Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Scleroderma (SSc), a female-biased autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and fibrosis in skin and internal organs, lacks effective treatment options. Our previous work, including single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-Seq) of skin from a large cohort of SSc patients, suggested that Hippo pathway regulates a female-specific immune gene network and drives myofibroblast differentiation in SSc skinI. Our objective herein was to assess if inhibiting Hippo pathway pharmacologically can suppress disease signaling in SSc.
I Ma F, Tsou PS, Gharaee-Kermani M, Plazyo O, Xing X, Kirma J, Wasikowski R, Hile GA, Harms PW, Jiang Y, Xing E, Nakamura M, Ochocki D, Brodie WD, Pillai S, Maverakis E, Pellegrini M, Modlin RL, Varga J, Tsoi LC, Lafyatis R, Kahlenberg JM, Billi AC, Khanna D, Gudjonsson JE. Systems-based identification of the Hippo pathway for promoting fibrotic mesenchymal differentiation in systemic sclerosis. Nat Commun . 2024 Jan 3;15(1):210. PMID: 38172207.
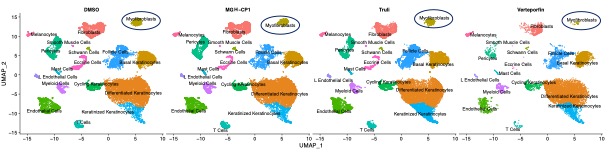
Methods: We targeted distinct steps of Hippo pathway using 3 inhibitors (TRULI, Verteporfin, and MGH-CP1) that were applied to SSc skin biopsies ex vivo (n=3 patients per treatment group). Biopsies from the same patients were treated in parallel with DMSO to be used as a patient-specific vehicle control. Molecular changes in affected cell populations were assessed by extensive scRNA-Seq analyses.
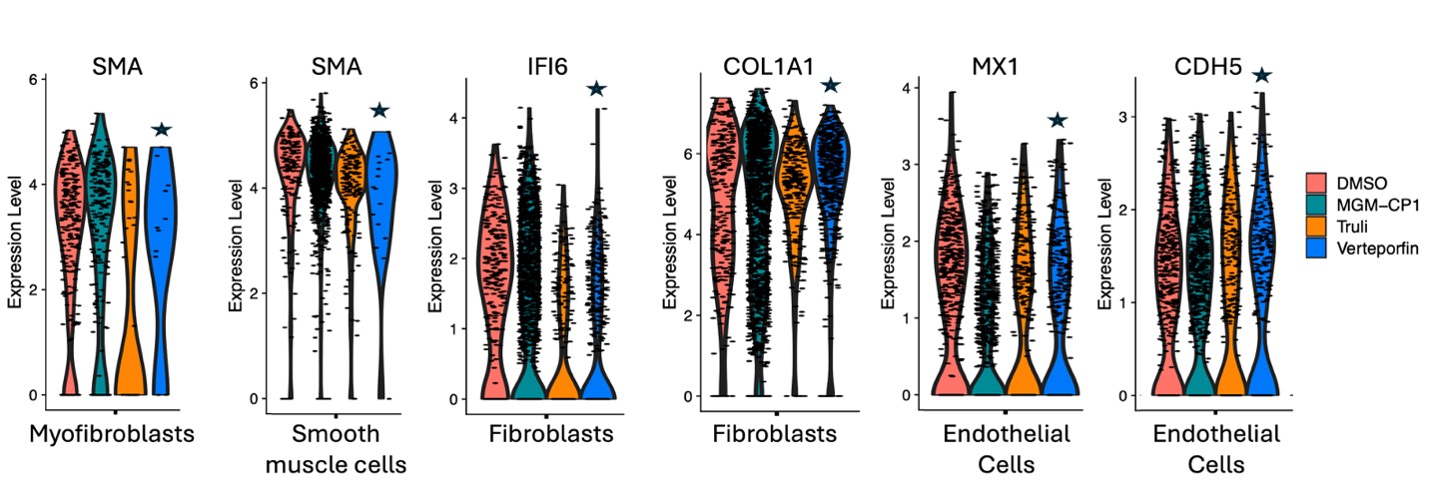
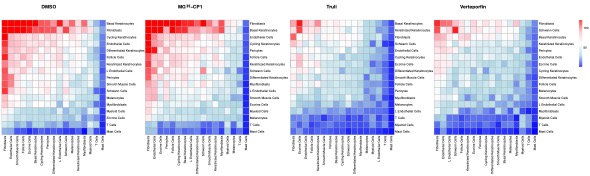
Results: We found that Verteporfin, which prevents interaction of TEADs with YAP and likely with VGLL3, selectively depleted myofibroblasts and endothelial-mesenchymal transition cells (EndoMTs) – the stromal cells pathologically activated in SSc. It also reduced expression of inflammatory, pro-fibrotic, and endothelial activation markers. Moreover, cell-cell interactions that sustain disease signaling were markedly hindered by Verteporfin. We saw a striking overlap between the genes downregulated by Verteporfin and those upregulated in SSc vs healthy patients across cell populations.
Conclusion: Thus, targeting Hippo pathway by Verteporfin effectively reverses molecular hallmarks of SSc. Our data further showcase the utility of this novel approach for modeling drug targeting ex vivo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Plazyo O, Wasikowski R, Gharaee-Kermani M, Tsou E, Tsoi L, Billi A, Kahlenberg J, Varga J, Gudjonsson J, Khanna D. Targeting Hippo Pathway Diminishes Disease Signaling in Scleroderma Skin [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-hippo-pathway-diminishes-disease-signaling-in-scleroderma-skin/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-hippo-pathway-diminishes-disease-signaling-in-scleroderma-skin/