Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Biologic therapies, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors (TNFi) and interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i) may affect the cardio-metabolic profile of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). We aimed to assess the short-term effects of TNFi and IL-17i on serum metabolites in patients with PsA, and determined whether these metabolite changes differed across the two drug classes.
Methods: A nested cohort study was conducted among participants with available serum samples from a longitudinal PsA cohort who initiated TNFi or IL-17i therapy. Serum samples prior to initiation of therapy, and three to six months after initiation of therapy, were used to quantify 64 metabolic biomarkers using a Nuclear Magnetic Resonance targeted metabolomics panel, which comprised lipid particles, apolipoproteins, fatty acids, amino acids and various other low-molecular metabolites. T-tests were used to compare differences in metabolite levels before versus after therapy within each drug class. Linear mixed effects models assessed the effect of each drug class on changes in metabolite levels adjusting for age, sex, lipid lowering drugs, diabetes, hypertension and menopause.
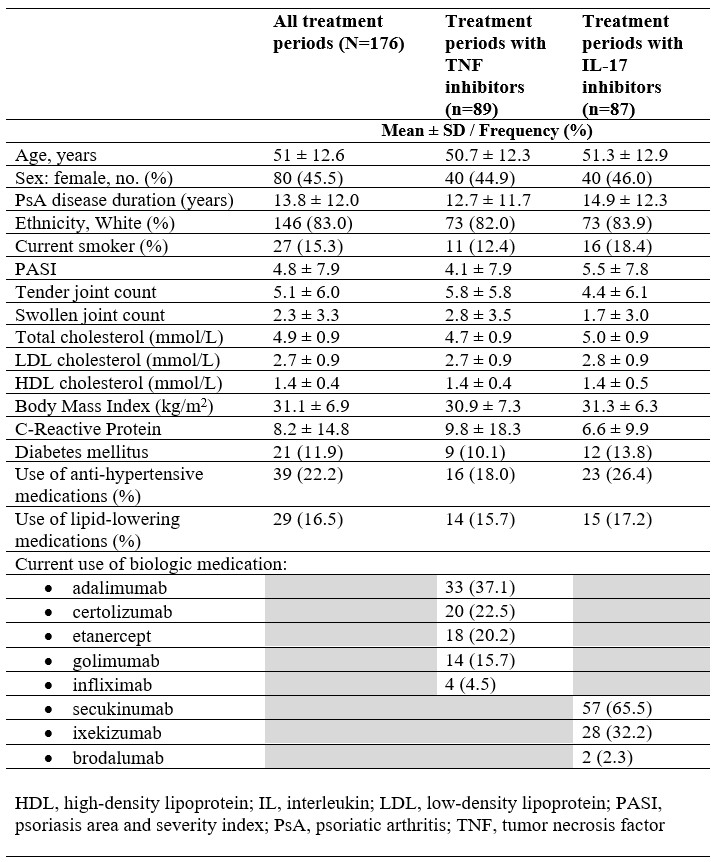
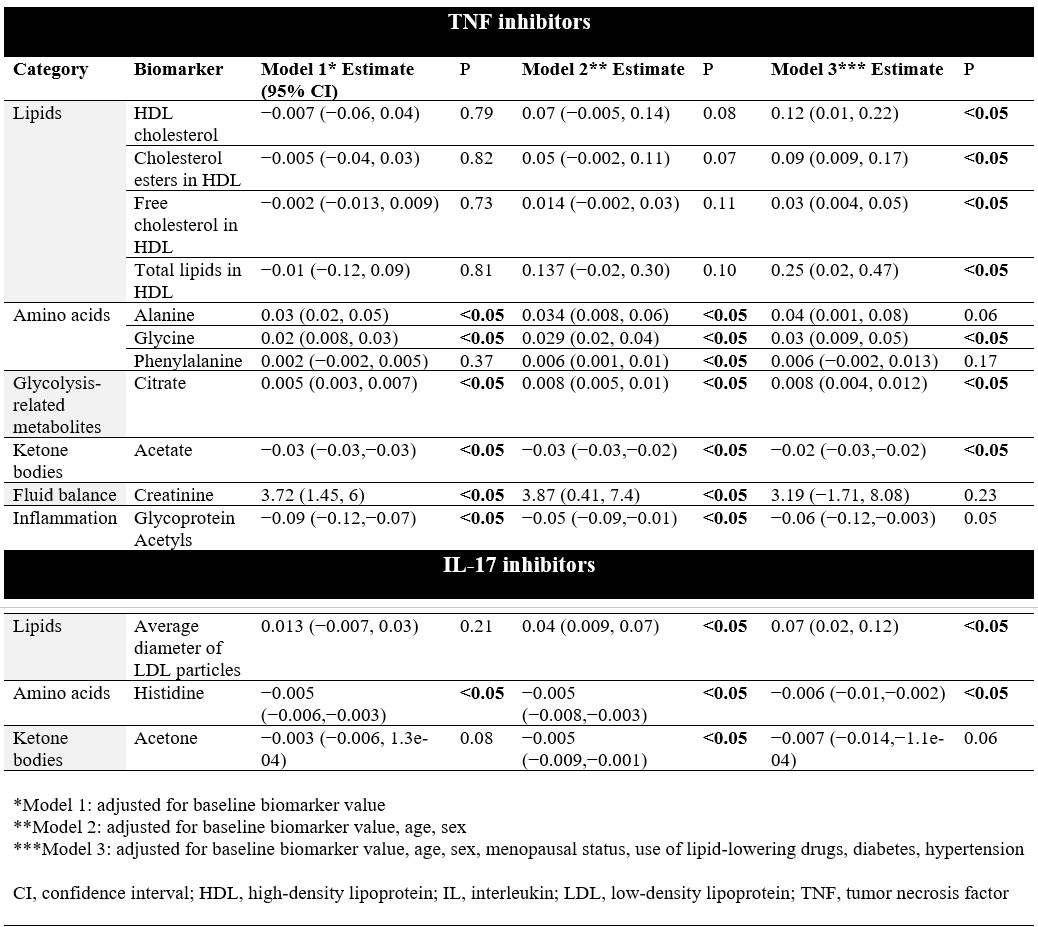
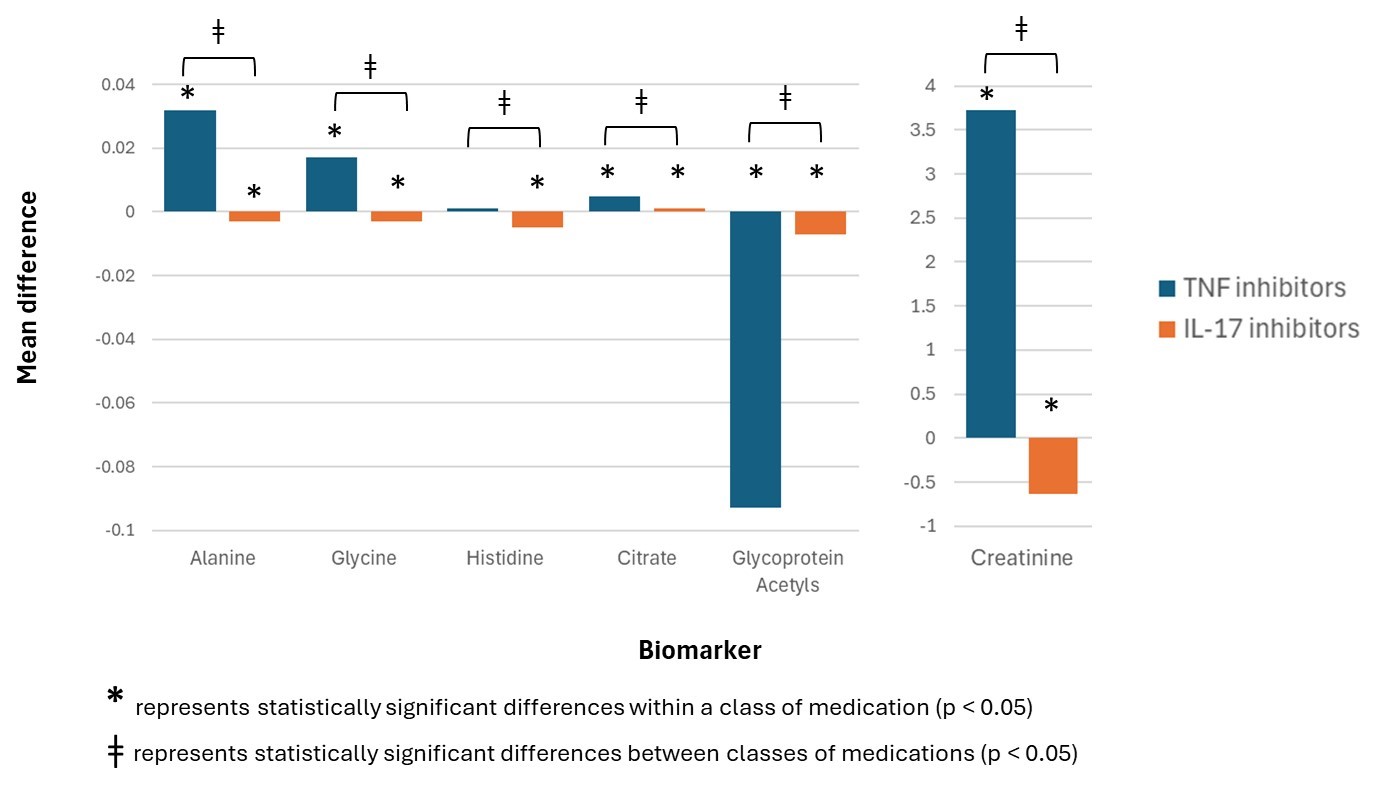
Results: A total of 176 treatment periods (163 patients) were analyzed between 2013 and 2021 (mean age 51 ± 12.6 years, 45.5% female) (Table 1). Among users of TNFi, levels of alanine, glycine, citrate and creatinine significantly increased post-treatment, whereas levels of glycoprotein acetyls (GlycA), a marker of systemic inflammation, decreased (Figure 1). Among users of IL-17i, concentrations of citrate significantly increased post-treatment, whereas alanine, glycine, histidine, GlycA and creatinine decreased. When comparing biomarkers between classes of medications, post- and pre-treatment levels differed significantly for alanine, glycine, histidine, citrate, GlycA and creatinine. In linear mixed effects models adjusted for age and sex involving TNFi users, levels of alanine (Estimate [EST] 0.034; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.008, 0.06), glycine (EST 0.029; 95% CI 0.02, 0.04), phenylalanine (EST 0.006; 95% CI 0.001, 0.01), citrate (EST 0.008; 95% CI 0.005, 0.01) and creatinine (EST 3.87; 95% CI 0.41, 7.4) increased post-treatment, whereas acetate (EST −0.03; 95% CI −0.03,−0.02) and GlycA (EST −0.05; 95% CI −0.09,−0.01) decreased (Table 2). In models adjusted for age and sex involving IL-17i users, changes were observed among fewer biomarkers, with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particle size (EST 0.04; 95% CI 0.009, 0.07) increasing post-treatment, and levels of histidine (EST−0.005; 95% CI −0.008,−0.003) and acetone (EST −0.005; 95% CI −0.009,−0.001) decreasing.
Conclusion: TNFi and IL-17i appear to differentially affect the serum metabolic profile of patients with PsA. Treatment with TNFi was associated with more changes in metabolite profiles than IL-17i, including changes associated with systemic inflammation (GlycA) and amino acids. The implication of these changes on long-term cardio-metabolic risk needs further research.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Colaco K, bumbulis l, Chandran V, Cook R, Gladman D, Eder L. The Effect of Biologic Therapies on Serum Metabolic Biomarkers in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-biologic-therapies-on-serum-metabolic-biomarkers-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-biologic-therapies-on-serum-metabolic-biomarkers-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/