Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patient reported outcomes (PROs) have gained relevance in the evaluation of axial SpA (axSpA), as they convey a more objective patient perspective. The concept of minimally clinical important difference (MCID) informs if a numerical difference on a given outcome measure (ie, PRO) over time is related to a relevant clinical effect (1).
This review assessed the efficacy of different biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) on several PROs in randomised controlled trials (RCT) in axSpA.
Methods: A systematic literature review (SLR) was performed using the MEDLINE (May 1st, 2018) with the filters “published in the last 10 years” and “humans”. The PICO (P, population; I, intervention; C, comparison; O, outcome) concept was used according to: P: adults (>18 years old) with radiographic axSpA (r-axSpA) or non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA); I: any bDMARD regardless of formulation or duration; C: placebo (PBO) and/or any different drug; O: BASDAI, BASFI, the Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life (ASQoL), the EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D), the Short Form 36 Health Survey physical component summary (SF36-PCS), the Short Form 36 Health Survey mental component summary (SF36-MCS), and the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy – Fatigue (FACIT-F). The efficacy of bDMARDs on PROs was evaluated through MCID concept or differences between baseline and a later timepoint.
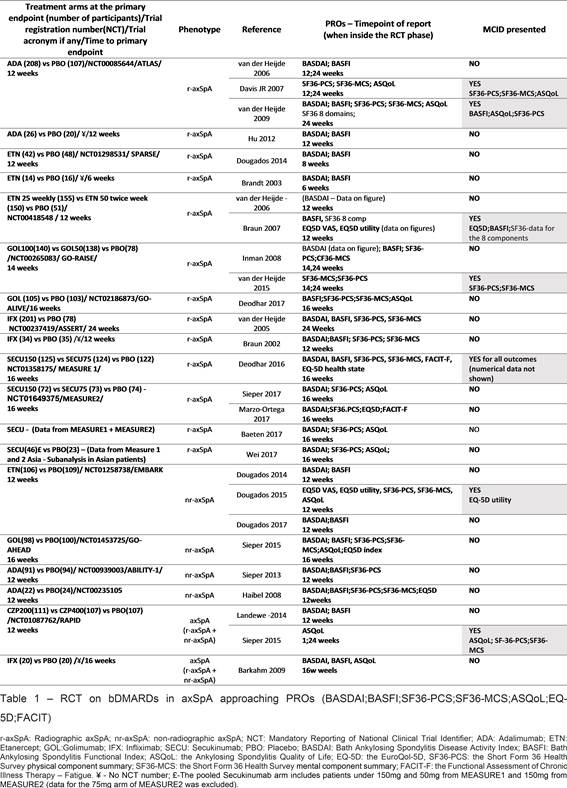
Results: After screening 84 initial references and manually adding other 9, 17 RCTs fullfilled the inclusion criteria (11 r-axSpA, 4 nr-SpA and 2 with both phenotypes), corresponding to 27 publications (table 1). All of them assessed TNF inhibitors (TNFi) or IL17 inhibitors (IL17i).
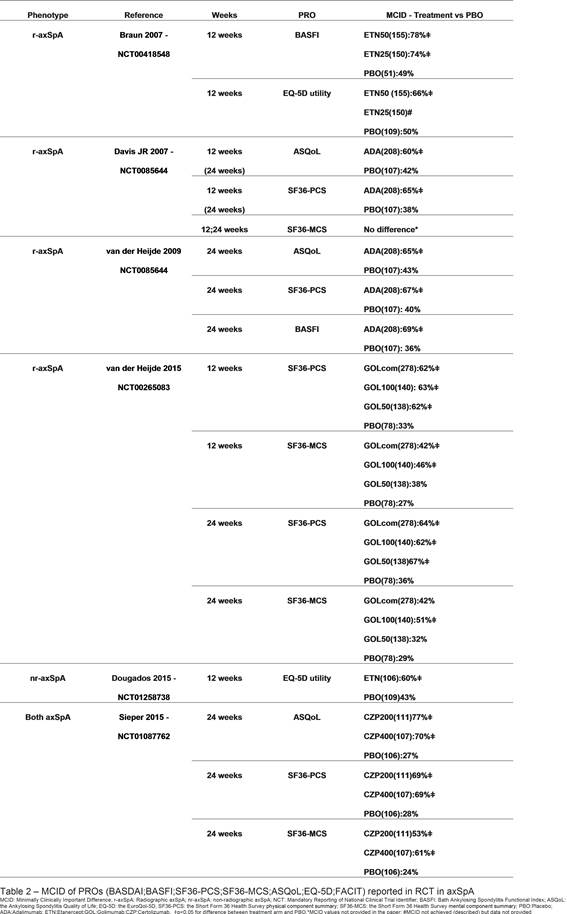
Only 6 RCTs reported quantitative differences in MCID achievement between treatment arms (table 2). Most of the RCTs reported the mean difference of a given PRO between baseline and a later timepoint (as absolute values or percentage of variation), providing a statistical test (confidence interval and/or p-value) to express the magnitude of the difference between the treatment and PBO arm. A significant high proportion of MCID achievement is recorded using bDMARDs (table2).
Conclusion: PROs are reported in an unstandardized way, and there is scarce information regarding clinical implications of the differences achieved (ie MCID). Our results launch a call for reporting PROs in a clinically relevant and standardized way and to define cut-offs that may reflect remission. However, bDMARDS seems to contribute to MCID achievement in a high proportion of patients.
References
1 – Deodhar. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Dec;68(12):2901-10
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodrigues Manica S, Leite Silva J, Machado AR, Coelho C, Duarte J, Vieira-Sousa E, Tavares Costa J, Pimentel-Santos F. The Effect of Biologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Patient Reported Outcomes in Axial Spondyloarthritis; A Systematic Literature Review and a Call for Action [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-biologic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-patient-reported-outcomes-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-systematic-literature-review-and-a-call-for-action/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-biologic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-patient-reported-outcomes-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-systematic-literature-review-and-a-call-for-action/