Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I (0387–0413)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by skin and internal organs tissue fibrosis including the myocardium. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) parametric mapping is a promising modality to detect diffuse myocardial fibrosis.
The study aims to detect early-stage cardiac involvement in SSc using CMR parametric mapping and evaluate the associations with clinical and laboratory findings.
Methods: 24 controls (12 female, 58.0±18.9 years) and 57 SSc patients (51 female, 59.4±12.9 years) underwent CMR at 3.0T and analyzed myocardial damage using parametric mapping and compared with clinical data.
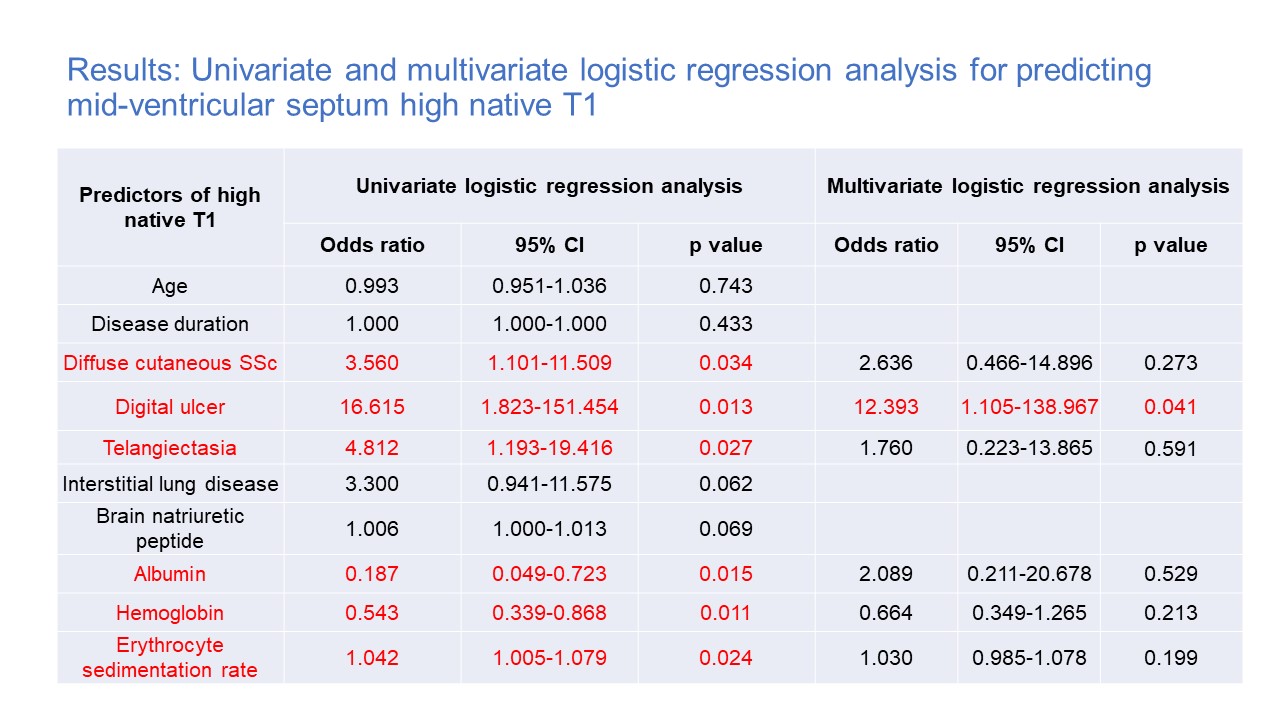
Results: The mean disease duration in the SSc group was 3.9±7.4 years, and four patients had pulmonary hypertension. The mean left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction was 58.3±8.1 in the SSc group and 56.9±7.0 in the control group. LV global longitudinal and circumferential strain evaluated by CMR feature tracking showed no significant differences between the two groups. Focal fibrosis on late gadolinium enhancement was found in 9 SSc patients (15.7%) but none of the controls. Mid-ventricular native T1 and extracellular volume fraction were significantly higher in SSc patients compared with the control group (1331.2±65.4mesc vs. 1253.6±44.1msec, p< 0.0001 and 32.4±4.1% vs. 28.3±3.3%, p< 0.0001, respectively). There was a significant correlation between native T1 and BNP levels (r=0.353, p=0.008) in the SSc group. SSc patients were divided into two groups, low and medium native T1 group (n=37) and high native T1 group (n=19). Cutaneous vascular symptoms including digital ulcer and telangiectasia were significantly higher in the high native T1 SSc group compared with the low and medium native T1 SSc group (6 (31.5%) vs. 1 (2.7%), p=0.005 and 7 (36.8%) vs. 4 (10.8%), p=0.027). There were no differences in biventricular volume and contraction, but the left and right atrial volume index were significantly larger in the high native T1 SSc group than the low and medium native T1 SSc group (all p< 0.05). In univariate logistic regression analysis revealed that diffuse cutaneous SSc, the coexistence of digital ulcer, telangiectasia, albumin, hemoglobin, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were independent predictors of mid-ventricular high native T1 values. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, the coexistence of digital ulcers was the only independent predictor of mid-ventricular high native T1 values in the SSc group (p=0.013 odds ratio=12, CI 1.1-138.9).
Conclusion: Native T1 mapping is a useful method to detect early myocardial damage in SSc patients. The clinician should take notice of cardiac involvement in SSc patients with progressed skin lesions even without cardiac symptoms.
Results: Myocardial native T1 and ECV values compared between controls and SSc
Results: Baseline characteristics of patients with SSc
Results: Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis for predicting mid-ventricular septum high native T1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Purevsuren M, Uehara M, Ishizuka M, Hara T, Kakuda N, Tsuji T, Yamazaki T, Miki M, Sumida H, Yoshizaki A, Asano Y, Sato S, Hatano M, Issei K. The Clinical Role of T1 Mapping Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Detecting Cardiac Involvement in the Early Stage of Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-role-of-t1-mapping-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-imaging-for-detecting-cardiac-involvement-in-the-early-stage-of-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-role-of-t1-mapping-cardiac-magnetic-resonance-imaging-for-detecting-cardiac-involvement-in-the-early-stage-of-systemic-sclerosis/