Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Interleukin (IL)-9, a member of IL-2 cytokine family was recently attributed to a novel CD4 T cell subset termed Th9 cells in the murine system. It is secreted by naïve CD4+ T cells in response to TGF-β and IL-4. IL-9 can also be secreted by Th17 cells and itself induces Th17 cells to differentiate and regulate autoimmune and inflammatory diseases by enhancing their secretion of IL-17. These observations provoked us to elucidate the pathogenic role of IL-9 in autoimmune arthritis.
Methods: From peripheral blood and synovial fluid (SF) of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) (n = 8), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n = 10) and osteoarthritis (OA, n = 10) patients, mononuclear cells were obtained and magnetically sorted for CD3+ T cells. IL-9 levels in SF and serum were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Proliferative effect of human recombinant IL-9 (rIL-9) on CD3+ T cells of peripheral blood and SF was assessed by MTT (3-(4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, a yellow tetrazole) and CFSE dilution (Carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester) assays. The CD3+ cells from peripheral blood were activated with anti-CD3/CD28 cocktail.
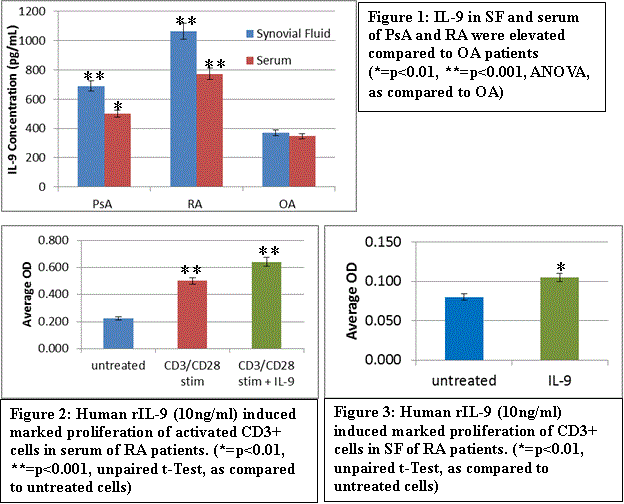
Results: IL-9 levels were significantly elevated in SF and serum of PsA patient and RA patients as compared to SF and serum of OA (Figure 1). Further we demonstrated that activated synovial T cells of PsA and RA patients produced significantly more IL-9 than those of OA patients. In MTT and CFSE dilution assays, rIL-9 (MTT, OD: 0.642 ± 0.02) induced significant proliferation of CD3+ T cells of peripheral blood (Figure 2) and SF (Figure 3) derived from RA and PsA patients compared to media. Further, initial observations suggest that IL-9 receptor ab inhibits IL-9 induced proliferation of the activated SF derived T cells in inflammatory arthritis.
Conclusion: Our data showed that serum and SF of PsA and RA patients have higher concentration of IL-9 than matched OA controls. Moreover, rIL-9 induced marked proliferation of RA and PsA derived activated CD3+ T cells of SF from RA and PsA patients. Thus, IL-9 is likely to play a critical role in the inflammatory cascades of autoimmune arthritis. More importantly IL-9 provides a unique target to develop therapy for PsA patients where we do not have many options like in RA.
Disclosure:
S. Raychaudhuri,
None;
A. Mitra,
None;
A. Datta Mitra,
None;
C. Abria,
None;
S. K. Raychaudhuri,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/th9-cells-in-inflammatory-cascades-of-autoimmune-arthritis/