Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:45AM-10:00AM
Background/Purpose: Avacopan, an oral C5a receptor inhibitor, was evaluated in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV). Efficacy and safety results were reported previously. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) changes are reported here.
Methods: A 52-week blinded trial (ADVOCATE) randomized 331 AAV patients 1:1 to either full-dose daily oral prednisone with taper (‘Prednisone SOC’), or avacopan with no daily oral prednisone (‘Avacopan Group’). Both received standard of care (SOC): rituximab induction or cyclophosphamide. Glucocorticoid (GC) exposure including pre-randomization tapering into the blinded treatment period, co-administration with rituximab, and flares was expected and balanced between groups. The total dose of prednisone was ~2500 mg less with avacopan treatment over the entire trial. Primary efficacy endpoints were % patients achieving disease remission at Week 26 and sustained remission at Week 52 using Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (BVAS). HRQoL was assessed by Short Form-36 Health Survey version 2 (SF-36), a generic measure of HRQoL that performs well across vasculitis trials, including AAV1 and giant cell arteritis2, and EuroQoL Group 5-Dimensions 5-Levels Questionnaire (EQ-5D-5L).
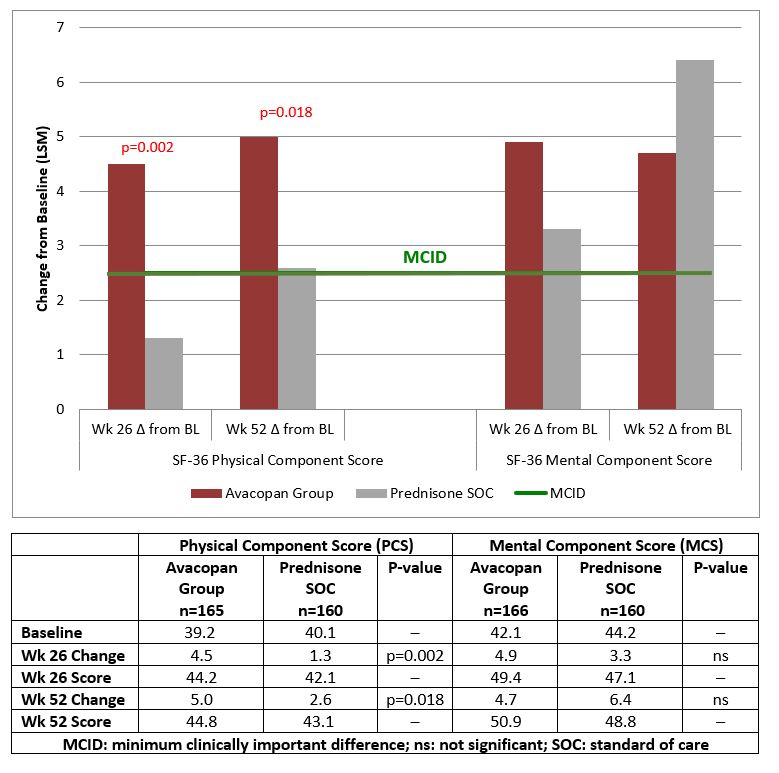
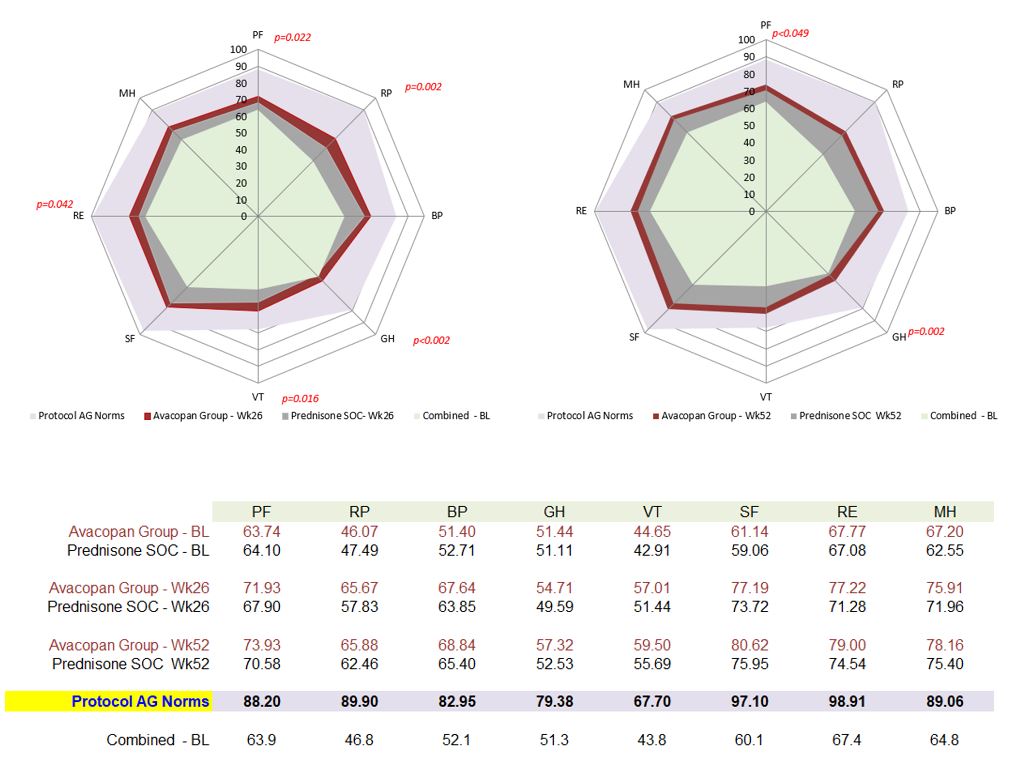
Results: Week 26 improvements in physical component summary (PCS) score with Avacopan Group: 4.5 points vs Prednisone SOC: 1.3 points (least squared means, LSM, for all analyses); statistically significant (p=0.002) and >minimum clinically important difference (MCID) = 2.5 points3 (Fig. 1). Mental component summary scores (MCS) were: Avacopan Group: 4.9 points; Prednisone SOC: 3.3 points, > MCID in both groups. At Week 26 improvements in physical function (PF), role physical (RP), general health (GH), vitality (VT) and role emotional (RE) domains with Avacopan Group were large (3.1 to 16.8 points); statistically significant vs Prednisone SOC (p< 0.002 to p=0.002), and >MCID of 5.0 points in 4 domains (Fig. 2). This reflects improvements in physical function and activities; also fatigue, energy, emotional role limitations, and general health perceptions.
Week 52 improvements with Avacopan Group vs Prednisone SOC were maintained or improved. PCS score was 5.0 vs 2.6 points, clinically meaningful, and statistically significant (p=0.018). Improvements in PF and GH domains exceeded MCID and were statistically significant (p< 0.049 and p< 0.002). The health utility score, SF-6D, based on calculation across all 8 domains of SF-36, indicated broad improvements in patient-reported health status. Improvements at Weeks 26 and 52 were greater with Avacopan Group compared to Prednisone SOC (Fig. 3); >MID (0.041)3 and consistent with reported improvements in EQ-5D-5L utility score, which was statistically significant at week 52 (p=0.009).
Conclusion: Treatment of AAV with avacopan and a reduced-dose glucocorticoid regimen led to significant improvements in HRQoL compared to SOC. These findings have important clinical implications for treatment of patients with AAV.
1. Pugnet G, et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016; 34(3 Suppl 97):S54-S59
2. Strand V, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019; 21:64
3. Strand V, et al. J Rheumatol. 2011; 38;1720-17271
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Bekker P, Yue H, Jayne D, Merkel P. The Effect of Treatment with the Complement C5a Receptor Inhibitor Avacopan on Health-Related Quality of Life in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-treatment-with-the-complement-c5a-receptor-inhibitor-avacopan-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-treatment-with-the-complement-c5a-receptor-inhibitor-avacopan-on-health-related-quality-of-life-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/