Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) activity associates with cardiovascular (CV) risk. Anticitrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) were linked to higher activity and lower remission rates. Treatment responses may, likewise, vary by seropositivity status. We hypothesized that the relationship between disease activity and CV risk may vary between ACPA positive and negative patients. Rheumatoid factor (RF) associated with higher RA activity independently of ACPA. We posited that the effect of RA activity on CV risk may differ in RF positive vs. negative patients. Variance in disease activity, characteristics and outcomes were reported in seronegative vs. single or double positive patients. We explored whether the relationship between RA activity and CV risk varied according to ACPA and RF status.
Methods: We evaluated 3952 patients free of CV disease, enrolled in an international consortium. Main outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, or CV death. Missing data were imputed using multiple imputation with 10 repetitions. Multivariable Cox models stratified by center risk explored the impact of baseline 28-joint disease activity score with C-reactive protein (DAS28CRP), ACPA positivity, RF positivity and the two- and three-way interactions of DAS28CRP with ACPA and/or RF on risk of MACE. All models adjusted for age, gender, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, family history of CV disease, total cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein ratio, and disease duration.
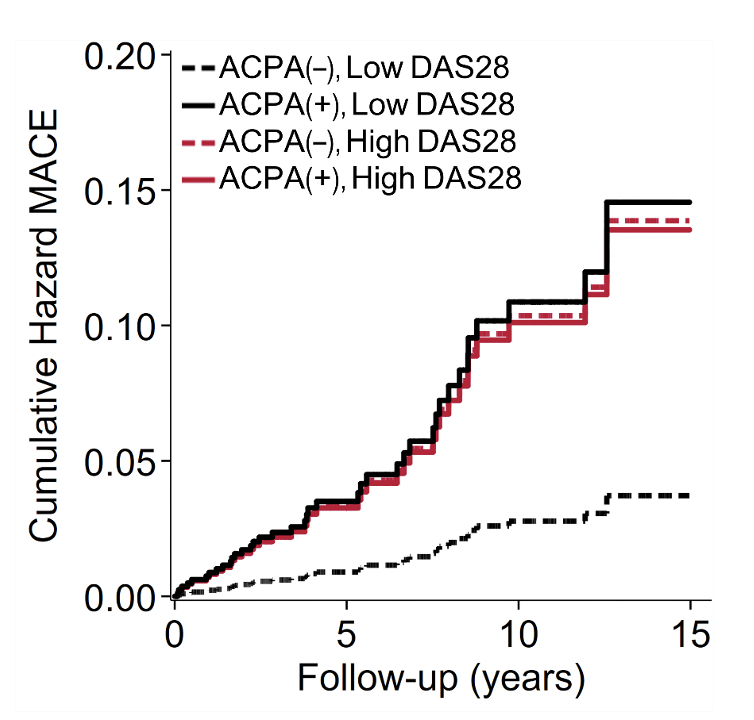
Of 3952 patients, 1007 (25.5%) were seronegative, 306 (7.7%) ACPA positive and RF negative, 557 (14.1%) ACPA negative and RF positive, and 2082 (52.7%) double positive at diagnosis. Mean (standard deviation) DAS28CRP was 3.74 (1.28). Over 22,981 patient years, 184 MACE occured. There was a main effect of DAS28CRP (HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.03-1.36, p=0.016), but not ACPA (HR 1.24, 95% CI 0.84-1.81, p=0.279) or RF (HR 1.27, 95% CI 0.83-1.96, p=0.268) on MACE risk after multivariable adjustment. Yet, there were main effects of single and double seropositivity; compared to seronegative, single (HR 1.69, 95% CI 1.03-2.75, p=0.036) and double seropositivity (HR 1.72, 95% CI 1.12-2.65,p=0.014) associated with risk of MACE. A significant three-way interaction between DAS28CRP, ACPA and RF positivity was observed (p-interaction=0.034) suggesting that the influence of RA activity on MACE risk varied according to ACPA and RF status. Among RF negative patients, the ACPA × DAS28CRP interaction was significant (p=0.011) and DAS28CRP associated with MACE in ACPA negative (HR 1.58, 95% CI 1.08-2.33, p=0.020) but not positive patients (HR 1.05, 95% CI 0.67-1.64, p=0.823, figure 1). Among RF positive patients, the ACPA × DAS28CRP interaction (p=0.861) and ACPA main effect (HR 1.04, 95% CI 0.70-1.55, p=0.855) were not significant, though the main effect of DAS28CRP was (HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.01-1.38, p=0.044).
Conclusion: Single and double seropositive patients incurred higher risk of MACE compared to seronegatives. RA activity associated with MACE risk among RF positive patients regardless of ACPA status. Among RF negative, disease activity associated with CV risk only in ACPA negative ones.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Pascual Ramos V, Myasoedova E, Gonzalez-Gay M, Corrales-Martínez a, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Sfikakis P, Dessein P, Tsang L, Hitchon C, El Gabalawy H, Van RIel P, Contreras Yanez I, Colunga Pedraza I, Galarza-Delgado D, Azpiri-Lopez j, Semb A, Misra D, Durez P, Bridal Logstrup B, Hauge E, Kitas G, Ormseth S. The Effect of Disease Activity on Cardiovascular Risk Varies According to Rheumatoid Factor and Anticitrullinated Protein Antibody Status in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-disease-activity-on-cardiovascular-risk-varies-according-to-rheumatoid-factor-and-anticitrullinated-protein-antibody-status-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-disease-activity-on-cardiovascular-risk-varies-according-to-rheumatoid-factor-and-anticitrullinated-protein-antibody-status-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/