Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ARHP)
Authors: Greysen, H.1., Lee, K.1
1. School of Nursing, University of California San Francisco
Title: Tai Chi and Yoga Are Effective for Improving Physical Function in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis – A Meta-Analysis
Background/Purpose: Recent research suggests that mind-body physical activity such as yoga and tai chi can significantly improve physical function in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Yoga and Tai Chi are gentle physical activities that promote strength, flexibility, balance and positive mental health. However, it is difficult to assess the effectiveness of these activities given that prior studies have small sample sizes. Therefore we conducted a systematic meta-analysis to assess the effectiveness of these exercises on improvement of physical function in adults with RA.
Methods: Medline was searched using the keywords: Yoga, Tai Chi, Physical Function, and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Included articles were those which measured the pre-intervention and post-intervention physical function scores using a validated physical function measurement tool for adults with a clinical diagnosis of RA who participated in a yoga or Tai Chi intervention lasting at least 6 weeks. Articles were excluded if the population was younger than 18, if the physical function measure was not a validated tool and if the reported results combined disease conditions such as RA and lupus. Effect sizes with confidence intervals were calculated using a fixed effects model for each intervention study by comparing the mean pre-intervention physical function score to the mean post-intervention score.
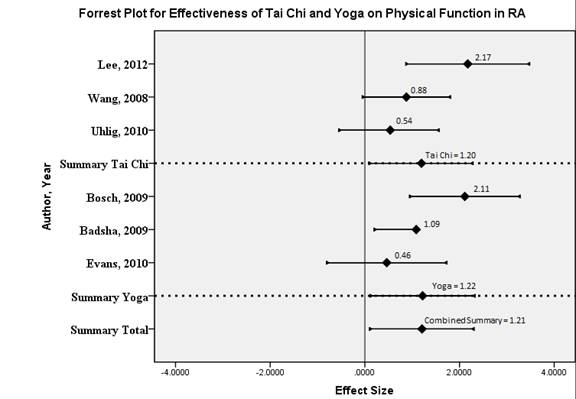
Results: The Medline search retrieved 219 English articles. The final analysis included 6 articles. There were 3 tai chi studies, 1 RCT and 2 pre/post intervention assessments, with a total of 22 participants. There were 3 yoga studies, 2 controlled clinical trials and 1 pre/post intervention assessment, with a total of 30 participants. There is strong evidence for the effectiveness of Tai Chi (standardized mean difference (SMD) = 1.20, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.13, 2.31) and for yoga (SMD = 1.22, 95% CI = 0.10, 2.27) on improving physical function in adults with RA who have participated in a physical activity program for at least 6 weeks. See Forrest plot.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that Tai Chi and Yoga are largely effective in improving physical function in adults with RA. Providers may be able to assist in improving the physical function of this population by discussing health promotion strategies such as yoga or tai chi physical activity programs.
Disclosure:
H. Greysen,
None;
K. Lee,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tai-chi-and-yoga-are-effective-for-improving-physical-function-in-adults-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-meta-analysis/