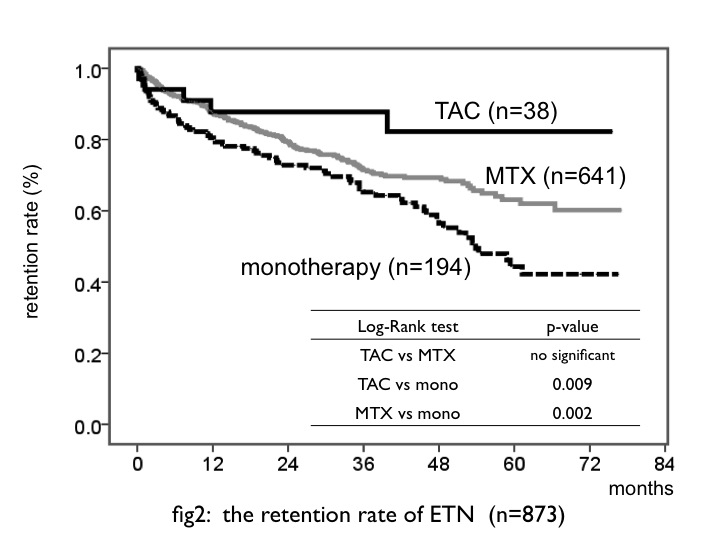
Results: In total 1541 patients, 91 patients (5.9%) administered each biologics concomitant with TAC (ETN: n=38, 101.0 patient-years (PY) ADA: n=13, 12.8 PY TCZ: n=24, 40.8 PY ABT: n=17, 16.2 PY). Average dosages of TAC at starting were ETN: 2.1
Conclusion: We suspected that combination therapy ETN and TAC are subsequent options for treatment to RA patient, especially in whom MTX cannot be administration.
Disclosure:
K. Terabe,
None;
T. Kojima,
None;
N. Takahashi,
None;
K. Funahashi,
None;
A. Kaneko,
None;
D. Kida,
None;
Y. Yabe,
None;
Y. Hirano,
None;
M. Hayashi,
None;
N. Ishiguro,
Takeda, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Astellas, Chugai, Abbott, BMS, Eisai, Janssen, Kaken and Pfizer,
2,
Takeda, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Astellas, Chugai, Abbott, BMS, Eisai, Janssen, Kaken, Pfizer, Taisho-Toyama and Otsuka,
8.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effectiveness-of-biological-agents-concomitant-with-tacrolimus-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/