Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
C4b Binding Protein (C4BP) is the main inhibitor of the classical complement pathway. Both β2glycoprotein-I (β2GPI), the main antigen in the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), and C4BP, belong to the Complement Control protein (CCP) family. C4BP binds to protein S (PS) in circulation. Low C4BP levels are reported in the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL) and during treatment with vitamin K antagonists (VKA). / To investigate if levels of C4BP vary with aPL profile, clinical manifestations and anticoagulant treatment in primary (p) and secondary (s) APS.
Methods:
C4BP, complement proteins and PS were investigated in 67 patients with pAPS, 67 age and sex matched controls and 15 individuals with repeated positivity (++) for aPL (nonSLE-aPL++) without clinical manifestations. Moreover, 118 SLE-aPL++, of which 56 with sAPS, 291 aPL negative SLE patients (SLE-aPL-) and 322 controls were included. Clinical characteristics, including treatment, were tabulated. C4BP was determined with a magnetic bead-beased sandwich immunoassay. Additional proteins in the complement cascade (C1q, C2, C3, C4, C3a, C3dg, sC5b-9, Factor I) were measured.
Results:
C4BP is 20% decreased in aPL++ patients, independently of SLE or clinical manifestations (fig. 1). We report positive associations between C4BP and complement proteins C1q, C2, C3, C4, whereas C4BP associates negatively with complement activation products (C3a, C3dg) (p< 0.05 for all). Treatment with warfarin contributes to C4BP reduction by 9% (fig.2) according to mediation analysis performed in the SLE group: since warfarin is mostly prescribed to aPL+ patients, it is considered a mediator in the reducing effect of aPL on C4BP.
Conclusion:
Both the presence of aPL and warfarin treatment are associated with decreased levels of C4BP. Furthermore, higher complement degradation products are observed in patients with low C4BP levels, indicating that depressed levels of C4BP may, through reduced inhibition, contribute to complement activation in APS.
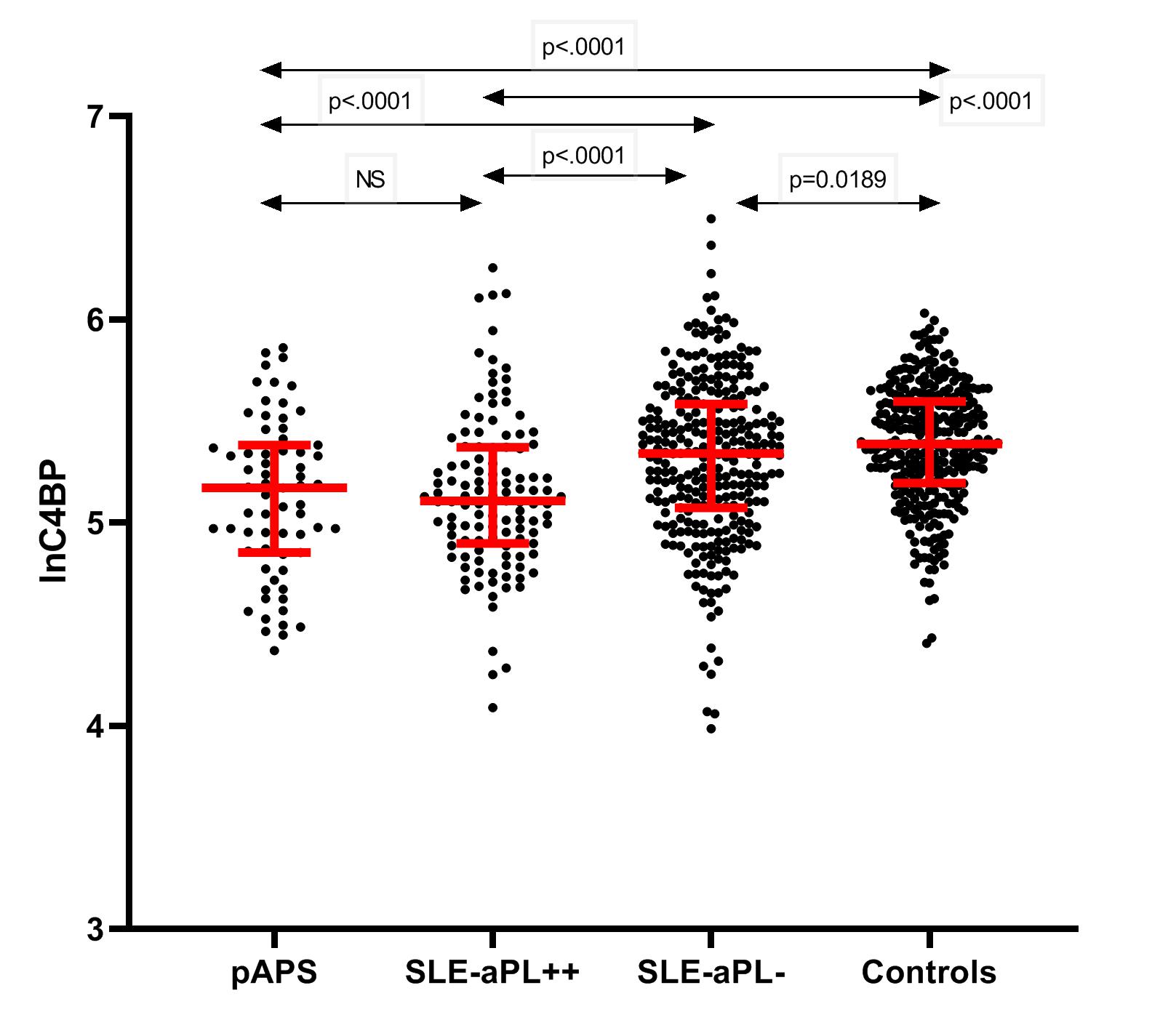 Levels of C4BP in different subgroups of patients: pAPS (n=67), SLEaPL++ (n=118), SLEaPL- (n=291) and controls (n=322)
Levels of C4BP in different subgroups of patients: pAPS (n=67), SLEaPL++ (n=118), SLEaPL- (n=291) and controls (n=322)
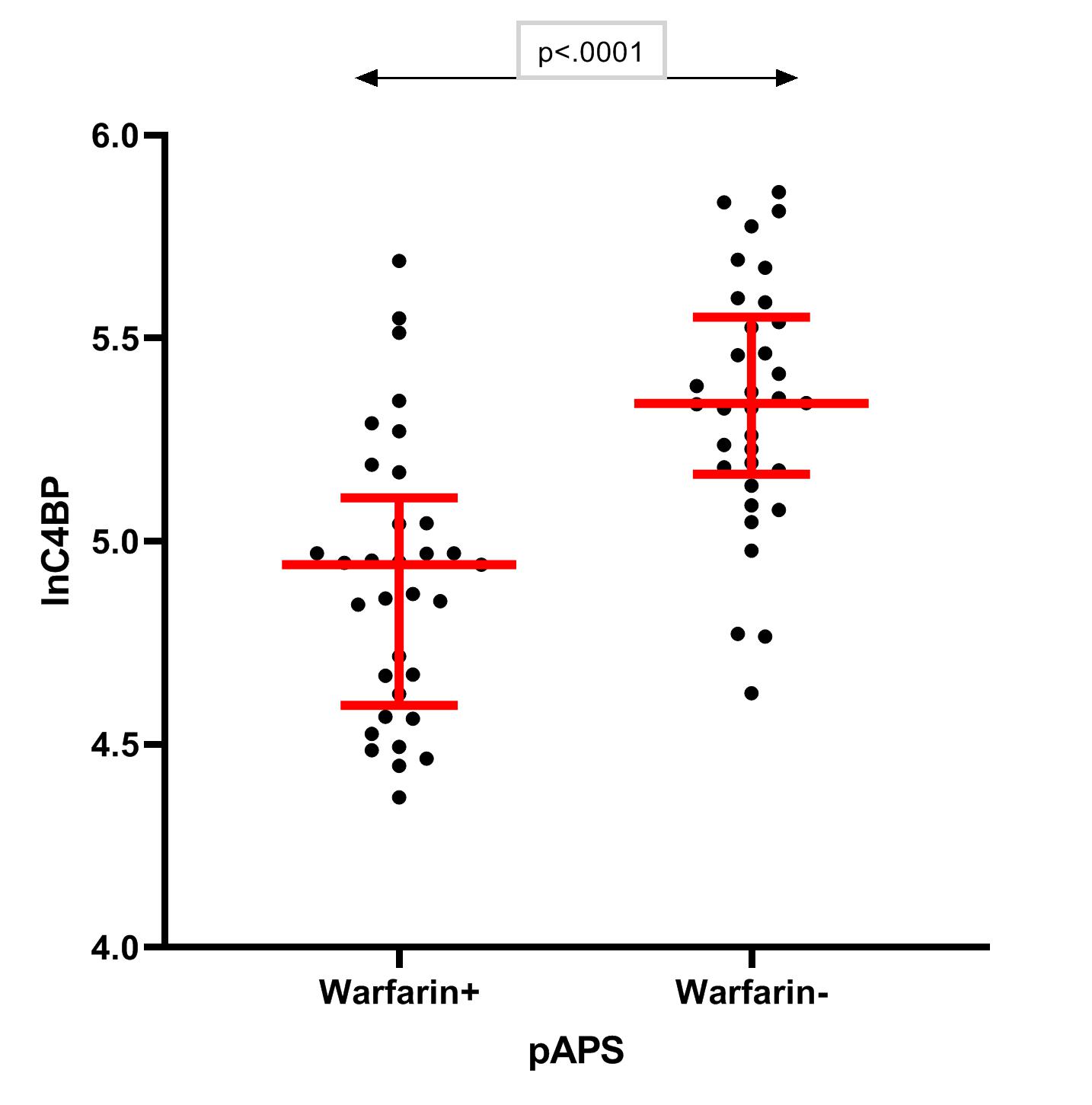 C4BP in 67 pAPS patients, 33/67 on warfarin
C4BP in 67 pAPS patients, 33/67 on warfarin
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Grosso G, Sandholm K, Antovic A, Gunnarsson I, Zickert A, Vikerfors A, Truedsson L, Bruzelius M, Nilsson B, Nilsson Ekdahl K, Svenungsson E. The Complex Relationship Between C4b Binding Protein, Warfarin and Antiphospholipid Antibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-complex-relationship-between-c4b-binding-protein-warfarin-and-antiphospholipid-antibodies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-complex-relationship-between-c4b-binding-protein-warfarin-and-antiphospholipid-antibodies/
