Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: It is known that seronegative rheumatoid arthritis has different characteristics from seropositive RA. Objectives: To estimate the frequency of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a cohort of patients who consulted for polyarthralgia, including arthralgia of the hands, and to identify differential features, at diagnosis, between patients with seropositive RA and seronegative RA.
Methods: Prospective cohort study, which included patients over 18 years of age who were admitted for polyarthralgia, including hand arthralgias, to the ¨Reuma-check¨® program from August 2017 to March 2020. In this program, in the first visit (baseline) was performed: laboratory studies (including acute phase reactants, RF and anti-CCP), X-rays of hands and feet, ultrasound of hands with power Doppler technique (22 joints: wrists, MCFs and IFPs bilaterally and 20 tendons: 6 carpal extensor compartments and flexor tendons of 2nd to 5th fingers bilaterally) and interview where sociodemographic data (age, sex), clinical data (time of evolution of arthralgias, comorbidities) and clinimetry ( Global VAS of the patient, joint count, HAQ); each evaluator (laboratory, imaging and clinical) did not know the data of the other studies carried out. In subsequent visits (only patients who completed at least 2 visits were included), the results were evaluated, and the definitive diagnosis of RA was established or not according to the ACR / EULAR 2010 classification criteria. It was considered as seronegative RA when the patients were negative for both RF and anti-CCP.
Statistical analysis: descriptive statistics, Chi2 test, Fisher’s exact test, Student’s T-test and Mann Whitney were performed.
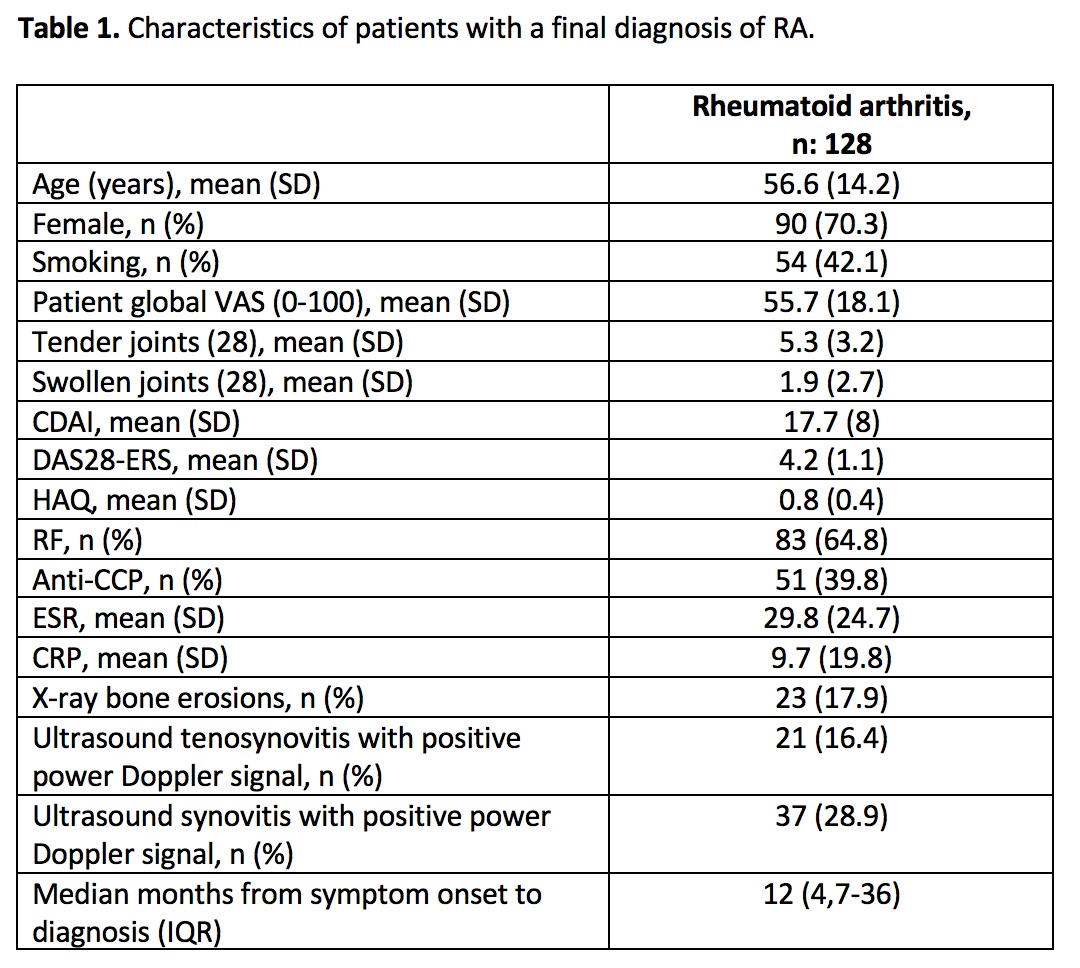
Results: A total of 746 (74.4% female and mean age 53.6 years, SD: 14.5) patients with polyarthralgia, including hand arthralgias, were included, of which 128 (17.1%, 95% CI: 14.6- 20) ended with a final diagnosis of RA (Table 1). Of these 128 patients, 87 (67.9%) were seropositive (RF and/or anti-CCP positive), while 41 (32%) were seronegative (RF and anti-CCP negative).
Table 2 shows a comparison of the different features between patients with seropositive RA and seronegative RA. The only feature that showed significant differences was the presence of tenosynovitis detected by ultrasound with a positive power Doppler signal, 13.7% of the patients with seropositive RA vs 41.6% of the patients with seronegative RA (p = 0.0028).
Conclusion: The frequency of RA in our cohort of patients with polyarthralgia, including hand arthralgias, was 17.1% and the only differential feature of patients with seronegative RA was the higher proportion of tenosynovitis detected by ultrasound with a positive power Doppler signal in comparison with patients with seropositive RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sanchez Prado E, Ruta S, Cuellar L, Magri S, Garcia Salinas R. Tenosynovitis Detected by Power Doppler Ultrasound: A Differential Feature of Patients with Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tenosynovitis-detected-by-power-doppler-ultrasound-a-differential-feature-of-patients-with-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tenosynovitis-detected-by-power-doppler-ultrasound-a-differential-feature-of-patients-with-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis/