Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Many patients with systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARDs) using immunomodulators have blunted humoral responses to COVID-19 vaccines. As such, the initial mRNA vaccine series is defined as 3 doses for this population and a 4th (or first “booster”) dose was recommended by the CDC in October 2021. However, 4th dose uptake among patients with SARDs has been low. In the general population, a 4th vaccine dose reduces the risk of breakthrough infection; its effectiveness in SARDs receiving immunomodulators has not been established.
Methods: We conducted an emulated target trial in a large US healthcare system, comparing receiving vs. not receiving a 4th vaccine. Eligible patients had SARDs by a validated algorithm including immunomodulator use and were eligible (by CDC guidelines) to receive a 4th dose of BNT162b2 or mRNA-1273 between 1/16/22-6/11/22. We excluded recipients of Ad26.COV2.S. To account for temporal changes in COVID-19 variants and guidance on 4th dose eligibility, the study period was divided into 1-week intervals. Cases were included in a 1-week interval if they received a 4th mRNA dose in that interval; comparators were eligible for a 4th dose but had not yet received it before or during the interval and had similar duration from 3rd dose to account for waning. The index date for cases was the date of 4th dose; for comparators, it was a random date within the interval.
The primary outcome was COVID-19 infection (positive COVID-19 PCR or antigen test or positive COVID-19 flag in the electronic record). Follow-up ended at the earliest of: (1) COVID-19; (2) bivalent vaccine availability (9/1/22); (3) “deviation” from the assigned arm (i.e., 5th dose for cases, 4th dose for comparators); (4) or non-COVID death as a competing risk. The propensity score (PS) for receiving the 4th dose was calculated weekly using logistic regression. We performed time-stratified, overlap PS-weighted Cox regressions to examine the relation of the 4th dose to the risk of each outcome.
Results: We included a total of 4,010 patients who received ≥3 mRNA vaccines and were eligible for a 4th during the study period; of this group, 2994 received a 4th dose and 1014 did not. Baseline covariates before and after overlap weighting are shown in Table 1. The mean age was 67 years, 72% were female, 88% were White, and most had RA (54%). The most common treatments were conventional synthetic DMARDs (58%) and biologic DMARDs (39%). Prior to the 3rd dose, 599 (14.9%) had had COVID-19.
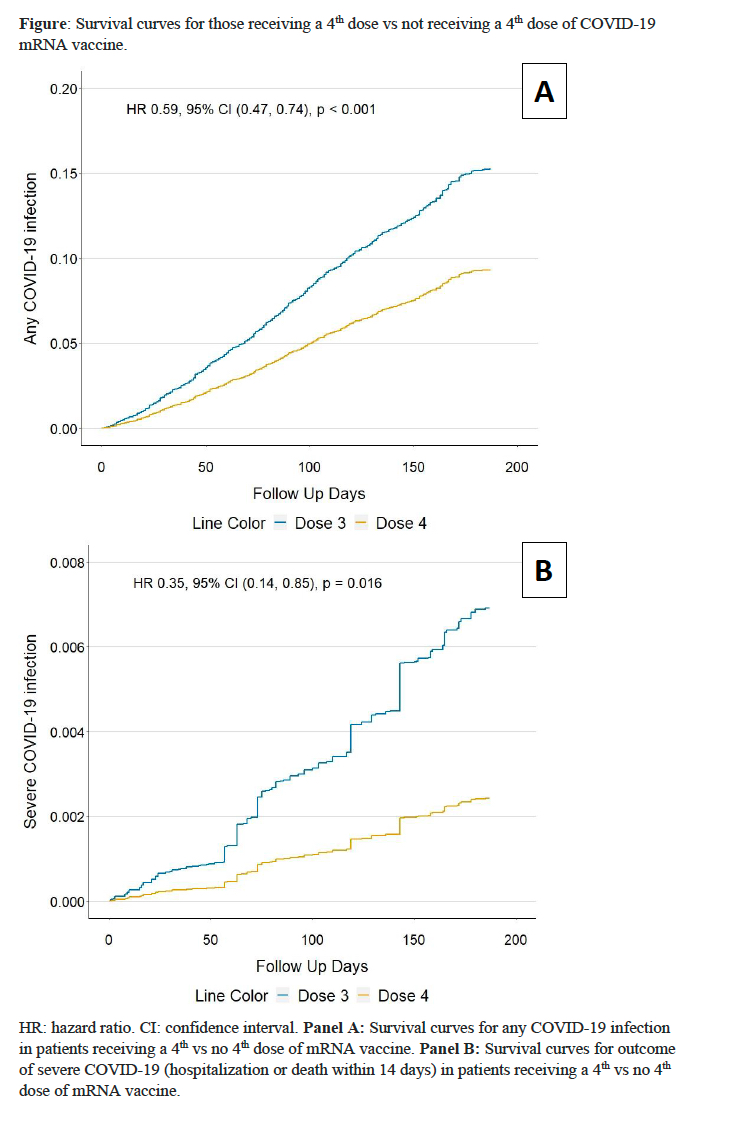
The incidence of COVID-19 was lower in the 4th dose cohort than comparator cohort (14.8 vs 23.7 per 1000 person-months) (Table 2). The rate difference between the two cohorts was -8.85 (95% CI: -13.37 to -4.33) per 1000 person-months with an HR of 0.59 (95% CI: 0.47-0.74), favoring a 4th dose (Figure). The risk of hospitalization or death within 14 days from COVID infection was lower in the 4th dose cohort than comparators (0.36 vs. 0.93 events/1000 person-months) with an HR of 0.35 (95% CI: 0.14-0.85).
Conclusion: In this emulated target trial, a 4th dose of mRNA vaccine reduced the risk of COVID-19 by 41% and severe COVID-19 by 65% among patients with SARDs using immunomodulators during the Omicron era. Patients with SARDs should be encouraged to receive at least 4 doses of mRNA vaccines.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hanberg J, Fu X, Wang X, Patel N, Kawano Y, Schiff A, Kowalski E, Cook C, Vanni K, Guzzo K, Qian G, Bade K, Saavedra A, Venkat R, Srivatsan S, Zhang Y, Sparks J, Wallace Z. The Effectiveness of a Fourth Dose of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine in Patients with Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases Using Immunomodulators: An Emulated Target Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effectiveness-of-a-fourth-dose-of-covid-19-mrna-vaccine-in-patients-with-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-using-immunomodulators-an-emulated-target-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effectiveness-of-a-fourth-dose-of-covid-19-mrna-vaccine-in-patients-with-systemic-autoimmune-rheumatic-diseases-using-immunomodulators-an-emulated-target-trial/