Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster II: Clinical/Epidemiology Studies
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
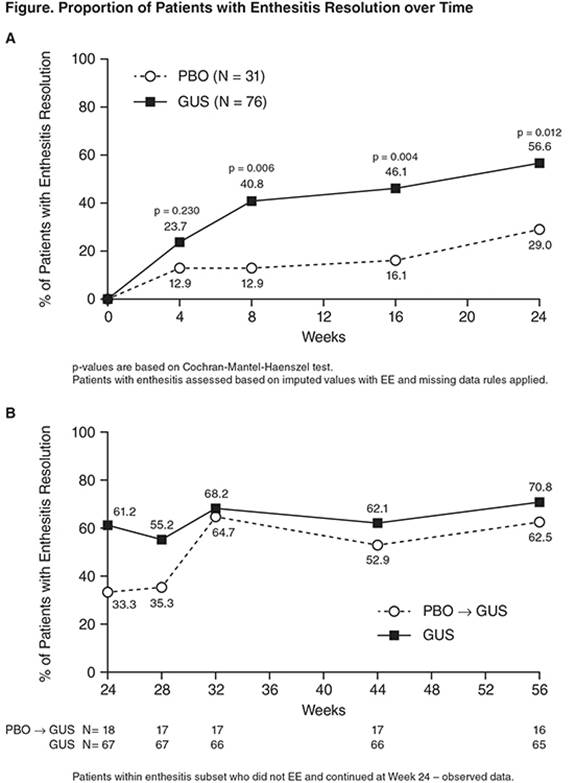
Background/Purpose: In a Phase 2 study, Guselkumab (GUS) was shown to be safe & effective in pts w/active PsA w/meaningful improvements in enthesitis. To evaluate the effect of GUS on enthesitis in a subset of pts w/enthesitis at baseline (BL) from the Phase 2 PsA study of GUS.
Methods: Pts w/active PsA & ≥3% BSA of plaque PsO, despite current or previous treatment, were randomized 2:1 to 100mg SC GUS or PBO at wks 0,4, →q8w during a 24-wk double-blind treatment period. At wk16, pts w/<5% improvement in swollen & tender joint counts(SJC&TJC) early escaped(EE) to open-label ustekinumab. At wk24, the PBO group crossed over to GUS at wks24,28 →q8w(PBO→GUS) & the GUS group continued receiving GUS(GUS→GUS) through wk44. Enthesitis was assessed using the Leeds enthesitis index(LEI). Enthesitis scores during the 24wk double-blind treatment was analyzed using LOCF imputation for missing data & EE. Enthesitis after wk24 was analyzed using observed data.
Results: Of 149 total pts w active PsA,107(72%) presented w/enthesitis at BL(PBO N=31,mean[SD] LEI=2.6[1.48], median[range]=2.0[1, 6]; GUS N=76,mean(SD) LEI=2.7[1.54], median[range]=2.0[1, 6])& 85 continued at Wk24(PBO→GUS N=18;GUS→GUS N=67). Except for higher TJC/SJC & CRP, BL characteristics of enthesitis subset was similar to overall population. GUS significantly reduced the LEI by wk8(mean[SD]] change from BL, PBO:-0.4[1.59]; GUS:-1.2[1.65];p=0.037),& through wk24(mean[SD] change from BL, PBO:-0.7[1.53]; GUS:-1.5[1.81];p=0.045). GUS also significantly increased the % of pts w/enthesitis resolution(Figure). After wk24, PBO→GUS group achieved rapid, sustained resolution(wk56: mean[SD] change from BL=-2.1[1.65];62.5% of pts w/resolution), similar to GUS→GUS group(wk56:mean[SD] change from BL=-1.9[1.59],70.8% of pts w/resolution). Improvement in enthesitis was observed at each enthesitis site assessed, & was greater in ACR20(Table) responders vs non-responders in GUS-treated pts & was correlated w/improvement in TJC (R=0.37, p=0.001) & SJC (R=0.27,p=0.020), physician’s(R=0.47,p<0.0001) & pts global assessment of disease activity(R=0.32,p=0.005), & SF36 PCS(R=0.27,p=0.02) & MCS(R=0.35,p=0.002).
Conclusion: GUS treatment produces rapid & sustained improvement of enthesitis in pts w/active PsA, which correlates w/improvement in joint symptoms & pt-reported outcomes.
Table. Change in LEI in ACR20/50 and PASI75 Responders and Non-responders
|
Mean (SD) change from BL in LEI at Wk24 |
|||
|
Non-responders |
Responders |
p-value |
|
|
ACR 20 |
-0.93(2.054), n=28 |
-2.06(1.660), n=47 |
0.002 |
|
ACR 50 |
-1.55(2.190), n=49 |
-1.81(1.132), n=26 |
0.057 |
|
PASI 75 |
-1.25(1.138), n=12 |
-1.71(1.995), n=63 |
0.524 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Helliwell P, Gottlieb AB, Deodhar AA, Boehncke WH, McGonagle D, Xu XL, Xu S, Wang Y, Hsia EC, Karyekar CS, Mease PJ. The Effect of Guselkumab on Enthesitis: Results from a Phase 2 Study in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-guselkumab-on-enthesitis-results-from-a-phase-2-study-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-guselkumab-on-enthesitis-results-from-a-phase-2-study-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis/