Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: PTPN22 R620W is a common genetic variation that is a known risk factor for the development of autoimmune disease, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This PTPN22 variant results in increased downstream signaling from the T cell receptor. Whether this variant results in higher disease activity in patients with RA is unknown.We compared disease activity by R620W genotype and the HLA DRB1 shared epitope (SE) in patients with RA, hypothesizing that the R620W variant is associated with higher disease activity and seropositivity.
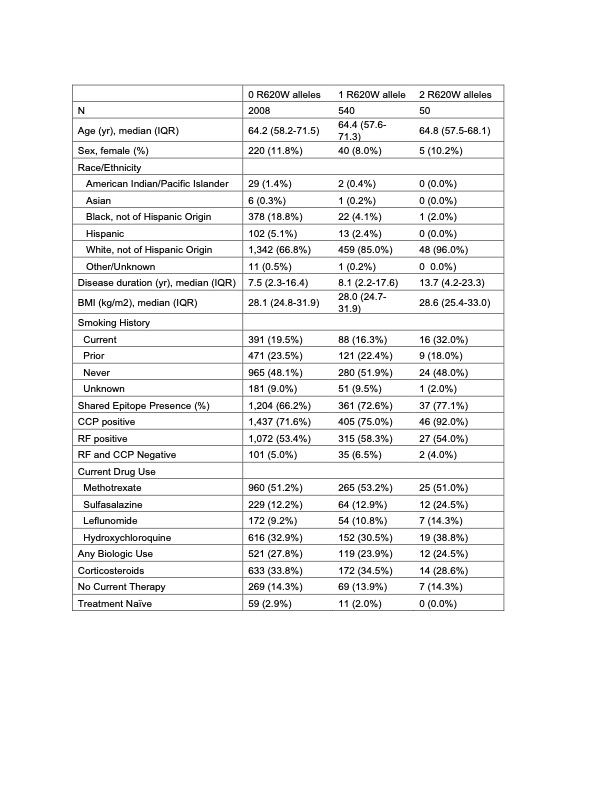
Methods: Participants from the Veterans Affairs RA registry (VARA), a longitudinal prospective cohort of veterans with RA, were genotyped for PTPN22 R620W (rs2476601) using the Infinium Global Screening Array-24 v2.0. Participants had SE determination through either sequencing for HLA DRB1 using AlleleSEQR HLA-DRB1 kit or using a PCR-based sequence specific oligonucleotide probe system; participants were considered have SE with the following alleles:*0101, *0102, *0104, *0105, *0401, *0404, *0405, *0408,*0409, *1001, *1402 and *1406. Disease activity components were recorded by treating providers during routine clinical encounters and extracted from the electronic health record. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor were measured using serum samples collected at enrollment.The effect of R620W genotype and SE (0, 1, or 2 copies of a high-risk HLA allele) on disease activity scores as well as the presence of erosive disease and other disease characteristics was assessed using linear and logistic regression, adjusted for sex, age, and five principal components of population structure. Testing for interaction between R620W and SE shared epitope was performed.
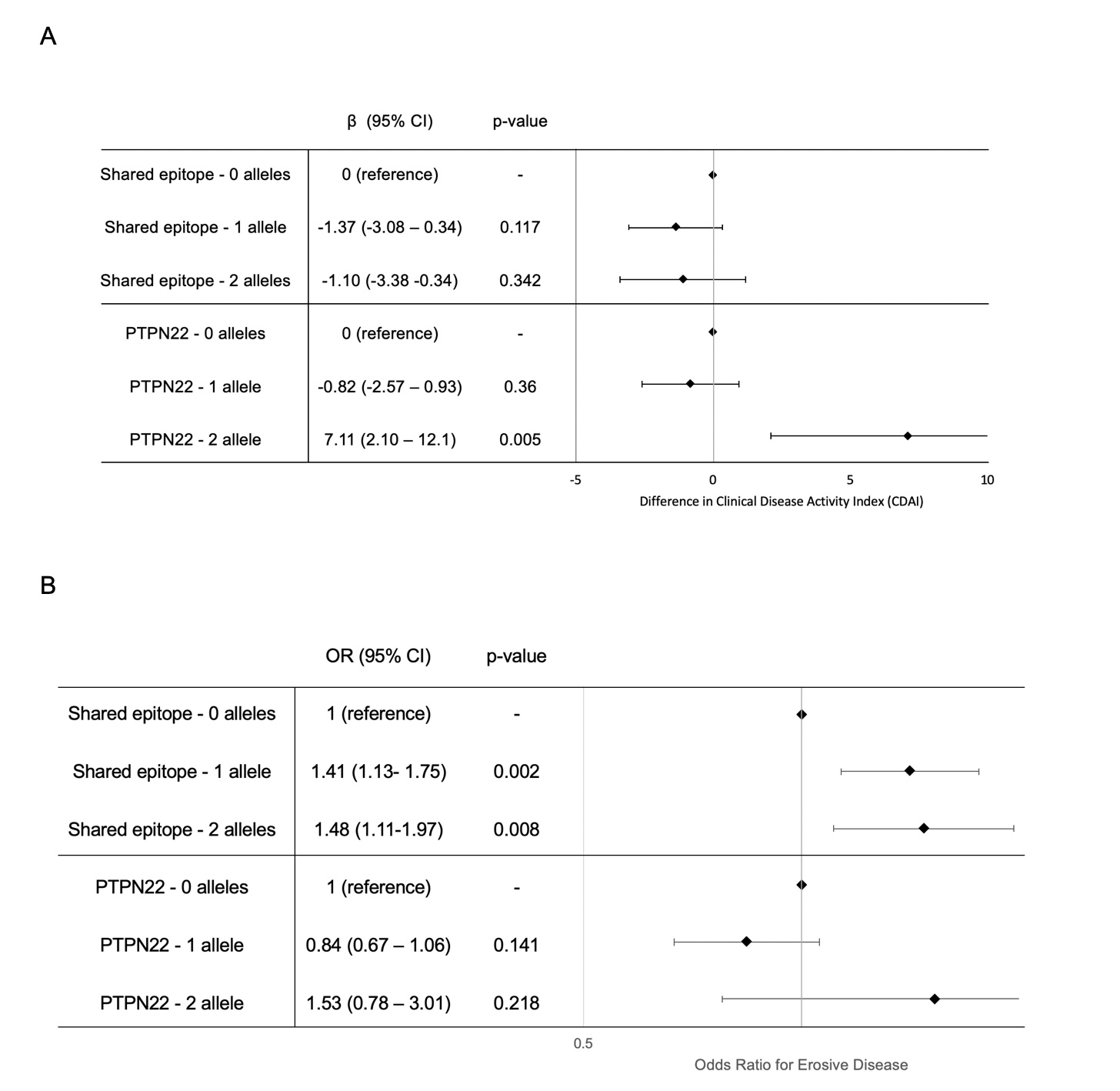
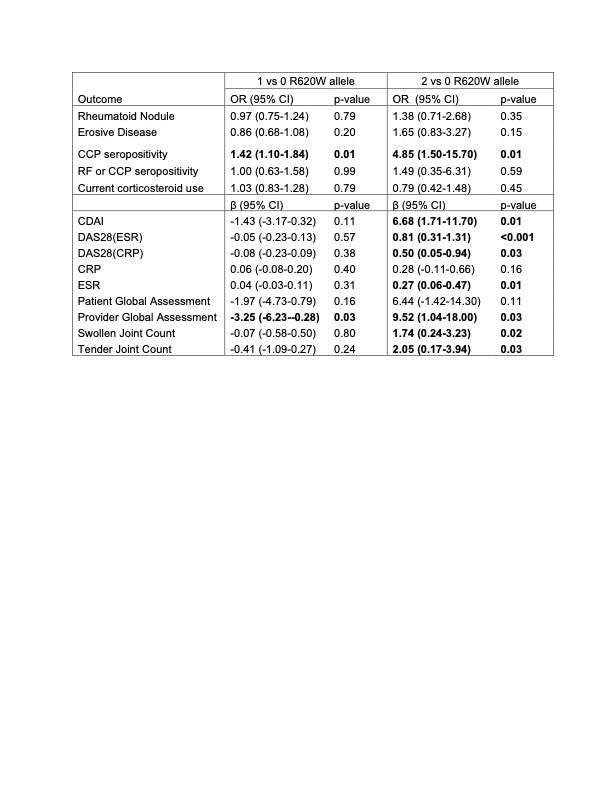
Results: In 2598 participants with genotyping for PTPN22, 540 (26.9%) were heterozygous and 50 (2.5%) were homozygous for R620W (Table 1). In 2363 participants who also underwent SE testing, 1177 (49.8%) had one copy of SE and 425 (18.0%) had two copies.At enrollment, compared to those with 0 copies of R620W, those with 2 copies had higher CDAI [β=6.80, 95% CI 1.84-11.77, p =0.007]; no difference was observed for those with one R620W allele or SE (Fig 1, Table 2). Those with 2 R620W alleles also had higher DAS28(ESR), ESR, provider global, swollen joint count, and tender joint count (Table 2). Participants with 1 and 2 copies of R620W demonstrated significantly increased odds of CCP seropositivity (Table 2). R620W alleles were not associated with erosive disease; those with SE had an increased odds of erosive disease (Fig 1, Table 2). An interaction between 2 R620W alleles and shared epitope was observed for CDAI, though not other disease activity scores (CDAI: effect with shared epitope 9.39 , 95% CI 3.75, 15.0, p for interaction 0.038).
Conclusion: The presence of PTPN22 R620W homozygosity was associated with greater disease activity at enrollment in patients with RA. In contrast, presence of SE was not associated with disease activity, but was associated with erosive disease. Overall, these findings support the hypothesis that the genetics of disease susceptibility may also contribute to disease activity and severity during the disease course, including genes residing outside the HLA region.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Riley T, Wheeler A, England B, Cannon g, brian S, Kunkel G, Wysham K, Wallace B, Elam R, Monach P, Reimold A, Kerr G, Smith I, Richards J, Lee I, Xiao R, Damrauer S, George M, Mikuls T, Baker J. The Association of Genetic Variation in PTPN22 and Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-of-genetic-variation-in-ptpn22-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-association-of-genetic-variation-in-ptpn22-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-disease-activity/