Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2377–2436) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Timely SLE diagnosis and treatment are critical to preventing irreversible organ damage and preserving quality of life. However, conventional biomarkers often underperform in patients presenting with non-specific signs and symptoms. We systematically evaluated a multianalyte assay panel (MAP) index incorporating cell-bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs) to address this diagnostic gap.
Methods: We analyzed biomarker data from multiple clinical studies (2011–2024), comprising 1,208 SLE patients meeting 1997 ACR criteria, 667 healthy controls, and 1,234 autoimmune rheumatic disease and chronic pain controls. CB-CAPs were measured by semi-quantitative flow cytometry and reported as net mean fluorescent intensity. Autoantibodies were measured by ELISA and complement C3 and C4 were measured by immunoturbidimetry. Diagnostic odds ratios (DOR), likelihood ratios (LR+/-), and sensitivities were calculated. Sensitivity comparisons between the MAP index, and conventional markers (anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith, and complement C3/C4) were performed within the SLE cohort using McNemar’s test. Sensitivity odds ratios were calculated from discordant pairs, with p-values adjusted using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. Effect sizes were expressed as the difference in sensitivities with corresponding 95% confidence intervals.
Results: The SLE cohort was predominantly female (62%), mean age 43.5 (±14.1) years, and mostly White (40%) [Table 1]. The MAP index consistently outperformed conventional biomarkers across both healthy and disease control comparisons. Against healthy controls, MAP achieved the highest diagnostic odds (DOR = 101.6), compared to CB-CAPs alone (DOR = 55.1), anti-dsDNA/Smith antibodies (DOR = 36.2), and complement C3/C4 (DOR = 7.9) [Figure 1A]. Against autoimmune and chronic pain controls, MAP maintained superior performance (DOR = 22.3), exceeding that of anti-dsDNA/Smith (DOR = 20.3), CB-CAPs (DOR = 13.7), and complement (DOR = 9.1) [Figure 1B]. The MAP index yielded the highest positive likelihood ratio (LR+ = 32.7) and strongest rule-out utility (LR– = 0.3), outperforming all individual markers. Sensitivity comparisons within the SLE group revealed significantly higher odds of MAP positivity versus anti-dsDNA (OR = 24.8), anti-Smith (OR = 1382.0), and CB-CAP subsets (ORs = 17.3–19.0), all with adjusted p-values < 0.001 and moderate-to-large effect sizes (sensitivity differences = 0.31-0.57) [Figure 2A]. Integration of the MAP index identified 24% more SLE cases than conventional markers alone and reduced the proportion of patients testing negative for all biomarkers from 36% to 28% (Figure 2B-C). Overlap analysis confirmed MAP captured unique diagnostic information beyond traditional serologies and complement levels.
Conclusion: Systematic analysis demonstrates the MAP index integrating CB-CAPs improves lupus diagnostic precision. With unique utility for both rule-in and rule-out decisions, particularly in cases of intermediate lupus probability, the MAP index addresses critical diagnostic gaps. Robust performance across diverse patient populations further supports its clinical generalizability and practical value for enhancing lupus management.
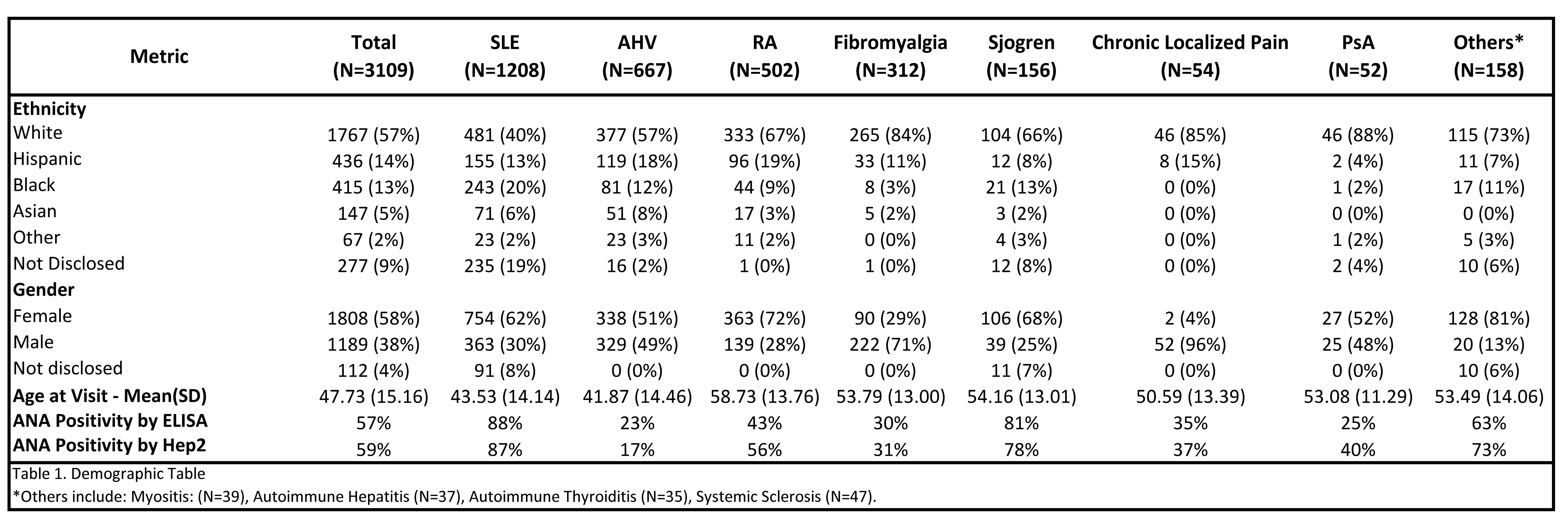 Figure 1. Demographic characteristics
Figure 1. Demographic characteristics
.jpg) Figure 1. Pre-test vs. post-test probability for SLE figures comparing MAP index to CB-CAPs and conventional markers
Figure 1. Pre-test vs. post-test probability for SLE figures comparing MAP index to CB-CAPs and conventional markers
.jpg) Figure 2. Sensitivity for SLE comparison between MAP, CB-CAPs and conventional biomarkers
Figure 2. Sensitivity for SLE comparison between MAP, CB-CAPs and conventional biomarkers
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kyttaris V, Taghavi S, Nagle C, Schleif C, Partain B, O'Malley T. The Clinical Utility of a Multianalyte Lupus Risk Score Incorporating Cell-bound Complement Activation Products: A Systematic Evaluation [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-utility-of-a-multianalyte-lupus-risk-score-incorporating-cell-bound-complement-activation-products-a-systematic-evaluation/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-utility-of-a-multianalyte-lupus-risk-score-incorporating-cell-bound-complement-activation-products-a-systematic-evaluation/
