Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: It is important to understand how to select among the multiple treatment options for active psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Since individual patient domains may influence treatment choice, it is useful to evaluate individual American College of Rheumatology (ACR) components in large trials. SPIRIT-H2H showed superiority of ixekizumab (IXE) over adalimumab (ADA) in patients with PsA and inadequate response (IR) to conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs) [1]. This analysis describes the effect of IXE and ADA on individual ACR components at week (Wk) 52, with and without concomitant methotrexate (MTX) and csDMARDs.
Methods: Patients from SPIRIT-H2H (NCT03151551, 52 Wk randomized multicenter study) who met Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) (N=566), were randomized (1:1, stratified by baseline concomitant csDMARDs and moderate-to-severe PsO) to IXE or ADA on-label PsA or PsO dosing. Patients were bDMARD-naïve with IR to csDMARDs, active PsA (≥3 tender joints [TJC] and ≥3 swollen joints [SJC]) and had psoriasis (PsO) ≥3% BSA (body surface area). Patient’s Global Assessment (PtGA) and Physicians Global Assessment (PGA), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and joint pain were assessed by visual analog scale, and TJC and SJC as well as C-reactive protein (CRP) were analyzed. All post-hoc analyses were performed on the intent-to-treat (ITT) population. Change from baseline (CFB) in individual ACR components was analyzed using an Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) model, for overall as well as with and without concomitant therapies (e.g., MTX or csDMARD). Least square mean (LSM) and standard error (SE) are presented. Missing data were imputed using modified baseline observation carried forward (mBOCF). Nine patients with active PsO and BSA ≥3% were assessed as Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI)=0 at baseline, a medical inconsistency that was resolved using medical judgment. These patients were considered PASI100 responders if PASI =0 and BSA =0 at post baseline visits.
Results: A total of 566 patients received either IXE (N=283) or ADA (N=283). Baseline values for individual ACR components were balanced between IXE and ADA (Table). At Wk 52, IXE demonstrated efficacy across all individual ACR components in the ITT population, specifically in PGA, PtGA and Joint Pain; ADA also demonstrated numerical efficacy (Fig. A). Improvements from baseline for IXE were observed across ACR components, with or without MTX or csDMARD (Fig. B-E). The effect of MTX (with or without) was notably different between IXE and ADA in TJC68, PGA, Joint Pain, and PtGA.
Conclusion: In this analysis, there was improvement with IXE in all components of the ACR composite score at Wk 52, irrespective of MTX or csDMARD use (with or without). In the ITT population, IXE showed comparable efficacy to ADA at Wk 52 in all components of ACR, demonstrating improvement across musculoskeletal domains. These results may provide further confidence of the clinical benefits of ixekizumab across musculoskeletal domains in patients with PsA, regardless of MTX or csDMARD use.
- Mease PJ. et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79(1)
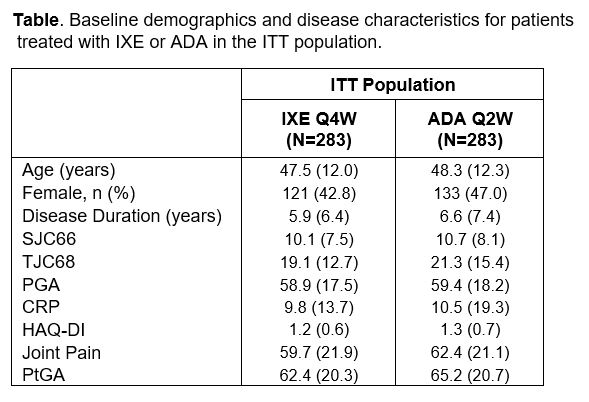 Data presented as mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. Abbreviations: ADA, adalimumab; CRP, C-reactive protein; HAQ-DI, health assessment questionnaire disability index; ITT, intent-to-treat; IXE, ixekizumab; PGA, physicians’ global assessment, PtGA, patients global assessment; Q2W, every two weeks; Q4W, every four weeks; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count.
Data presented as mean (SD) unless otherwise specified. Abbreviations: ADA, adalimumab; CRP, C-reactive protein; HAQ-DI, health assessment questionnaire disability index; ITT, intent-to-treat; IXE, ixekizumab; PGA, physicians’ global assessment, PtGA, patients global assessment; Q2W, every two weeks; Q4W, every four weeks; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count.
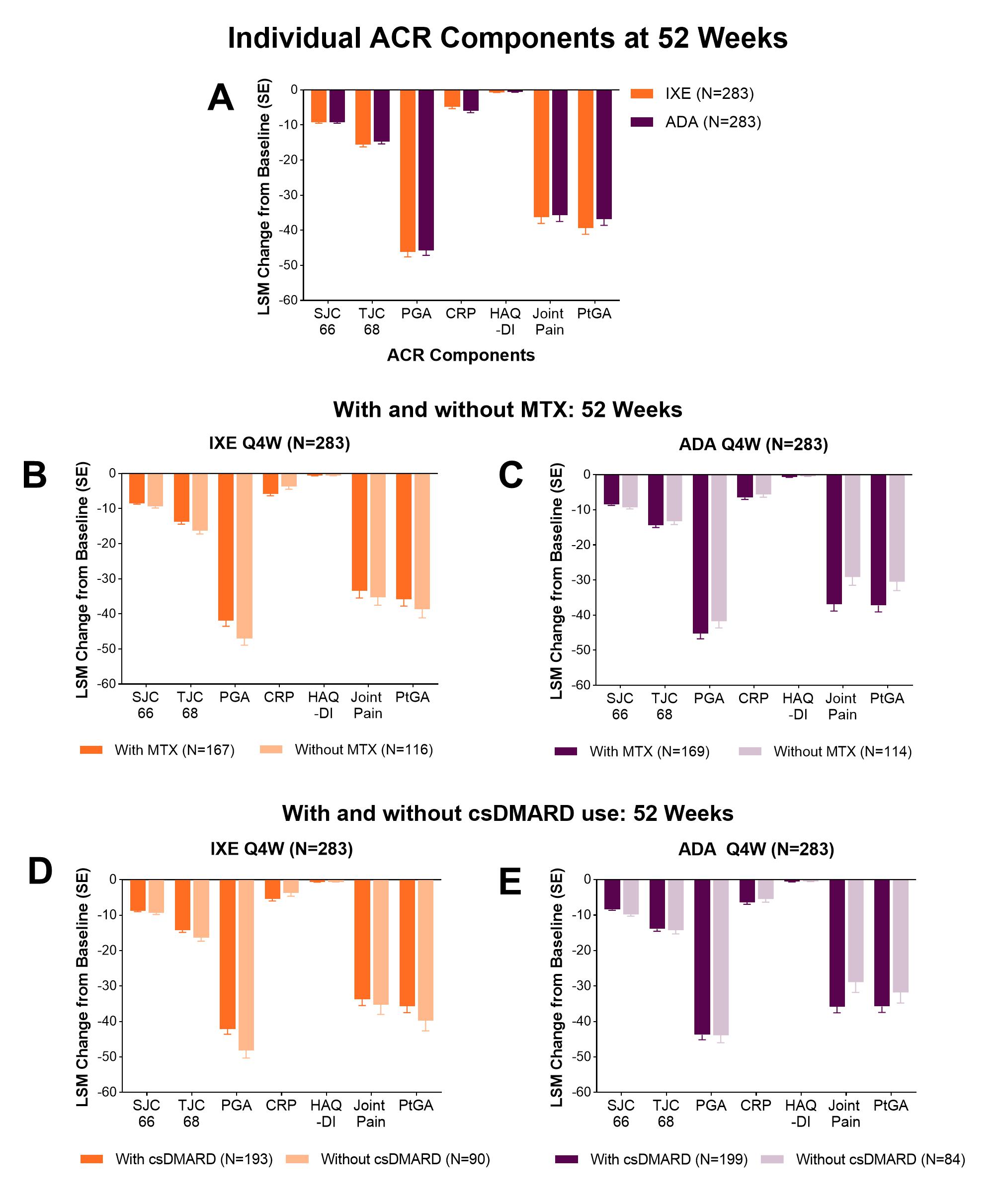 Change from baseline in the individual components of the ACR composite score at week 52 in patients treated with IXE or ADA (A) in the ITT population, (B and C) with and without MTX use at baseline and (D and E) with and without csDMARD use at baseline. Data presented as least square mean (LSM) change from baseline (mBOCF) + SE. Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; ADA, adalimumab; CRP, C-reactive protein; csDMARD, conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drug; HAQ-DI, health assessment questionnaire disability index; ITT, intent-to-treat; IXE, ixekizumab; mBOCF, modified baseline observation carried forward; MTX, methotrexate; PGA, physicians global assessment, PtGA, patients global assessment; Q2W, every two weeks; Q4W, every four weeks; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count.
Change from baseline in the individual components of the ACR composite score at week 52 in patients treated with IXE or ADA (A) in the ITT population, (B and C) with and without MTX use at baseline and (D and E) with and without csDMARD use at baseline. Data presented as least square mean (LSM) change from baseline (mBOCF) + SE. Abbreviations: ACR, American College of Rheumatology; ADA, adalimumab; CRP, C-reactive protein; csDMARD, conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drug; HAQ-DI, health assessment questionnaire disability index; ITT, intent-to-treat; IXE, ixekizumab; mBOCF, modified baseline observation carried forward; MTX, methotrexate; PGA, physicians global assessment, PtGA, patients global assessment; Q2W, every two weeks; Q4W, every four weeks; SJC, swollen joint count; TJC, tender joint count.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Husni E, Kamat S, Stenger K, Bolce R, Holzkaemper T, Helt C, Park S, Lisse J, Idolazzi L. The Effect of Ixekizumab versus Adalimumab on Individual Components of the ACR Composite Score, with and Without Concomitant Methotrexate or Other Conventional Synthetic DMARDs at 52 Weeks in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-ixekizumab-versus-adalimumab-on-individual-components-of-the-acr-composite-score-with-and-without-concomitant-methotrexate-or-other-conventional-synthetic-dmards-at-52-weeks-in-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-ixekizumab-versus-adalimumab-on-individual-components-of-the-acr-composite-score-with-and-without-concomitant-methotrexate-or-other-conventional-synthetic-dmards-at-52-weeks-in-patients/
