Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: The Addressing Lupus Pillars for Health Advancement (ALPHA) Project is a global consensus effort to identify, prioritize and address top barriers in lupus impacting diagnosis, care, treatment and research. Prior publications outlined mixed methodology of expert interviews and surveys to identify and prioritize barriers across drug development, clinical care and access to care among global lupus stakeholders including: clinicians, researchers, biopharmaceutical and government representatives, patients and caregivers.1,2 This abstract details methodology used to develop a roadmap of specific recommendations to address the barriers.
Methods: An in-person stakeholder meeting of ALPHA Global Advisory Committee (GAC) members and a 2-round scoring survey were used to elicit recommendations. Prior to the meeting, held in Jan. 2020 in Washington, DC, GAC members (n=15) defined ‘success’ across drug development, clinical care and access to care using prior identified barriers as a framework. The meeting included 14 GAC members, 2 patients, an added clinician-researcher and Lupus Foundation of America and Tufts Center for the Study of Drug Development staff. Participants were divided into 3 breakout groups, with patient and specialty representation in each group, and identified at least 1 actionable solution to achieve ‘success’ per pillar. After full group discussion, participants voted on 1 top solution per pillar. Post-meeting, solutions were evaluated by feasibility, impact and timeline for implementation (FIT; Table 1). Each meeting participant completed 2 rounds of scoring in Qualtrics software. Potential FIT component values were between 1-3 and total scores between 3-9. Higher scores represent higher achievability based on the composite of the 3 criteria.
Results: Table 2 shows ranked solutions per pillar based on in-person voting, and Table 3 shows FIT scores. Simplifying and standardizing outcomes measures, such as steroid-sparing (drug development), and defining the lupus spectrum (clinical care) ranked as the highest priority solutions during the GAC meeting and received high FIT scores. Leveraging social media (access to care) received the highest FIT score across all pillars. Cross-cutting themes included leveraging digital technology and applying specific considerations for pediatric populations, as drug development has been limited and outcomes may differ from adults.
Conclusion: ALPHA has developed a roster of actionable solutions to barriers collectively impacting drug development, clinical care and access to care, and assessed achievability of each to improve the quality of life of adults and children with lupus. Simplifying and standardizing outcome measures, including steroid-sparing, may be pivotal to advance lupus drug development. Further clarifying the lupus spectrum may improve time to diagnosis and aid both provider and patient understanding of lupus. These findings are also an important indicator of patient preferences, highly relevant in patient-focused drug development.
References:
1Lupus Sci Med 2019;6:e000342. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2019-000342
2 Ann Rheum Dis, volume 79, supplement 1, year 2020, page 1953
 Table 1. Feasibility, Impact, and Timeline (FIT) Scoring Guide
Table 1. Feasibility, Impact, and Timeline (FIT) Scoring Guide
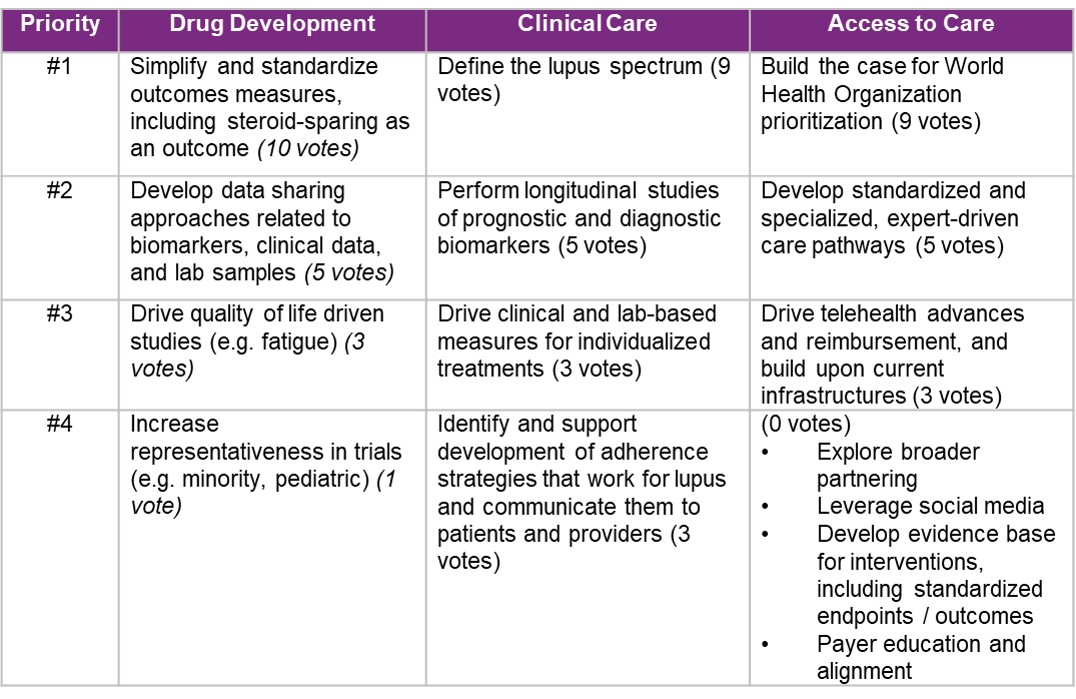 Table 2. Ranked Solutions per Pillar Identified During GAC In-Person Meeting
Table 2. Ranked Solutions per Pillar Identified During GAC In-Person Meeting
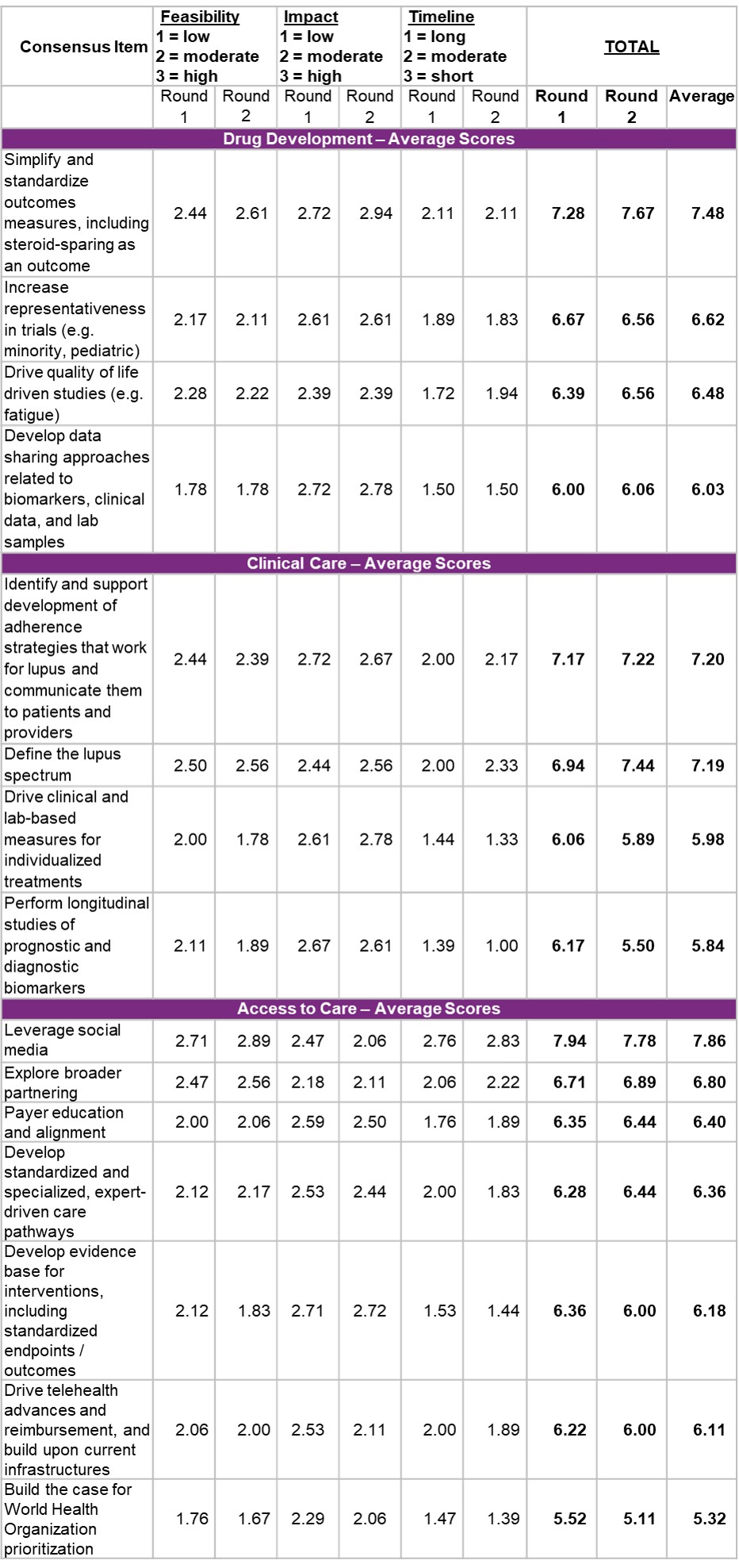 Table 3. Feasibility, Impact, and Timeline Scoring Results, Listed by Highest Average Score
Table 3. Feasibility, Impact, and Timeline Scoring Results, Listed by Highest Average Score
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tse K, Sangodkar S, Arntsen K, Bae S, Bloch L, Bruce I, Connolly-Strong E, Costenbader K, Dörner T, Evans S, Franson T, Getz K, Kao A, Kalunian K, Dickerson B, Manzi S, Morand E, Peña Y, Raymond S, Rovin B, Schanberg L, Von Feldt J, Werth V, Williams A, Zook D, Hanrahan L. The Addressing Lupus Pillars for Health Advancement (ALPHA) Project: Establishing Consensus and Prioritization of Global Community Recommendations to Address Major Challenges in Lupus Diagnosis, Care, Treatment and Research [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-addressing-lupus-pillars-for-health-advancement-alpha-project-establishing-consensus-and-prioritization-of-global-community-recommendations-to-address-major-challenges-in-lupus-diagnosis-care/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-addressing-lupus-pillars-for-health-advancement-alpha-project-establishing-consensus-and-prioritization-of-global-community-recommendations-to-address-major-challenges-in-lupus-diagnosis-care/
