Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tapering of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors may be considered in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) with low disease activity. However, there is still a lack of evidence that TNF inhibitors can be safely tapered and maintained with low medical costs. The aim of this study was to analyze the pattern of tapering of each TNF inhibitor and to evaluate the reduction of healthcare costs due to tapering of TNF inhibitors in patients with AS using an insurance claims database.
Methods: Data was obtained from an insurance claims database of the Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service in South Korea. Patients with AS who initiated TNF inhibitors such as etanercept, adalimumab, golimumab, and infliximab between July 1, 2013 to June 30, 2016 were enrolled. Among them, patients treated with TNF inhibitors for more than 2 years were included. Tapering of the TNF inhibitor was defined as a reduction of 50% or more of the recommended dose. We compared the rate of tapering and the time to 50% reduction of recommended dose between each TNF inhibitor. In addition, the implication of tapering on healthcare costs related to AS based on whether patients were subjected to a tapering dose was analyzed.
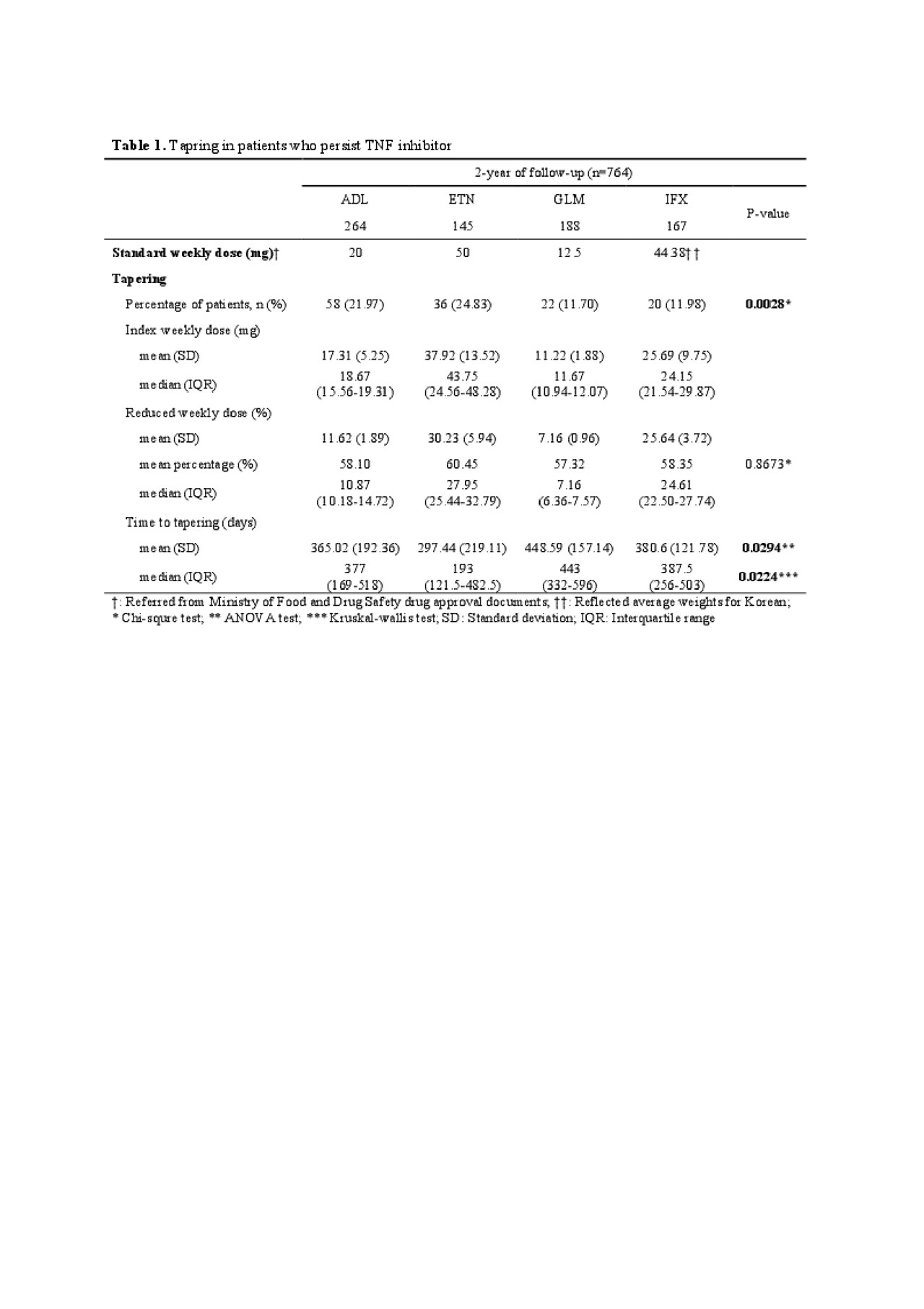
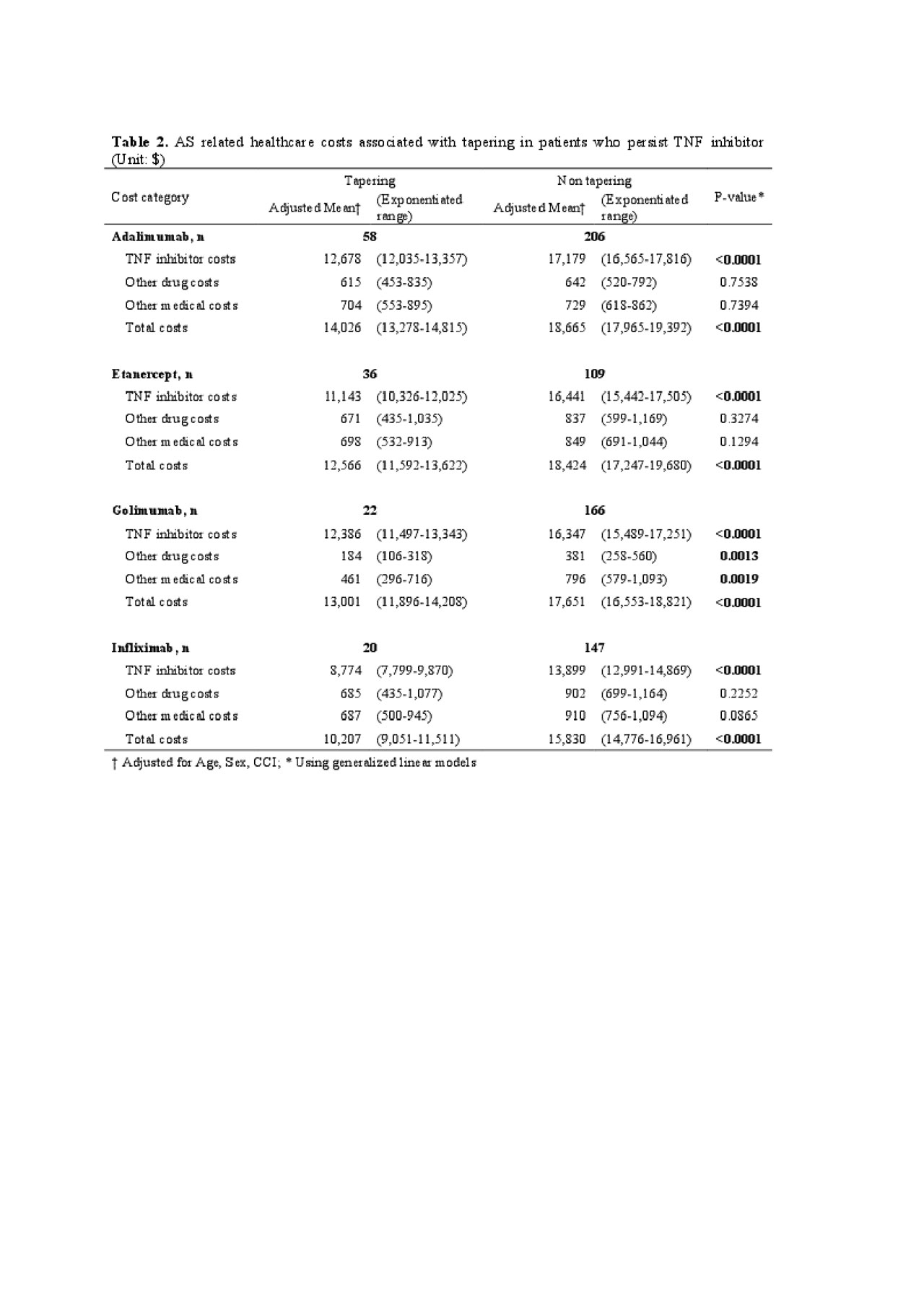
Results: A total of 1,352 patients were included in the study. Among them, 264 patients were continuously treated with adalimumab, 145 patients with etanercept, 188 patients with golimumab, and 167 patients with infliximab (Table 1). Of these, tapering of TNF inhibitors was more frequently observed in 58 (22.0%) patients on adalimumab and 36 (24.83%) on etanercept compared to 22 (11.7%) on golimumab and 20 (12.0%) on infliximab (p=0.0028). The mean time to 50% reduction was shorter in etanercept (297.4 ± 219.1 days) compared to adalimumab (365.0 ± 192.36 days), golimumab (448.59 ± 157.14 days), and infliximab (380.6 ± 121.78 days) (p=0.0294). The costs of TNF inhibitors was the highest among all AS-related healthcare costs. In addition, tapering significantly reduced AS-related total costs for all TNF inhibitors (Table 2).
Conclusion: TNF inhibitors with short intervals tended to be more frequently tapered in patients with AS. Tapering of TNF inhibitors may also help reduce healthcare costs related to AS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koo B, Lim Y, Lee M, Jeon J, Yoo H, Oh I, Shin J, Kim T. Tapering of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor and Healthcare Cost Differences in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Retrospective Analysis of Korean National Health Insurance Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tapering-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-and-healthcare-cost-differences-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-retrospective-analysis-of-korean-national-health-insurance-data/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tapering-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitor-and-healthcare-cost-differences-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-a-retrospective-analysis-of-korean-national-health-insurance-data/